Ks0267 keyestudio APDS-9930 Attitude Sensor Module: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<br> | |||
==Keyestudio APDS-9930 Attitude Sensor Module== | ==Keyestudio APDS-9930 Attitude Sensor Module== | ||
<br>[[File:KS0267- | <br>[[File:KS0267--.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Keyestudio APDS-9930 attitude sensor module mainly uses APDS-9930 chip. APDS-9930 in a single 8 pin package can provide the ambient light sensor which is compatible with I2C interface and the infrared LED proximity sensor. <br> | |||
Keyestudio APDS-9930 attitude sensor module mainly uses APDS-9930 chip. APDS-9930 in a single 8 pin package can provide the ambient light sensor which is compatible with I2C interface and the infrared LED proximity sensor. The ambient light sensor uses double light diode to approximate the visual response of low lumen human under 0.01 lux illumination, and its high sensitivity allows the device to operate in the | The ambient light sensor uses double light diode to approximate the visual response of low lumen human under 0.01 lux illumination, and its high sensitivity allows the device to operate in the dark glass. <br> | ||
The proximity sensor which is completely adjusted can detect 100 mm object, and exempt the factory calibration requirements of terminal equipment as well as sub-components. From the bright sunlight to the dark room, proximity sensor’s proximity detection function can operate well. This module added micro optical lens can provide infrared energy efficient transmission and reception, which can reduce the overall power consumption. In addition, its internal state machine can make the device into a low power mode, bringing a very low average power consumption. | The proximity sensor which is completely adjusted can detect 100 mm object, and exempt the factory calibration requirements of terminal equipment as well as sub-components. From the bright sunlight to the dark room, proximity sensor’s proximity detection function can operate well. <br> | ||
This module added micro optical lens can provide infrared energy efficient transmission and reception, which can reduce the overall power consumption. In addition, its internal state machine can make the device into a low power mode, bringing a very low average power consumption. <br> | |||
<br>[[File:KS0267-(1.jpg|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:KS0267-(1.jpg|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | |||
==Performance Parameters== | ==Performance Parameters== | ||
*Working Voltage:DC 3.3-3.8V | *Working Voltage:DC 3.3-3.8V | ||
| Line 14: | Line 19: | ||
*Temperature Range:-40℃ to +85℃ | *Temperature Range:-40℃ to +85℃ | ||
<br> | |||
==Features == | ==Features == | ||
* Optical module integrated with ALS, infrared LED and proximity detector; | * Optical module integrated with ALS, infrared LED and proximity detector; | ||
| Line 30: | Line 36: | ||
* Sleep mode power - 2.2μA (typical value). | * Sleep mode power - 2.2μA (typical value). | ||
<br> | |||
==Connection Diagram == | ==Connection Diagram == | ||
<br>[[File:KS0267.png| | <br>[[File:KS0267.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | |||
==Sample Code== | ==Sample Code== | ||
<br> | |||
'''Libraries Download of Wire and APDS9930:''' [http://www.keyestudio.com/files/index/download/id/1505456458/] | |||
<br> | |||
* Hardware Connections:<br> | |||
<span style=color:red> IMPORTANT: The APDS-9960 can only accept 3.3V!<br> | |||
Arduino Pin APDS-9960 Board Function <br> | |||
3.3V - VCC - Power <br> | |||
GND - GND - Ground <br> | |||
A4 - SDA - I2C Data <br> | |||
A5 - SCL - I2C Clock <br> | |||
2 - INT - Interrupt <br> | |||
13 - - - LED <br> | |||
* Resources: <br> | |||
Include Wire.h and SparkFun_APDS-9960.h <br> | |||
Development environment specifics:<br> | |||
Written in Arduino 1.5.6 | |||
<br> | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
#include <Wire.h> | #include <Wire.h> | ||
#include < | #include <SparkFun_APDS9960.h> | ||
// Pins | // Pins | ||
#define | #define APDS9960_INT 2 // Needs to be an interrupt pin | ||
#define LED_PIN 13 // LED for showing interrupt | #define LED_PIN 13 // LED for showing interrupt | ||
// Constants | // Constants | ||
#define | #define LIGHT_INT_HIGH 1000 // High light level for interrupt | ||
#define | #define LIGHT_INT_LOW 10 // Low light level for interrupt | ||
// Global variables | // Global variables | ||
SparkFun_APDS9960 apds = SparkFun_APDS9960(); | |||
uint16_t ambient_light = 0; | |||
uint16_t | uint16_t red_light = 0; | ||
uint16_t | uint16_t green_light = 0; | ||
uint16_t | uint16_t blue_light = 0; | ||
int isr_flag = 0; | |||
uint16_t threshold = 0; | |||
void setup() { | |||
// Set LED as output | |||
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); | |||
pinMode(APDS9960_INT, INPUT); | |||
// Initialize Serial port | |||
Serial.begin(9600); | |||
Serial.println(); | |||
Serial.println(F("-------------------------------------")); | |||
Serial.println(F("SparkFun APDS-9960 - Light Interrupts")); | |||
Serial.println(F("-------------------------------------")); | |||
// Initialize interrupt service routine | |||
attachInterrupt(0, interruptRoutine, FALLING); | |||
// Initialize APDS-9960 (configure I2C and initial values) | |||
if ( apds.init() ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("APDS-9960 initialization complete")); | |||
} else { | |||
Serial.println(F("Something went wrong during APDS-9960 init!")); | |||
} | |||
// Set high and low interrupt thresholds | |||
if ( !apds.setLightIntLowThreshold(LIGHT_INT_LOW) ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("Error writing low threshold")); | |||
} | |||
if ( !apds.setLightIntHighThreshold(LIGHT_INT_HIGH) ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("Error writing high threshold")); | |||
} | |||
// Start running the APDS-9960 light sensor (no interrupts) | |||
if ( apds.enableLightSensor(false) ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("Light sensor is now running")); | |||
} else { | |||
Serial.println(F("Something went wrong during light sensor init!")); | |||
} | |||
// Read high and low interrupt thresholds | |||
if ( !apds.getLightIntLowThreshold(threshold) ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("Error reading low threshold")); | |||
} else { | |||
Serial.print(F("Low Threshold: ")); | |||
Serial.println(threshold); | |||
} | |||
if ( !apds.getLightIntHighThreshold(threshold) ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("Error reading high threshold")); | |||
} else { | |||
Serial.print(F("High Threshold: ")); | |||
Serial.println(threshold); | |||
} | |||
// Enable interrupts | |||
if ( !apds.setAmbientLightIntEnable(1) ) { | |||
Serial.println(F("Error enabling interrupts")); | |||
} | |||
// Wait for initialization and calibration to finish | |||
delay(500); | |||
} | } | ||
void loop() { | void loop() { | ||
// If interrupt occurs, print out the light levels | |||
if ( isr_flag == 1 ) { | |||
// Read the light levels (ambient, red, green, blue) and print | |||
if ( !apds.readAmbientLight(ambient_light) || | |||
!apds.readRedLight(red_light) || | |||
!apds.readGreenLight(green_light) || | |||
!apds.readBlueLight(blue_light) ) { | |||
Serial.println("Error reading light values"); | |||
} else { | |||
Serial.print("Interrupt! Ambient: "); | |||
Serial.print(ambient_light); | |||
Serial.print(" R: "); | |||
Serial.print(red_light); | |||
Serial.print(" G: "); | |||
Serial.print(green_light); | |||
Serial.print(" B: "); | |||
Serial.println(blue_light); | |||
} | |||
// Turn on LED for a half a second | |||
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); | |||
delay(500); | |||
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); | |||
// Reset flag and clear APDS-9960 interrupt (IMPORTANT!) | |||
isr_flag = 0; | |||
if ( !apds.clearAmbientLightInt() ) { | |||
Serial.println("Error clearing interrupt"); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | } | ||
void interruptRoutine() { | void interruptRoutine() { | ||
isr_flag = 1; | |||
} | } | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<br> | |||
==Test Result== | ==Test Result== | ||
Wiring as the above diagram and burning the code, after | Wiring as the above diagram and burning the code, after powered-on, open the serial monitor, as the graph shown below.<br> | ||
<br>[[File:KS0267-3.png|600px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==Resources == | |||
* '''Libraries and Code Download:''' <br> | |||
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0267 | |||
<br> | |||
==Buy from == | |||
''' | *[https://www.keyestudio.com/keyestudio-apds-9930-attitude-sensor-module-for-arduino-p0377-p0377.html '''Official Website''' ] | ||
*[https://www.aliexpress.com/store/product/Keyestudio-APDS-9930-Attitude-Sensor-Module-for-Arduino/1452162_32823142352.html '''Aliexpress store''' ] | |||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07F1R4HJ1 '''Shop on amazon store''' ] | |||
[[Category:Module]] | [[Category:Module]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:52, 8 January 2021
Keyestudio APDS-9930 Attitude Sensor Module
Introduction
Keyestudio APDS-9930 attitude sensor module mainly uses APDS-9930 chip. APDS-9930 in a single 8 pin package can provide the ambient light sensor which is compatible with I2C interface and the infrared LED proximity sensor.
The ambient light sensor uses double light diode to approximate the visual response of low lumen human under 0.01 lux illumination, and its high sensitivity allows the device to operate in the dark glass.
The proximity sensor which is completely adjusted can detect 100 mm object, and exempt the factory calibration requirements of terminal equipment as well as sub-components. From the bright sunlight to the dark room, proximity sensor’s proximity detection function can operate well.
This module added micro optical lens can provide infrared energy efficient transmission and reception, which can reduce the overall power consumption. In addition, its internal state machine can make the device into a low power mode, bringing a very low average power consumption.
Performance Parameters
- Working Voltage:DC 3.3-3.8V
- Output Current:0-20mA
- Temperature Range:-40℃ to +85℃
Features
- Optical module integrated with ALS, infrared LED and proximity detector;
- Ambient Light Sensing,similar to the human eye’s visual response;
- Programmable interruption function with upper and lower thresholds;
- Up to 16-bit resolution;
- High sensitivity of operation in the back of dark glass;
- 0.01lux low lumen performance;
- Proximity detection, fully calibrated to 100 mm detection;
- Integrate infrared LED and synchronous LED driver;
- Eliminate factory calibration for proximity sensors;
- Programmable waiting timer, waiting state’s power consumption - 90μA (typical value);
- Programmable range is from 2.7 milliseconds to 8 seconds;
- Compatible with I2C interface, up to 400kHz (I2C fast mode);
- Dedicated interruption pin;
- Sleep mode power - 2.2μA (typical value).
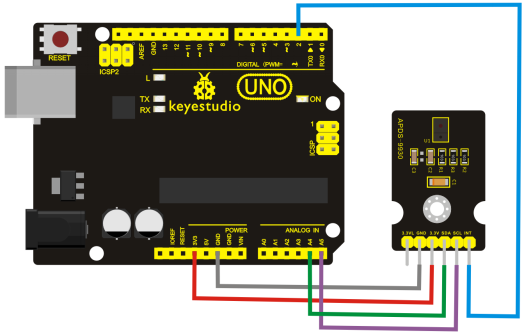
Connection Diagram
Sample Code
Libraries Download of Wire and APDS9930: [1]
- Hardware Connections:
IMPORTANT: The APDS-9960 can only accept 3.3V!
Arduino Pin APDS-9960 Board Function
3.3V - VCC - Power
GND - GND - Ground
A4 - SDA - I2C Data
A5 - SCL - I2C Clock
2 - INT - Interrupt
13 - - - LED
- Resources:
Include Wire.h and SparkFun_APDS-9960.h
Development environment specifics:
Written in Arduino 1.5.6
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SparkFun_APDS9960.h>
// Pins
#define APDS9960_INT 2 // Needs to be an interrupt pin
#define LED_PIN 13 // LED for showing interrupt
// Constants
#define LIGHT_INT_HIGH 1000 // High light level for interrupt
#define LIGHT_INT_LOW 10 // Low light level for interrupt
// Global variables
SparkFun_APDS9960 apds = SparkFun_APDS9960();
uint16_t ambient_light = 0;
uint16_t red_light = 0;
uint16_t green_light = 0;
uint16_t blue_light = 0;
int isr_flag = 0;
uint16_t threshold = 0;
void setup() {
// Set LED as output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(APDS9960_INT, INPUT);
// Initialize Serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("-------------------------------------"));
Serial.println(F("SparkFun APDS-9960 - Light Interrupts"));
Serial.println(F("-------------------------------------"));
// Initialize interrupt service routine
attachInterrupt(0, interruptRoutine, FALLING);
// Initialize APDS-9960 (configure I2C and initial values)
if ( apds.init() ) {
Serial.println(F("APDS-9960 initialization complete"));
} else {
Serial.println(F("Something went wrong during APDS-9960 init!"));
}
// Set high and low interrupt thresholds
if ( !apds.setLightIntLowThreshold(LIGHT_INT_LOW) ) {
Serial.println(F("Error writing low threshold"));
}
if ( !apds.setLightIntHighThreshold(LIGHT_INT_HIGH) ) {
Serial.println(F("Error writing high threshold"));
}
// Start running the APDS-9960 light sensor (no interrupts)
if ( apds.enableLightSensor(false) ) {
Serial.println(F("Light sensor is now running"));
} else {
Serial.println(F("Something went wrong during light sensor init!"));
}
// Read high and low interrupt thresholds
if ( !apds.getLightIntLowThreshold(threshold) ) {
Serial.println(F("Error reading low threshold"));
} else {
Serial.print(F("Low Threshold: "));
Serial.println(threshold);
}
if ( !apds.getLightIntHighThreshold(threshold) ) {
Serial.println(F("Error reading high threshold"));
} else {
Serial.print(F("High Threshold: "));
Serial.println(threshold);
}
// Enable interrupts
if ( !apds.setAmbientLightIntEnable(1) ) {
Serial.println(F("Error enabling interrupts"));
}
// Wait for initialization and calibration to finish
delay(500);
}
void loop() {
// If interrupt occurs, print out the light levels
if ( isr_flag == 1 ) {
// Read the light levels (ambient, red, green, blue) and print
if ( !apds.readAmbientLight(ambient_light) ||
!apds.readRedLight(red_light) ||
!apds.readGreenLight(green_light) ||
!apds.readBlueLight(blue_light) ) {
Serial.println("Error reading light values");
} else {
Serial.print("Interrupt! Ambient: ");
Serial.print(ambient_light);
Serial.print(" R: ");
Serial.print(red_light);
Serial.print(" G: ");
Serial.print(green_light);
Serial.print(" B: ");
Serial.println(blue_light);
}
// Turn on LED for a half a second
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
// Reset flag and clear APDS-9960 interrupt (IMPORTANT!)
isr_flag = 0;
if ( !apds.clearAmbientLightInt() ) {
Serial.println("Error clearing interrupt");
}
}
}
void interruptRoutine() {
isr_flag = 1;
}
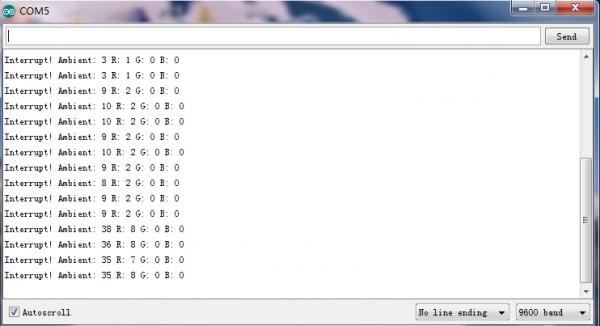
Test Result
Wiring as the above diagram and burning the code, after powered-on, open the serial monitor, as the graph shown below.
Resources
- Libraries and Code Download:
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0267