Ks0191 keyestudio Smart Small Turtle Robot: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1,553: | Line 1,553: | ||
==Resources == | ==Resources == | ||
Everything you need is in the following link: | |||
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0191 | |||
<br> | |||
==Buy from == | |||
'''Official Website:''' <br> | |||
http://www.keyestudio.com/keyestudio-smart-small-turtle-robot.html | |||
''' | |||
'''Available on amazon:''' <br> | |||
''' | https://www.amazon.com/dp/B01J7HAM7M | ||
[[Category: Smart Car]] | [[Category: Smart Car]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:09, 25 May 2020
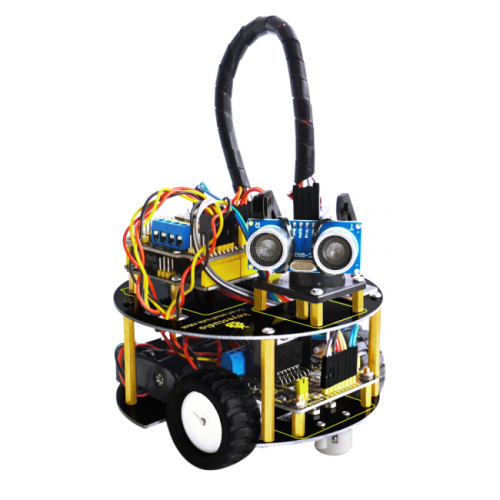
keyestudio Smart Small Turtle Robot
Introduction
keyestudio small turtle robot is a learning application development system of microcontroller. It's based on ARDUINO microcontroller series atmega-328. It has functions such as line tracking, obstacle avoidance, infrared remote control and Bluetooth wireless remote control. This kit contains many interesting programs. It can also be expanded to have external circuit module to have other functions. This kit is designed to help you interestingly learn Arduino. You can learn Arduino MCU development ability while having fun.
Parameters
1. Motor parameters: voltage range: 1.5-12V; motor shaft length: 10 mm; revolving speed: 6.0 V 100 RPM/min.
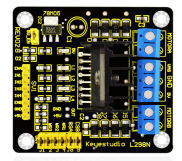
2. Use L298N driver module for motor control, true separation from microcontroller.
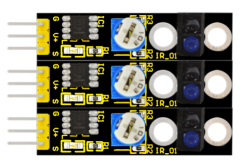
3. Three line tracking modules, detecting black and white line, high precision, can also be used in fall prevention.
4. Infrared remote communication module makes up the remote control system.
5. Ultrasonic module makes up the obstacle avoidance system.
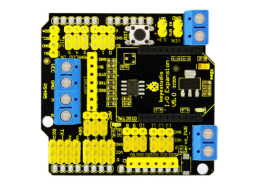
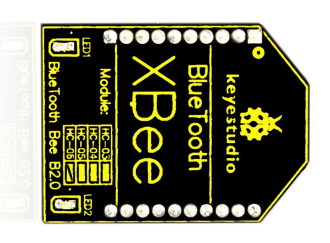
6. With bluetooth wireless module, remotely control the robot after bluetooth pairing with mobile phone.
7. Can be used under external 7 ~ 12V voltage, also with various sensor modules to realize various functions.
Component List
Project List
1.Application of L298N motor driver board
2.Tracking smart car
3.Ultrasonic obstacle avoidance smart car
4.Infrared remote control smart car
5.Arduino bluetooth remote control programmable smart car
6.4 in 1 (line tracking; obstacle avoidance; Infrared remote control; bluetooth remote control) multi-functional program
Application of Arduino
Introduction
What’s Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source hardware project platform. This platform includes a circuit board with simple I/O function and program development environment software. It can be used to develop interactive products. For example, it can read signals of multiple switches and sensors, and control light, servo motor and other various physical devices. It’s widely applied in robot field.
Arduino installation and program upload:
First, download the Arduino development software, click below hyperlink:
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/OldSoftwareReleases#1.5.x
Downloaded file is a arduino-1.5.6-r2-windows.zip compressed folder, unzip it to your hard drive.
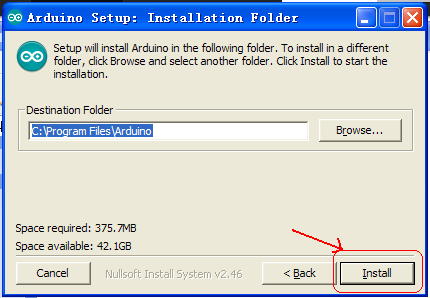
Double click Arduino-1.5.6 .exe. Click “I agree”;
Click “Next”;
And then “Install”;
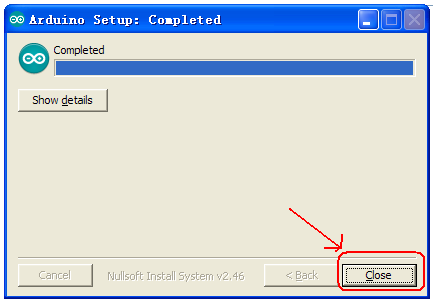
Wait for the installation to be completed, click close.
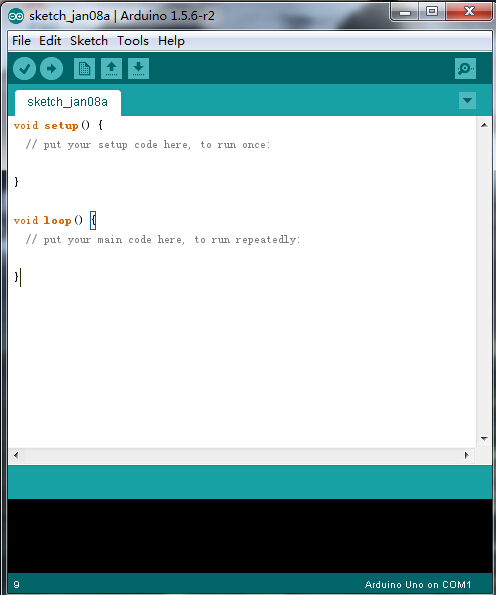
Below is how Arduino 1.5.6 looks like.
Next, let’s install Arduino driver.
For different operating system, there may be slight difference in installation method. Below is an example in WIN 7.
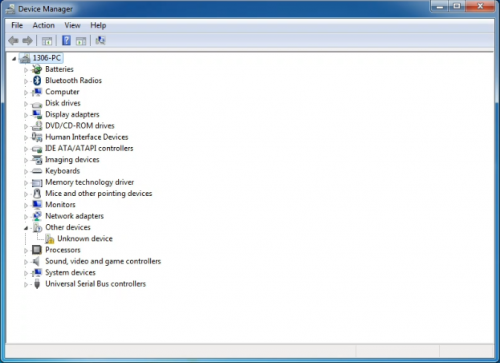
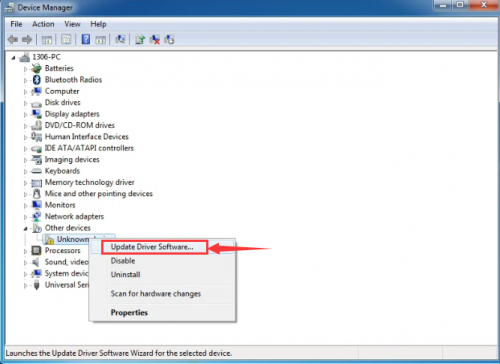
When you connect Arduino Uno to your computer the first time, right click “Computer” —> “Properties”—> “Device manager”, you can see “Unknown devices”.
Click “Unknown devices”, select “Update Driver software”.
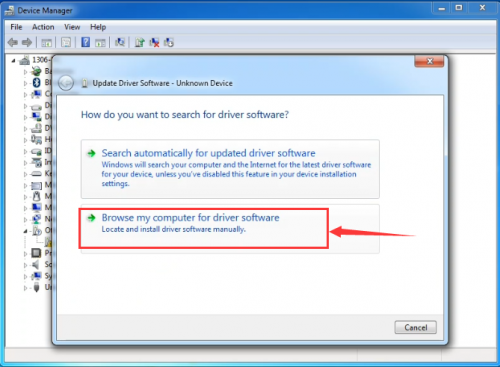
In this page, click “Browse my computer for driver software”.
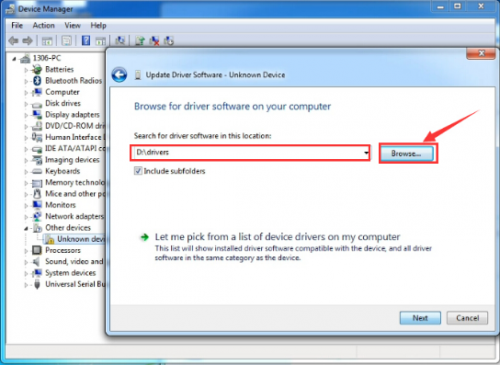
Find the “drivers” file.
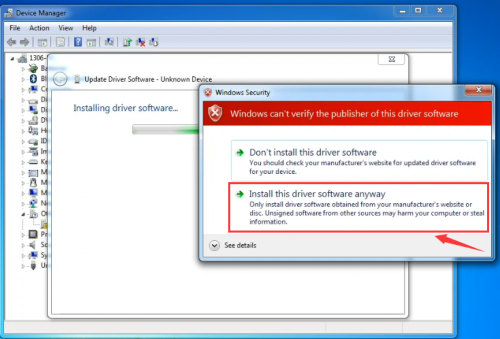
Click “Next”; select “Install this driver software anyway” to begin the installation.
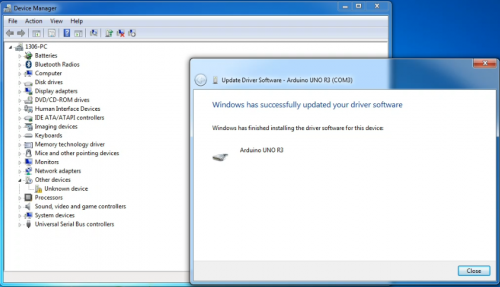
Installation completed; click “Close”.
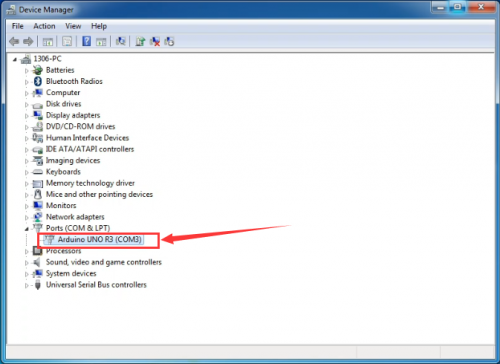
After driver is installed, go to “Device manager” again. Right click “Computer” —> “Properties”—> “Device manager”, you can see UNO device as below figure shows, also the Com port info.
Following is a sketch uploading example called “Hello World!”.
First, open Arduino IDE. In this example sketch, we program Arduino to display “Hello World!” in serial monitor when it receives a specific character string “R”; also the on-board D13 LED will blink once each time it receives “R”.
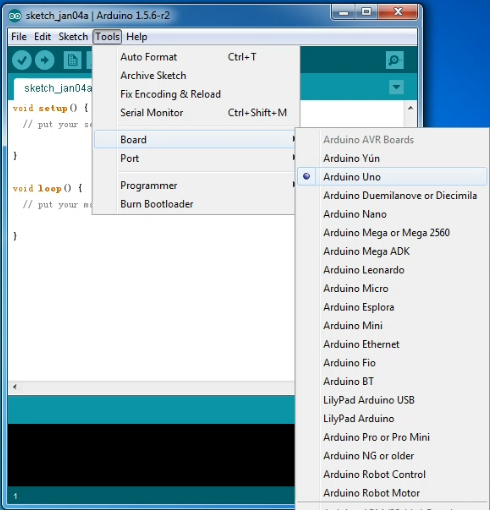
First, set up board; In “Tools”, select “Arduino Uno”.
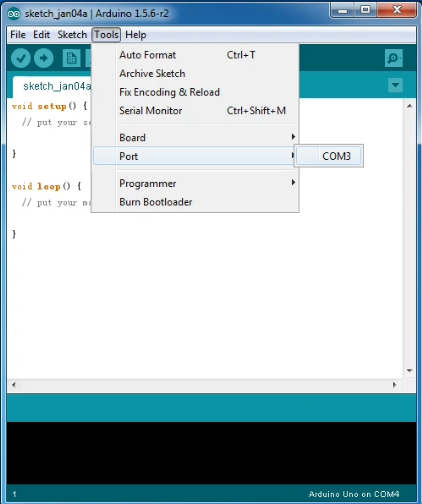
Next, set up COM port; In “Tools”, select “COM3”.
After selection, you can see indicated area is the same with settings in “Device manager”.
Copy the example sketch and paste it to the IDE; click “Verify ![]() ” to check compiling mistakes; click “Upload
” to check compiling mistakes; click “Upload ![]() ” to upload the program to the board.
” to upload the program to the board.
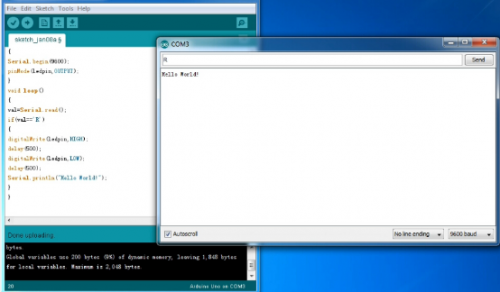
After uploading is done, open “serial monitor![]() ”; enter “R”; click “Send”, the serial monitor will display “Hello World!” and the D13 LED will blink once.
”; enter “R”; click “Send”, the serial monitor will display “Hello World!” and the D13 LED will blink once.
Congratulations! Your first sketch uploading is a success!
Project Details
1) The application of L298N motor driver board
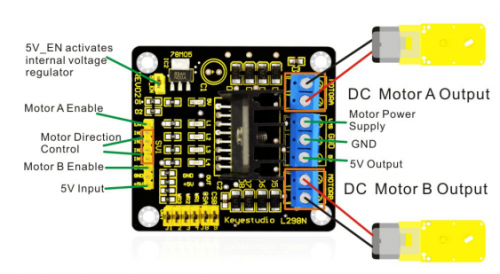
For the instruction for L298N driver board please refer to (L298N dual-H bridge DC motor driver board manual). Some of you still don't know how to control dual DC motor. Here are the details.
For the VMS driver part, power supply can be external power source, generally about 9V. For the logic part, power supply can be from the board internally; with terminals in suspense state, they can also be connected to +5V to +7V power. The three pins between each terminal are used to control the dual DC motor. EA and EB are connected to Arduino PWM interface for motor speed regulation. I1, I2, I3, I2 interface, connected to Arduino digital interfaces, are used for controlling the motor going forward, backward, steering and braking. Up until now, the preparatory work is completed. You can begin writing the program now. Here, the program for your reference includes car going straight, backward, turning left, turning right, and braking.
Program:
int pinI1=5;// define pin I1
int pinI2=6;// define pin I2
int speedpin=3;// define pin EA(PWM speed regulation)
int pinI3=10;// define pin I3
int pinI4=11;// define pin I4
int speedpin1=9;// define pin EB(PWM speed regulation)
void setup()
{
pinMode(pinI1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinI2,OUTPUT);
pinMode(speedpin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinI3,OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinI4,OUTPUT);
pinMode(speedpin1,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
// going straight
analogWrite(speedpin,100);// input analog value to set the speed
analogWrite(speedpin1,100);
digitalWrite(pinI4,LOW);// make the DC motor turn(right) anti-clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI3,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinI1,LOW);// make the DC motor turn(left) clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI2,HIGH);
delay(2000);
// going backwards
analogWrite(speedpin,100);// input analog value to set the speed
analogWrite(speedpin1,100);
digitalWrite(pinI4,HIGH);// make the DC motor turn(right) clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI3,LOW);
digitalWrite(pinI1,HIGH);//make the DC motor turn(left) anti-clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI2,LOW);
delay(2000);
// turning left
analogWrite(speedpin,60);// input analog value to set the speed
analogWrite(speedpin1,60);
digitalWrite(pinI4,LOW);// make the DC motor turn(right) anti-clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI3,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinI1,HIGH);//make the DC motor turn(left) anti-clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI2,LOW);
delay(2000);
// turning right
analogWrite(speedpin,60);//input analog value to set the speed
analogWrite(speedpin1,60);
digitalWrite(pinI4,HIGH);//make the DC motor turn(right) clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI3,LOW);
digitalWrite(pinI1,LOW);//make the DC motor turn(left) clockwise
digitalWrite(pinI2,HIGH);
delay(2000);
// braking
digitalWrite(pinI4,HIGH);// make the DC motor brake(right)
digitalWrite(pinI3,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinI1,HIGH);//make the DC motor brake(left)
digitalWrite(pinI2,HIGH);
delay(2000);
}
Note: in the program, there can be other ways to make the motor turning left or right. You can try it out yourself.
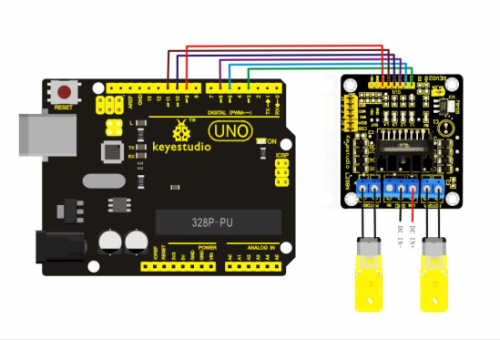
2) Line tracking smart car
Line tracking principle: the working principle of the TCRT5000 infrared double tube is to use the infrared's different reflectivity of different color, and convert the strength of the reflected signal into current signal. For black and white line tracking module, it's high level signal when detecting black line, low level when detecting white line. Detect height is 0-3cm.
Note: you can use a knob potentiometer in the circuit to adjust the sensitivity of this tracking module. TCRT5000 infrared double tube is widely applied in robot design, and industrial manufacture. It can be used for black and white line tracking robot and industrial counting sensors.
Usage:
1. For the sensor, there are 3 pins, namely GND, VCC, OUT. VCC and GND are for power supply. OUT is for signal output.
2. When it detects an object, the signal end outputs low level; when there is no object detected, the signal end outputs high level.
3. By judging whether the signal output is 0 or 1, it can know whether the object exists.
Performance parameter:
1. Detection distance: about 2cm for white paper floor. Different distance depends on the color difference, farthest for white color.
2. Power supply voltage: 2.5V to 12V, no more than 12V. (note: it is better to use low voltage power supply, high power supply voltage will result in shorter service life of the sensor. 5V power supply is preferred.)
2.Working current: 18~20ma when the supply voltage is 5V. After many tests, when the working current is 18~20ma, the sensor is at its best performance in anti-jamming capability.
3.When it detects an object, the signal end outputs low level; when there is no object detected, the signal end outputs high level.
5. The sensor outputs TTL level; can be directly connected to the IO port of 3.3V or 5V MCU.
Black or white line detecting principle:
1.For color black, it has characteristic of low reflectivity to light. When the surface color is not black, most of the red light the sensor sends will be reflected. The sensor outputs low level 0.
2. If there is black line on a surface, when the sensor is on it, color black has low reflectivity; reflected infrared light is not enough to reach the sensor action level, so the sensor output is still l.
3.To detect the black line, we only need a MCU to determine whether the sensor output is 0 or 1.
4. Detecting principle of white line is the same with black line. When white line is detected, the color surrounding the white line is close to black. We then adjust the adjustable resistor of the infrared sensor; lower the sensitivity until the surrounding color cannot be detected. The sensor can then detect the white line.
Test program:
int inputpin=7;// definedigital pin 7 as detection port
int val;// define variable
void setup()
{
pinMode(inputpin,INPUT);// set digital pin 7 as output
Serial.begin(9600);// set baud rate at 9600 for the serial port
}
void loop()
{
val=digitalRead(inputpin);// read the value of the digital port
Serial.println(val);// output the value of the digital port
}
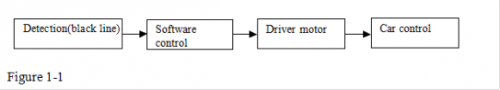
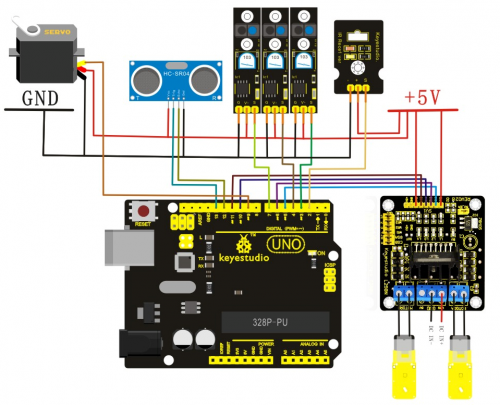
Line tracking smart car After some basic knowledge of line tracking module, let’s make our own line tracking smart car. This design of line tracking car system is base on Arduino . It includes software and hardware design. The controller unit of the car is Arduino UNO, using infrared photoelectric sensor to detect the black track and feedback the information to the Arduino board. Arduino board will have analysis of the acquired information, timely control the driver motor to adjust the moving direction of the car. So the car can drive automatically along the black track, realizing the line tracking function. the system design is as below figure 1-1.
Car tracking principle:here, tracking means the car will move along the black line on the white floor. Because the black line and the white floor has different reflection coefficient, the track can be determine by the strength of the reflected light. Usually, it adopts the method of infrared detection. That is to use infrared ray's feature of reflection over different color. When the car is driving, it will continually emit infrared ray to the ground. When the infrared ray encounters the floor made of white paper. It will be reflected. The reflected ray will be received by the receiver of the car. If it encounters the black track, infrared ray will be absorbed so the receiver won't receive infrared ray. The microcontroller will determine the location of the black line and the moving direction of the car. Note that the detection rage of the infrared detector is limited.
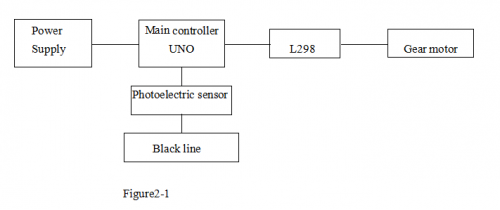
The control system of the line tracking car consists of a main control circuit module, power supply module, infrared detecting module, motor, and a driver module. The control system design is as below figure 2-1.
Flow chart of line tracking car:
When the car enters the tracking mode, it begins constantly scanning I/O port of the MCU. When the I/O port picks up a signal, it will enter the processing; firstly determine which detector detects the black line.
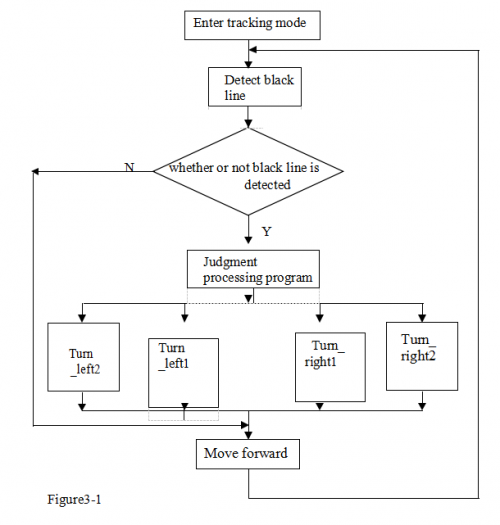
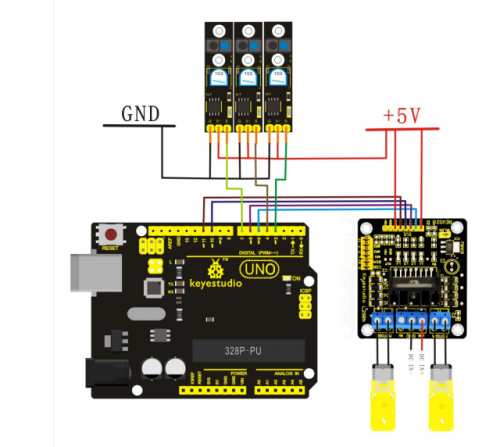
Circuit wiring of Arduino tracking car
Arduino program for tracking car:
int MotorRight1=5;
int MotorRight2=6;
int MotorLeft1=10;
int MotorLeft2=11;
const int SensorLeft = 7; // pin for sensor on the left
const int SensorMiddle= 4 ;// pin for sensor in the middle
const int SensorRight = 3;// pin for sensor on the right
int SL; // left sensor status
int SM; // middle sensor status
int SR; // right sensor status
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(MotorRight1, OUTPUT); // pin 8 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorRight2, OUTPUT); // pin 9 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorLeft1, OUTPUT); // pin 10 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorLeft2, OUTPUT); // pin 11 (PWM)
pinMode(SensorLeft, INPUT); // define left sensor
pinMode(SensorMiddle, INPUT);// define middle sensor
pinMode(SensorRight, INPUT); // define right sensor
}
void loop()
{
SL = digitalRead(SensorLeft);
SM = digitalRead(SensorMiddle);
SR = digitalRead(SensorRight);
if (SM == HIGH)// middle sensor in black area
{
if (SL == LOW & SR == HIGH) // black on left, white on right, turn left
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
analogWrite(MotorLeft1,0);
analogWrite(MotorLeft2,80);
}
else if (SR == LOW & SL == HIGH) // white on left, black on right, turn right
{
analogWrite(MotorRight1,0);// turn right
analogWrite(MotorRight2,80);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
}
else // white on both sides, going forward
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
analogWrite(MotorLeft1,200);
analogWrite(MotorLeft2,200);
analogWrite(MotorRight1,200);
analogWrite(MotorRight2,200);
}
}
else // middle sensor on white area
{
if (SL == LOW & SR == HIGH)// black on left, white on right, turn left
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
else if (SR == LOW & SL == HIGH) // white on left, black on right, turn right
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
}
else // all white, stop
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);;
}}}
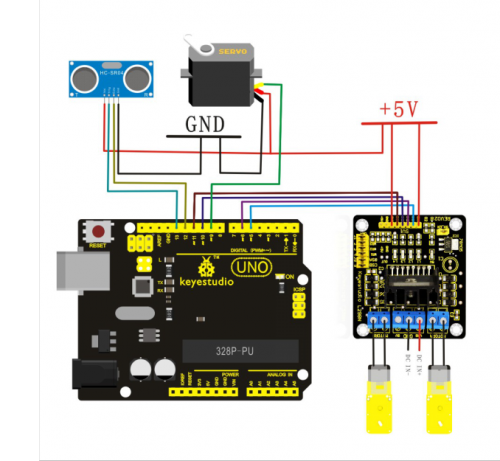
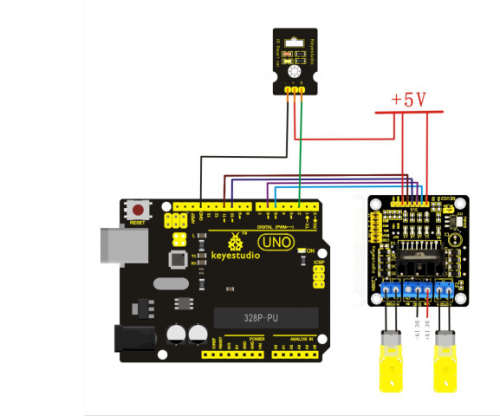
3) Ultrasonic Obstacle Avoidance Smart Car
Ultrasonic obstacle avoidance is easy to realize, simple in calculation. It is easy to control it in real time with practical measuring accuracy. Therefore, it has become a common method for obstacle avoidance. For the application method of ultrasonic, please refer to “Arduino ultrasonic ranging instruction”. Below is the connection diagram for ultrasonic obstacle avoidance:
1. Connection of motor
Motor 1 to L298N MOTOA
Motor 2 to L298N MOTOB
2. Power supply of L298N
Use 1 contact of battery case of 6 cells of AA batteries to supply power for L298N motor driver module, another contact for Arduino main board. The + of the power supply for L298N motor driver module is connected to the VMS of L298N; the - to the GND. + 5V interface of L298N is not connected to anything.
3. The enable and turning function of the motor (with program)
int pinLB=5; // define pin 5 for left and back, connected to pin PWM5of the controller int pinLF=6; // define pin 6 for left and front, connected to pin PWM6 of the controller board int pinRB=10; // define pin 10 for right and back, connected to pin PWM10 of the controller board int pinRF=11; // define pin 11 for right and front, connected to pin PWM11 of the controller board
4. Connection of the servo motor
myservo.attach(9); // set servo motor output as pin 9(PWM)
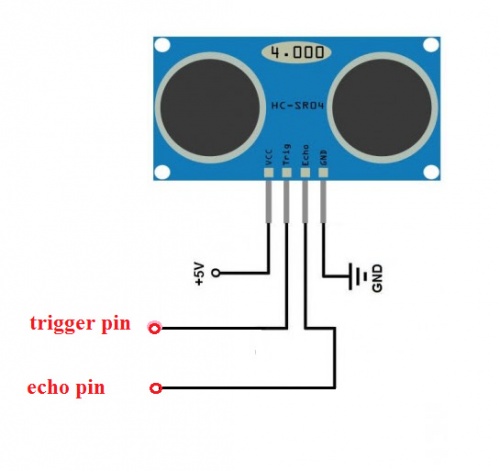
5.Connection of the ultrasonic sensor
4 pins for this sensor
VCC to +5V
TRIQ signal input
ECHO signal output GND to GND
int inputPin = 13; // define receiving pin for ultrasonic signal int outputPin =12; // define sending pin for ultrasonic signal
Ultrasonic obstacle avoidance smart car program (ARDUINO)
/*
L = left
R = right
F = front
B = back
*/
#include <Servo.h>
int pinLB=5; // define pin 6 as left and back
int pinLF=6; // define pin 9 as left and front
int pinRB=10; // define pin 10 as right and back
int pinRF=11; // define pin 11 as right and front
int inputPin = 13; // define receiving pin for ultrasonic signal
int outputPin =12; // define sending pin for ultrasonic signal
int Fspeedd = 0; // speed going forward
int Rspeedd = 0; // speed going right
int Lspeedd = 0; // speed going left
int directionn = 0; //F=8 B=2 L=4 R=6
Servo myservo; // set myservo
int delay_time = 250; // settling time for the servo motor moving backwards
int Fgo = 8; // going forward
int Rgo = 6; // going right
int Lgo = 4; // going left
int Bgo = 2; // going backwards
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // define motor output
pinMode(pinLB,OUTPUT); // pin 5 (PWM)
pinMode(pinLF,OUTPUT); // pin 6 (PWM)
pinMode(pinRB,OUTPUT); // pin 10 (PWM)
pinMode(pinRF,OUTPUT); // pin 11 (PWM)
pinMode(inputPin, INPUT); // define receiving pin for ultrasonic signal
pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT); // define sending pin for ultrasonic signal
myservo.attach(9);// set servo motor output as pin 9(PWM)
}
void advance(int a) // going forward
{
digitalWrite(pinRB,LOW); // motor move right and back
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,LOW); // motor move to left and back
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);
delay(a * 100);
}
void right(int b) // turn right(1 wheel)
{
digitalWrite(pinRB,LOW); //motor move right and back
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);
delay(b * 100);
}
void left(int c) // turn left(1 wheel)
{
digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,LOW); // motor move left and back
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);
delay(c * 100);
}
void turnR(int d) // turn right( 2 wheels)
{digitalWrite(pinRB,LOW); // motor move right and back
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLF,LOW); //motor move left and front
delay(d * 100);
}
void turnL(int e)// turn left(2 wheels)
{digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinRF,LOW); // motor move right and front
digitalWrite(pinLB,LOW); // motor move left and back
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);
delay(e * 100);
}
void stopp(int f)// stop
{digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);
delay(f * 100);
}
void back(int g)// going backwards
{digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH); // motor move right and back
digitalWrite(pinRF,LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH); // motor move left and back
digitalWrite(pinLF,LOW);
delay(g * 100);
}
void detection()// measure 3 angles(0.90.179)
{
int delay_time = 250; // settling time for the servo motor moving backwards
ask_pin_F();// read the distance upfront
if(Fspeedd < 10)// if distance less than 10cm
{
stopp(1);// clear output information
back(2);// going backwards for 0.2 second
}
if(Fspeedd < 25)// if distance less than 25cm
{
stopp(1);// clear output information
ask_pin_L();// read the distance on the left
delay(delay_time);// settling time for the servo
ask_pin_R();// read the distance on the right
delay(delay_time);// settling time for the servo
if(Lspeedd > Rspeedd) // if distance on the left is more than that on the right
{
directionn = Rgo;// going right
}
if(Lspeedd <= Rspeedd) // if distance on the left is less than that on the right
{
directionn = Lgo;// going left
}
if (Lspeedd < 10 && Rspeedd < 10) // if both distance are less than 10cm
{
directionn = Bgo;// going backwards
}
}
else// if the distance upfront is more than 25cm
{
directionn = Fgo;// going forward
}
}
void ask_pin_F() // measure the distance upfront
{
myservo.write(90);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // ultrasonic sends out low voltage 2μs delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); // ultrasonic sends out high voltage 10μs, at least 10μs
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW);// maintain low voltage sending
float Fdistance = pulseIn(inputPin, HIGH); // read the time difference
Fdistance= Fdistance/5.8/10;// convert time into distance(unit: cm)
Serial.print("F distance:");// output distance in cm
Serial.println(Fdistance);// display distance
Fspeedd = Fdistance;// read the distance data into Fspeedd
}
void ask_pin_L()// measure the distance on the left
{
myservo.write(9);
delay(delay_time);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // ultrasonic sends out low voltage 2μs
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH);// ultrasonic sends out high voltage 10μs, at least 10μs
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW);// maintain low voltage sending
float Ldistance = pulseIn(inputPin, HIGH); // read the time difference
Ldistance= Ldistance/5.8/10;// convert time into distance(unit: cm)
Serial.print("L distance:"); //output distance in cm
Serial.println(Ldistance);// display distance
Lspeedd = Ldistance;// read the distance data into Lspeedd
}
void ask_pin_R()// measure the distance on the right
{
myservo.write(177); delay(delay_time);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // ultrasonic sends out low voltage 2μs
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); // ultrasonic sends out high voltage 10μs, at least 10μs
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // maintain low voltage sending
float Rdistance = pulseIn(inputPin, HIGH); //read the time difference
Rdistance= Rdistance/5.8/10; // convert time into distance (unit: cm)
Serial.print("R distance:"); // output distance in cm
Serial.println(Rdistance);// display distance
Rspeedd = Rdistance;// read the distance data into Rspeedd
}
void loop()
{
myservo.write(90); // reset the servo motor and prepare it for the next measurement
detection(); // measure the angle and decide which direction to move
if(directionn == 2) //if directionn = 2
{
back(8);// going backwards
turnL(2);// slightly move to the left to avoid stuck in the dead end
Serial.print(" Reverse "); // display direction (backwards)
}
if(directionn == 6)// if direction = 6
{
back(1);
turnR(6);// turn right
Serial.print(" Right ");// display direction(right)
}
if(directionn == 4)//if direction = 4
{
back(1);
turnL(6);// turn left
Serial.print(" Left ");// display direction(left)
}
if(directionn == 8)//if direction= 8
{
advance(1);// going forward
Serial.print(" Advance "); //display direction(forward)
Serial.print(" ");
}
}
4) Infrared remote control smart car
Before the experiment:
1.Place the function library IRremote into the Arduino libraries directory.
2.Open IrReceive.pde to acquire the code for your infrared remote control ( IRcode will be displayed in Serial Monitor), write down IRcode and modify it in your IR code in the program.
/*
*IRRemote code test
*Example 1.2: display the type of IR protocol such as NEC, Sony SIRC, Philips RC5, Philips RC6
*/
#include <IRremote.h> // call IRRemote function library
const int irReceiverPin = 2; // set pin 2 as IR receiver signal OUTPUT
IRrecv irrecv(irReceiverPin); // set IRrecv to receive IR signal
decode_results results; // decode result will be put into the variable of the result in the decode_results
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);// set communication rate at 9600 bps
irrecv.enableIRIn();// start IR decoding
}
// display the type of IR protocol
void showIRProtocol(decode_results *results)
{
Serial.print("Protocol: ");
// determine the type of IR protocol
switch(results->decode_type) { case NEC:
Serial.print("NEC"); break;
case SONY: Serial.print("SONY"); break;
case RC5: Serial.print("RC5"); break;
case RC6: Serial.print("RC6"); break;
default:
Serial.print("Unknown encoding");
}
// serial print IR code to Serial port Serial.print(", irCode: ");
Serial.print(results->value, HEX); // IR code
Serial.print(", bits: ");
Serial.println(results->bits); // IR code bit
}
void loop()
{
if (irrecv.decode(&results)) { // finish decoding, receive IR signal
showIRProtocol(&results);// display the type of IR protocol
irrecv.resume();// continue receiving IR signal coming next
}
}
Replace the IR code in the IR control part program with the code from the test result IR remote control smart car program
IR remote control smart car program
#include <IRremote.h>
int RECV_PIN = 2;
int pinLB=5;// define pin for I1
int pinLF=6;// define pin for I2
int pinRB=10;// define pin for I3
int pinRF=11;// define pin for I4
//******IR control part********
long advence = 0x00FF629D;
long back = 0x00FFA857;
long stop = 0x00FF02FD;
long left = 0x00FF22DD;
long right = 0x00FFC23D;
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
decode_results results;
void dump(decode_results *results)
{ int count = results->rawlen;
if (results->decode_type == UNKNOWN)
{
Serial.println("Could not decode message");
}
else
{
if (results->decode_type == NEC)
{
Serial.print("Decoded NEC: ");
}
else if (results->decode_type == SONY)
{
Serial.print("Decoded SONY: ");
}
else if (results->decode_type == RC5)
{
Serial.print("Decoded RC5: ");
}
else if (results->decode_type == RC6)
{
Serial.print("Decoded RC6: ");
}
Serial.print(results->value, HEX);
Serial.print(" (");
Serial.print(results->bits, DEC);
Serial.println(" bits)");
}
Serial.print("Raw (");
Serial.print(count, DEC);
Serial.print("): ");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if ((i % 2) == 1) {
Serial.print(results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
else
{
Serial.print(-(int)results->rawbuf[i]*USECPERTICK, DEC);
}
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println("");
}
void setup()
{
pinMode(RECV_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(pinLB,OUTPUT); pinMode(pinLF,OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinRB,OUTPUT); pinMode(pinRF,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the receiver
}
int on = 0;
unsigned long last = millis();
void loop()
{
if (irrecv.decode(&results))
{
// If it's been at least 1/4 second since the last
// IR received, toggle the relay if (millis() - last > 250)
{
on = !on;
// digitalWrite(8, on ? HIGH : LOW);
digitalWrite(13, on ? HIGH : LOW);
dump(&results);
}
if (results.value == advence )
{digitalWrite(pinRB,LOW);// motor going right
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,LOW);// motor going left
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);}
if (results.value == back )
{digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH);// motor going right and BACK
digitalWrite(pinRF,LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);// motor going left and BACK
digitalWrite(pinLF,LOW);}
if (results.value == left )
{ digitalWrite(pinRB,LOW);// motor going right and STOP
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);// motor going left
digitalWrite(pinLF,LOW);}
if (results.value == right )
{ digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH);// motor going right
digitalWrite(pinRF,LOW);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);// motor going left and STOP
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);}
if (results.value == stop )
{
digitalWrite(pinRB,HIGH);// motor going right and STOP
digitalWrite(pinRF,HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinLB,HIGH);// motor going left and STOP
digitalWrite(pinLF,HIGH);
}
last = millis();
irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value
}
}
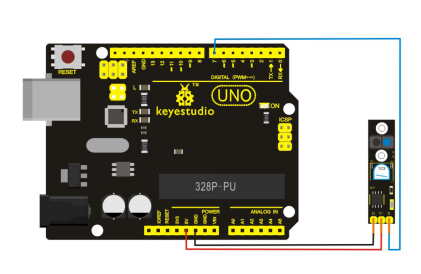
5) Bluetooth smart car controlled by mobile phone
keyestudio Bluetooh XBee Bluetooth wireless module HC-06 adopts XBEE design. It has features of compact size, compatible with XBEE shield, and suitable for various 3.3V MCU systems. The module can use AT command to set baud rate and master/slave mode. The default settings are baud rate 9600, paring password 1234, slave mode.
It comes with efficient on-board antenna. The exposed antenna ensures better signal quality and longer transmitting distance. Transparent serial port can be used to pair up with various Bluetooth adapters, Bluetooth phones. The humanized design offers convenience for secondary development. After testing, the module is known to be suitable in using with all Bluetooth adapters on the market (PC and phones with Bluetooth) .
Now, let’s move on to program. I’ll enter “r” and after Arduino receives my command “r”, the LED in PIN 13 will flicker and print character of “keyes”. The program is as follows:
char val;
int ledpin=13; void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(ledpin,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
val=Serial.read(); if(val=='r')
{
digitalWrite(ledpin,HIGH); delay((500); digitalWrite(ledpin,LOW); delay(500); Serial.println("keyes");
}
}
Now, let’s figure out how to make programmable smart car to go forward, backward, turning left or right via arduino bluetooth remote control. There are two ways to control the movement of smart car, by PC or mobile phone (The phone operating system must support Android 2.3.7 or later version and PC must carry bluetooth). The phone should be paired with bluetooth car during initial use (no need to locate wireless device after first pairing). Please check the following steps for first paring:
1. Don’t forget to turn on the bluetooth function of the phone. The software will remind users to turn on bluetooth function when the software is started.
2. Connect bluetooth device according to the text instructions on the photo. Please scan and pair with bluetooth device, otherwise, you would fail to connect with smart car.
3. The code for pairing with the smart car is “1234”, go try it!
Download the Bluetooth APP Here.
The program for Arduino bluetooth remote control programmable smart car is as follows:
//*******************************
int MotorRight1=5;
int MotorRight2=6;
int MotorLeft1=10;
int MotorLeft2=11;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(MotorRight1, OUTPUT); // pin 5 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorRight2, OUTPUT); // pin 6 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorLeft1, OUTPUT); // pin 10 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorLeft2, OUTPUT); // pin 11 (PWM)
}
void go()// go forward
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
}
void left() // turn right
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
}
void right() // turn left
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
void stop() // stop
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
void back() // go backwards
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
void loop()
{
char val = Serial.read();
Serial.write(val);
if (-1 != val) {
if ('U' == val)
go();
else if ('L' ==val)
left();
else if ('R' == val) right();
else if ('D' == val) back();
else if ('S' == val)
stop();
delay(500);
}
else
{
//stop(); delay(500);
}
}
6) 4 in 1(line tracking, obstacle avoidance, IR control, bluetooth control) program
//******************************
#include <IRremote.h>
#include <Servo.h>
//*********************** define motor pin *************************
int MotorRight1=5;
int MotorRight2=6;
int MotorLeft1=10;
int MotorLeft2=11;
int counter=0;
const int irReceiverPin = 2; // set pin 2 as IR receiver signal OUTPUT
char val;
//***********************set the IRcode from the test result*************************
long IRfront= 0x00FF629D; // code for going forward
long IRback=0x00FFA857; // going backward
long IRturnright=0x00FFC23D; // turn right
long IRturnleft= 0x00FF22DD; // turn left
long IRstop=0x00FF02FD; // stop
long IRcny70=0x00FF6897; // CNY70 aoto-movingmode
long IRAutorun=0x00FF9867; // ultrasonic aoto-movingmode
long IRturnsmallleft= 0x00FFB04F;
//************************* define pin CNY70************************************
const int SensorLeft = 7; // input pin for left sensor
const int SensorMiddle= 4 ; // input pin for middle sensor
const int SensorRight = 3; // input pin for right sensor
int SL; // left sensor status
int SM; // middle sensor status
int SR; // right sensor status
IRrecv irrecv(irReceiverPin); // set IRrecv to receive IR signal
decode_results results; // decode result will be put into the variable of the result in the
//************************* define pin for ultrasonic ******************************
int inputPin =13 ; // define ultrasonic signal receiving pin rx
int outputPin =12; // define ultrasonic signal sending pin'tx
int Fspeedd = 0; // distance upfront
int Rspeedd = 0; // distance on the right
int Lspeedd = 0; // distance on the left
int directionn = 0; // F=8 B=2 L=4 R=6
Servo myservo; // set myservo
int delay_time = 250; // settling time for the servo motor moving backwards
int Fgo = 8; // going forward
int Rgo = 6; // going right
int Lgo = 4;// going left
int Bgo = 2;// going backwards
//********************************************************************(SETUP)
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(MotorRight1, OUTPUT); // pin 8 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorRight2, OUTPUT); // pin 9 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorLeft1, OUTPUT); // pin 10 (PWM)
pinMode(MotorLeft2, OUTPUT); // pin 11 (PWM)
irrecv.enableIRIn(); // start IR decoding
pinMode(SensorLeft, INPUT); //define left sensor
pinMode(SensorMiddle, INPUT);// define middle sensor
pinMode(SensorRight, INPUT); // define right sensor
digitalWrite(2,HIGH);
pinMode(inputPin, INPUT); // define receiving pin for ultrasonic signal
pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT); // define sending pin for ultrasonic signal
myservo.attach(9); // set servo motor output as pin 5(PWM)
}
//******************************************************************(Void)
void advance(int a) // go forward
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
delay(a * 100);
}
void right(int b) //turn right(1 wheel)
{
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
delay(b * 100);
}
void left(int c) // turn left(1 wheel)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
delay(c * 100);
}
void turnR(int d) // turn right(2 wheels)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
delay(d * 100);
}
void turnL(int e) // turn left (2 wheels)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
delay(e * 100);
}
void stopp(int f) // stop
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
delay(f * 100);
}
void back(int g) // go backwards
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);;
delay(g * 100);
}
void detection() // measure 3 angles(0.90.179)
{
int delay_time = 250; // settling time for the servo motor moving backwards
ask_pin_F(); // read the distance upfront
if(Fspeedd < 10) // if distance less than 10cm
{
stopp(1); // clear output information
back(2); // oing backwards for 0.2second
}
if(Fspeedd < 15) // if distance less than 25cm
{
stopp(1); // clear output information
ask_pin_L(); // read the distance on the left
delay(delay_time); // settling time for the servo
ask_pin_R(); // read the distance on the right
delay(delay_time); // settling time for the servo
if(Lspeedd > Rspeedd) //if distance on the left is more than that on the right
{
directionn = Lgo; // go left
}
if(Lspeedd <= Rspeedd) // if distance on the left is less than that on the right
{
directionn = Rgo; // going right
}
if (Lspeedd < 10 && Rspeedd < 10) // if both distance are less than 10cm
{
directionn = Bgo; // going backwards
}
}
else // if the distance upfront is more than 25cm
{
directionn = Fgo; // going forward
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
void ask_pin_F() // measure the distance upfront
{
myservo.write(90);
delay(delay_time);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW);// ultrasonic sends out low voltage 2μs
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); // ultrasonic sends out high voltage 10μs, at least 10μs
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // maintain low voltage sending
float Fdistance = pulseIn(inputPin, HIGH); // read the time difference
Fdistance= Fdistance/5.8/10; // convert time into distance (unit: cm)
Serial.print("Fdistance:"); //output distance in cm
Serial.println(Fdistance);// display distance
Fspeedd = Fdistance; // read the distance data into Fspeedd
}
//*****************************************************************************
void ask_pin_L() // measure the distance on the left
{
myservo.write(177);
delay(delay_time);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // ultrasonic sends out low voltage 2μs
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); // ultrasonic sends out high voltage 10μs, at least 10μs
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // maintain low voltage sending
float Ldistance = pulseIn(inputPin, HIGH); // read the time difference
Ldistance= Ldistance/5.8/10; //converttime intodistance(unit: cm)
Serial.print("Ldistance:"); //output distance in cm
Serial.println(Ldistance);//display distance
Lspeedd = Ldistance; // read the distance data into Lspeedd
}
//*****************************************************************************
void ask_pin_R() // measure the distance on the right
{
myservo.write(5);
delay(delay_time);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW);// ultrasonic sends out low voltage 2μs
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); // ultrasonic sends out high voltage 10μs, at least 10μs
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); //maintain low voltage sending
float Rdistance = pulseIn(inputPin, HIGH); //read the time difference
Rdistance= Rdistance/5.8/10; //convert time into distance(unit: cm)
Serial.print("Rdistance:"); //output distance in cm
Serial.println(Rdistance);//display distance
Rspeedd = Rdistance; // read the distance data into Rspeedd
}
//******************************************************************************(LOOP)
void loop()
{
SL=digitalRead(SensorLeft);
SM = digitalRead(SensorMiddle);
SR = digitalRead(SensorRight);
performCommand();
//***************************************************normal remote control mode
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{ // finish decoding, receive IR signal
/***********************************************************************/
if (results.value == IRfront)// go forward
{
advance(10);// go forward
}
/***********************************************************************/
if (results.value == IRback)// go backward
{
back(5);// go backward
}
/***********************************************************************/
if (results.value == IRturnright)// turn right
{
right(5); // turn right
}
/***********************************************************************/
if (results.value == IRturnleft)// turn left
{
left(5); // turn left);
}
/***********************************************************************/
if (results.value == IRstop)// stop
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
//****************************************************** black and white line mode
if (results.value == IRcny70)
{
while(IRcny70)
{
SL= digitalRead(SensorLeft);
SM = digitalRead(SensorMiddle);
SR = digitalRead(SensorRight);
if (SM == HIGH)// middle sensor in black area
{
if (SL == LOW & SR == HIGH) // black on left, white on right, turn left
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
else if (SR == LOW & SL == HIGH) // white on left, black on right, turn right
{
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
}
else // white on both sides, going forward
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
}
}
else // middle sensor on white area
{
if (SL== LOW & SR == HIGH)// black on left, white on right, turn left
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
else if (SR == LOW & SL == HIGH) // white on left, black on right, turn right
{
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
}
else // all white, stop
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
}
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{
irrecv.resume();
Serial.println(results.value,HEX);
if(results.value==IRstop)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,HIGH);
break;
}
}
}
results.value=0;
}
//******************************************************** ultrasonic auto-moving mode
if (results.value ==IRAutorun )
{
while(IRAutorun)
{
myservo.write(90); // reset the servo motor and prepare it for the next measurement
detection(); // measure the angle and decide which direction to move
if(directionn == 8) // if directionn = 8
{
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{
irrecv.resume();
Serial.println(results.value,HEX);
if(results.value==IRstop)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
break;
}
}
results.value=0; advance(1); // going forward
Serial.print("Advance "); // display direction(forward)
Serial.print(" ");
}
if(directionn == 2) // if directionn = 2
{
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{
irrecv.resume();
Serial.println(results.value,HEX);
if(results.value==IRstop)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
break;
}
}
results.value=0;
back(2); // going backwards
turnL(3); // slightly move to the left to avoid stuck in the dead end
Serial.print(" Reverse "); // display direction (backwards)
}
if(directionn == 6) // if direction = 6
{
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{
irrecv.resume();
Serial.println(results.value,HEX);
if(results.value==IRstop)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
break;
}
}
results.value=0;
back(2);
turnR(3); // turn right
Serial.print(" Right "); // display direction(right)
}
if(directionn == 4) // if direction = 4
{
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{
irrecv.resume();
Serial.println(results.value,HEX);
if(results.value==IRstop)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
break;
}
}
results.value=0;
back(2);
turnL(3); // turn left
Serial.print(" Left "); // display direction(left)
}
if(irrecv.decode(&results))
{
irrecv.resume();
Serial.println(results.value,HEX);
if(results.value==IRstop)
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
break;
}
}
}
results.value=0;
}
/***********************************************************************/
else
{
digitalWrite(MotorRight1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorRight2,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft1,LOW);
digitalWrite(MotorLeft2,LOW);
}
irrecv.resume(); // continue receiving IR signal coming next
}
}
void performCommand()
{ if(Serial.available())
{ val = Serial.read();
}
if (val == 'U') { // Forward
advance(1);
} else if (val == 'D') { //Backward
back(1);
} else if (val == 'R') { // Right
turnR(1);
} else if (val == 'L') { // Left
turnL(1);
} else if (val== 'S') { // Stop
stopp(1) ;
}
}
Resources
Everything you need is in the following link:
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0191
Buy from
Official Website:
http://www.keyestudio.com/keyestudio-smart-small-turtle-robot.html
Available on amazon:
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B01J7HAM7M