Ks0172 keyestudio UNO with Pin Header Interface: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
| D13 | | D13 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |||
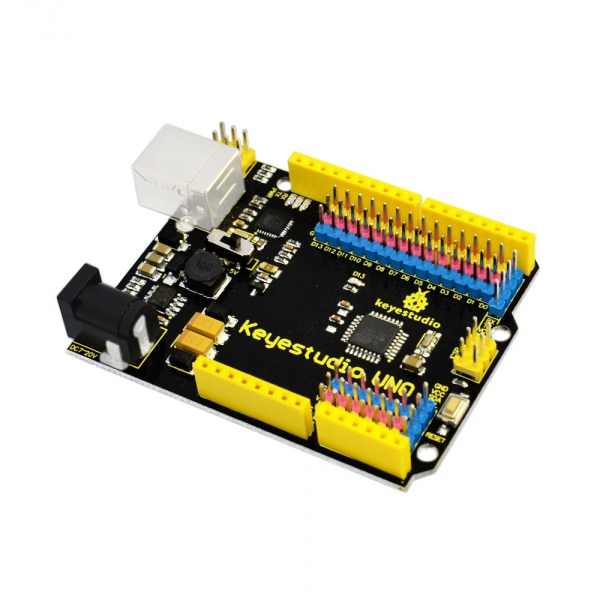
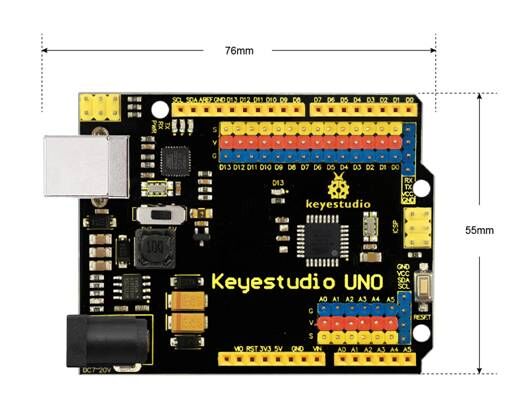
== Dimensions == | |||
<br>[[Image:KS0172-1.jpg|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
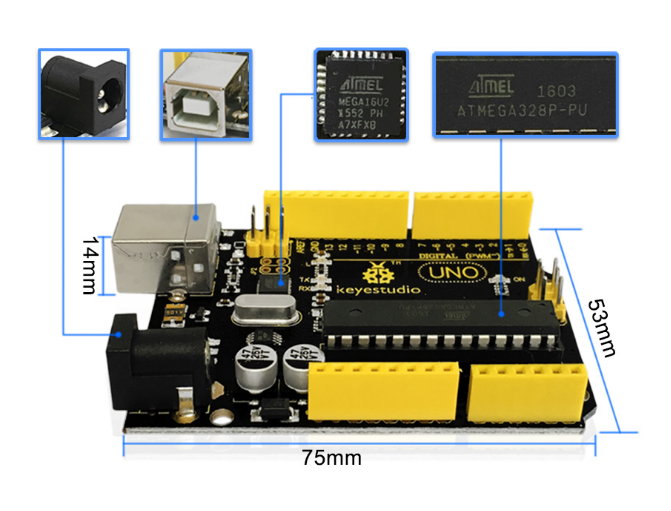
== Element and Interfaces == | |||
<br>[[Image:UNO dimensions.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
== Element and Pin Interfaces == | |||
Here is an explanation chart of what every element and interface of the board does: | |||
<br>[[Image:Ks0001-pinout.png|1000px|frameless]]<br> | |||
{| width="80%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-1.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) Header''' | |||
ICSP is the AVR, an Arduino micro-program header consisting of MOSI, MISO, SCK, RESET, VCC, and GND. It is often called the SPI (serial peripheral interface) and can be considered an "extension" of the output. In fact, slave the output devices under the SPI bus host.<br> | |||
When connecting to PC, program the firmware to ATMEGA328P-AU. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-2.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Serial Communication Pin''' | |||
Connect to serial communication. | |||
4Pins (GND, VCC (3.3V or 5V controlled by slide switch), RX, TX) | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-3.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Ground ''' | |||
Ground pins | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-4.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''V Pins (VCC)''' | |||
Power the external sensors and modules. Select the voltage of 3.3V or 5V via a slide switch. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-5.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Digital I/O''' | |||
It has 14 digital input/output pins, labeled D0 to D13 (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs). These pins can be configured as digital input pin to read the logic value (0 or 1). Or used as digital output pin to drive different modules like LED, relay, etc. The pin D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, and D11 can be used to generate PWM. | |||
For digital port, you can connect through female headers, or through pin headers (labeled S) of 2.54mm pitch. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-6.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''AREF ''' | |||
For Analog reference. | |||
Sometimes used to set an external reference voltage (0-5V) as the upper limit of analog input pins. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-7.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''SDA''' | |||
IIC communication pin | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-8.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''SCL''' | |||
IIC communication pin | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-9.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) Header''' | |||
ICSP is an AVR, an Arduino micro-program header consisting of MOSI, MISO, SCK, RESET, VCC, and GND. Connected to ATMEGA 16U2-MU. When connecting to PC, program the firmware to ATMEGA 16U2-MU. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-10.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Microcontroller''' | |||
Each control board has its own microcontroller. You can regard it as the brain of your board. | |||
Microcontrollers are usually from ATMEL. Before you load a new program on the Arduino IDE, you must know what IC is on your board. This information can be checked at the top of IC. | |||
The microcontroller used in this board is [http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/Atmel-7810-Automotive-Microcontrollers-ATmega328P_Datasheet.pdf ATMEGA328P-AU]. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-11.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''D13 LED ''' | |||
There is a built-in LED driven by digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-12.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''RX LED''' | |||
Onboard you can find the label: RX(receive ) | |||
When UNO board communicates via serial port, receive the message, TX led flashes. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-13.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''TX LED''' | |||
Onboard you can find the label: TX (transmit) | |||
When Arduino board communicates via serial port, send the message, TX led flashes. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-14.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Power LED''' | |||
LED on means that your circuit board is correctly powered on. Otherwise LED is off. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-15.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''USB Connection''' | |||
You can power the board via USB connection. Or can upload the program to the board via USB port. | |||
Connect the board to PC using a USB cable via USB port. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-16.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''ATMEGA 16U2-MU ''' | |||
USB to serial chip, can convert the USB signal into serial port signal. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-17.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Slide Switch''' | |||
You can slide the switch to control the voltage of pin V (VCC), 3.3V or 5V. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-18.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Voltage Regulator''' | |||
To control the voltage provided to the UNO board, as well as to stabilize the DC voltage used by the processor and other components. | |||
Convert an external input DC7-12V voltage into DC 5V, then switch DC 5V to the processor and other components, output DC 5V, drive current is 2A | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-19.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''DC Power Jack''' | |||
The board can be supplied with an external power DC7-12V from the DC power jack. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-20.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''IOREF ''' | |||
Used to configure the operating voltage of microcontrollers. Use it less. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-21.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''RESET Header ''' | |||
Connect an external button to reset the board. The function is the same as reset button | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-22.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Pin 3V3 Output''' | |||
Provides 3.3V voltage output | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-23.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Pin 5V Output''' | |||
Provides 5V voltage output | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-24.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Vin''' | |||
You can supply an external voltage input DC7-12V through this pin to the board. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-25.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''Analog Pins''' | |||
The UNO board has 6 analog inputs, labeled A0 through A5. | |||
Can also used as digital pins, A0=D14, A1=D15, A2=D16, A3=D17, A4=D18, A5=D19. | |||
For analog port, you can connect through female headers, or through pin headers (labeled S) of 2.54mm pitch. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-26.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''IIC Communication Pin''' | |||
Connect to the IIC communication. | |||
4Pins (GND, VCC (3.3V or 5V controlled by slide switch), SDA, SCL) | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | [[Image:KS0001 5-27.png|500px|frameless]] | |||
| align="light" | '''RESET Button''' | |||
You can reset your board to start the program from the initial status. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:33, 2 August 2018
Introduction
keyestudio UNO with pin headers has the same basic functions as keyestudio UNO R3 BOARD. It is a microcontroller board based on the ATMEGA328P-AU, which has the same function as ATMEGA328P(-PU), fully compatible with ARDUINO UNO REV3.
It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, 2 ICSP headers, and a reset button.
This UNO with pin headers makes the improvement based on keyestudio UNO R3 board.
It breaks out all the digital and analog pins in the form of 3PIN headers (G, V, S).
S pins correspond to all 14 digital pins, 6 analog pins. G pins for ground. V pins for VCC. You can control the voltage of VCC via a slide switch for 5V or 3.3V.
When switched to 5V, level on serial communication port is 5V, voltage of pins is 5V. When switched to 3.3V, level on serial communication port is 3.3V, voltage of pins is 3.3V.
It also breaks out two 4PIN headers for serial communication and IIC communication. So it is more easier to connect external sensors and modules.
As for keyestudio UNO R3 board, its voltage-regulator chip is NSP1117. When connect external power, output 5V, drive current is 1A.
But for this keyestudio UNO with headers, its voltage-regulator chip is MP2307DN. When connect external power, output 5V, drive current is 2A.
It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
Tech Specs
| Microcontroller | ATmega328P-PU |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | DC 7-12V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 (D0-D13) |
| PWM Digital I/O Pins | 6 (D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, D11) |
| Analog Input Pins | 6 (A0-A5) |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 20 mA |
| DC Current for 3.3V Pin | 50 mA |
| Flash Memory | 32 KB (ATmega328) of which 0.5 KB used by bootloader |
| SRAM | 2 KB (ATmega328P-PU) |
| EEPROM | 1 KB (ATmega328P-PU) |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| LED_BUILTIN | D13 |
Dimensions
Element and Interfaces
Element and Pin Interfaces
Here is an explanation chart of what every element and interface of the board does:
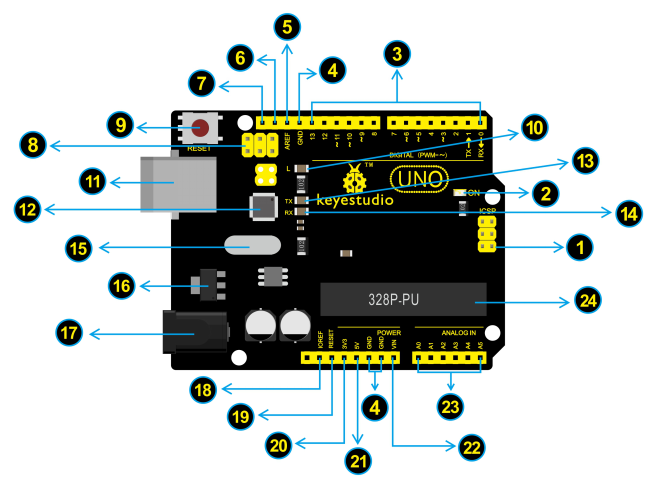

|
ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) Header
ICSP is the AVR, an Arduino micro-program header consisting of MOSI, MISO, SCK, RESET, VCC, and GND. It is often called the SPI (serial peripheral interface) and can be considered an "extension" of the output. In fact, slave the output devices under the SPI bus host. |

|
Serial Communication Pin
Connect to serial communication. 4Pins (GND, VCC (3.3V or 5V controlled by slide switch), RX, TX) |

|
Ground
Ground pins |

|
V Pins (VCC)
Power the external sensors and modules. Select the voltage of 3.3V or 5V via a slide switch. |

|
Digital I/O
It has 14 digital input/output pins, labeled D0 to D13 (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs). These pins can be configured as digital input pin to read the logic value (0 or 1). Or used as digital output pin to drive different modules like LED, relay, etc. The pin D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, and D11 can be used to generate PWM. For digital port, you can connect through female headers, or through pin headers (labeled S) of 2.54mm pitch. |

|
AREF
For Analog reference. Sometimes used to set an external reference voltage (0-5V) as the upper limit of analog input pins. |

|
SDA
IIC communication pin |

|
SCL
IIC communication pin |

|
ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) Header
ICSP is an AVR, an Arduino micro-program header consisting of MOSI, MISO, SCK, RESET, VCC, and GND. Connected to ATMEGA 16U2-MU. When connecting to PC, program the firmware to ATMEGA 16U2-MU. |

|
Microcontroller
Each control board has its own microcontroller. You can regard it as the brain of your board. Microcontrollers are usually from ATMEL. Before you load a new program on the Arduino IDE, you must know what IC is on your board. This information can be checked at the top of IC. The microcontroller used in this board is ATMEGA328P-AU. |

|
D13 LED
There is a built-in LED driven by digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off. |

|
RX LED
Onboard you can find the label: RX(receive ) When UNO board communicates via serial port, receive the message, TX led flashes. |

|
TX LED
Onboard you can find the label: TX (transmit) When Arduino board communicates via serial port, send the message, TX led flashes. |

|
Power LED
LED on means that your circuit board is correctly powered on. Otherwise LED is off. |

|
USB Connection
You can power the board via USB connection. Or can upload the program to the board via USB port. Connect the board to PC using a USB cable via USB port. |

|
ATMEGA 16U2-MU
USB to serial chip, can convert the USB signal into serial port signal. |

|
Slide Switch
You can slide the switch to control the voltage of pin V (VCC), 3.3V or 5V. |

|
Voltage Regulator
To control the voltage provided to the UNO board, as well as to stabilize the DC voltage used by the processor and other components. Convert an external input DC7-12V voltage into DC 5V, then switch DC 5V to the processor and other components, output DC 5V, drive current is 2A |

|
DC Power Jack
The board can be supplied with an external power DC7-12V from the DC power jack. |

|
IOREF
Used to configure the operating voltage of microcontrollers. Use it less. |

|
RESET Header
Connect an external button to reset the board. The function is the same as reset button |

|
Pin 3V3 Output
Provides 3.3V voltage output |

|
Pin 5V Output
Provides 5V voltage output |

|
Vin
You can supply an external voltage input DC7-12V through this pin to the board. |

|
Analog Pins
The UNO board has 6 analog inputs, labeled A0 through A5. Can also used as digital pins, A0=D14, A1=D15, A2=D16, A3=D17, A4=D18, A5=D19. For analog port, you can connect through female headers, or through pin headers (labeled S) of 2.54mm pitch. |

|
IIC Communication Pin
Connect to the IIC communication. 4Pins (GND, VCC (3.3V or 5V controlled by slide switch), SDA, SCL) |

|
RESET Button
You can reset your board to start the program from the initial status. |