KS0507 Keyestudio Smart RV Kit: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 586: | Line 586: | ||
We’ve known how line tracking sensor works, next, we connect an LED at pin 13. We will control LED on and off by line tracking sensor, as shown below<br> | We’ve known how line tracking sensor works, next, we connect an LED at pin 13. We will control LED on and off by line tracking sensor, as shown below<br> | ||
<br>[[File:0507--19.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:0507--19.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
Test Code<br> | |||
<pre> | |||
/* | |||
keyestudio smart RV | |||
lesson 4.2 | |||
Line Track sensor | |||
http://www.keyestudio.com | |||
*/ | |||
//LED pin | |||
#define LED 13 | |||
//Line Tracking Sensor | |||
#define L_pin 50 | |||
#define M_pin 51 | |||
#define R_pin 52 | |||
void setup() | |||
{ | |||
Serial.begin(9600); //set baud rate to 9600 | |||
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); //set LED to OUTPUT | |||
pinMode(L_pin, INPUT); //set the pin of line tracking sensor to INPUT | |||
pinMode(M_pin, INPUT); | |||
pinMode(R_pin, INPUT); | |||
} | |||
void loop () | |||
{ | |||
int L_val = digitalRead(L_pin); //read the value of left sensor | |||
int M_val = digitalRead(M_pin); //read the value of middle sensor | |||
int R_val = digitalRead(R_pin); //read the value of right sensor | |||
Serial.print(L_val); | |||
Serial.print(" "); | |||
Serial.print(M_val); | |||
Serial.print(" "); | |||
Serial.print(R_val); | |||
Serial.println(" "); | |||
delay(100); //delay in 100ms | |||
if (L_val == 0 || M_val == 0 || R_val == 0) { | |||
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); | |||
} | |||
else { | |||
digitalWrite(LED, LOW); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
//**************************************************************************** | |||
</pre> | |||
Revision as of 14:38, 11 March 2021
About keyestudio
Keyestudio is a best-selling brand owned by KEYES Corporation. Our product lines range from controller boards, shields and sensor modules to smart car and complete starter kits for Arduino, Raspberry Pi and BBC micro:bit, which can help customers at any level learn electronics and programming knowledge. Likewise, all of our products comply with international quality standards and are greatly appreciated in a variety of different markets throughout the world.
You can obtain the details and the latest information through visiting the following web sites:http://www.keyestudio.com
References and After-sales Service
1.Download Profile:https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0507
2.Feel free to contact us please, if there is missing part or you encounter some troubles. Welcome to send email to us:service@keyestudio.com. We will update projects and products continuously from your sincere advice.
Warning
1.This product contains tiny parts(screws, copper pillars), keep it out of reach of children under 7 years old please.
2.This product contains conductive parts (control board and electronic module). Please operate according to the requirements of tutorial. Improper operation may cause parts to overheat damage. Do not touch and immediately disconnect the circuit power.
Copyright
The keyestudio trademark and logo are the copyright of KEYES DIY ROBOT co.,LTD. All products under Keyestudio brand can’t be copied, sold and resold without authorization by anyone or company. If you’re interested in our items, please contact to our sales representatives: fennie@keyestudio.com
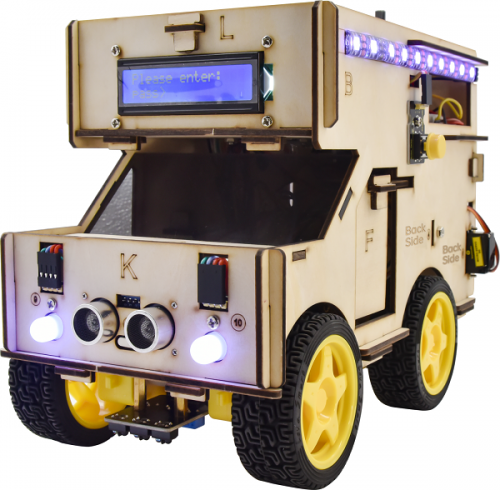
Description:
When it comes to programming, many think it difficult. However, KEYES group issues a smart RV kit to cope with this problem.
This is low cost, easy-to-build and open source programming kit-----smart RV.
It integrates smart home and robot car. In addition, it helps you absorb the knowledge of programming like electronics, control logic and computing and science.
In compliance with the tutorial, you can create your own robot by boards, slot connection and wiring. In the assembly process, the detailed projects will guide you to learn the working principle of sensors and modules.
What’s more, it a has temperature humidity sensor and an LCD display except LED, line tracking sensor, ultrasonic sensor, Bluetooth module and motor driving modules.
Should you are interested in STEM and code programming, you can customize your RV by altering code and adding extra modules.
That sounds entertaining, right? Let’s get started1
Features
- Multi-purpose function:obstacle avoidance, line tracking, Bluetooth control, ultrasonic follow, smart sensation and so on.
- Easy to build:Slot connection and without soldering circuit
- Novel style:Adopt strong wood board, acrylic board, RGB and lcd1602 modules.
- High extension:configure motor driving chip, preserve IIC, UART and SPI port and expand other sensor and module.
- Basic programming learning:use C language and code
Specification:
- Working voltage: 5v
- Input voltage: 7-12V
- Maximum output current: 3A
- Maximum power dissipation: 15W
- Motor speed: 200 rpm (4.5V)
- Motor driving form: TB6612 chip drive
- Ultrasonic sensing angle: <15 degrees
- Ultrasonic detection distance: 2cm-400cm
- Bluetooth remote control distance: 50 meters (measured)
- Bluetooth APP control: support Android and iOS system
Kit
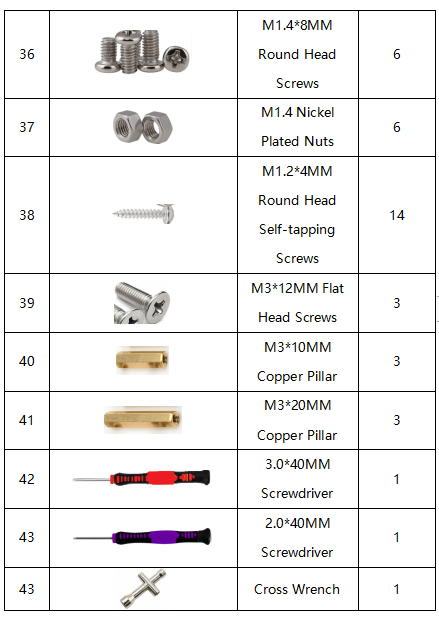
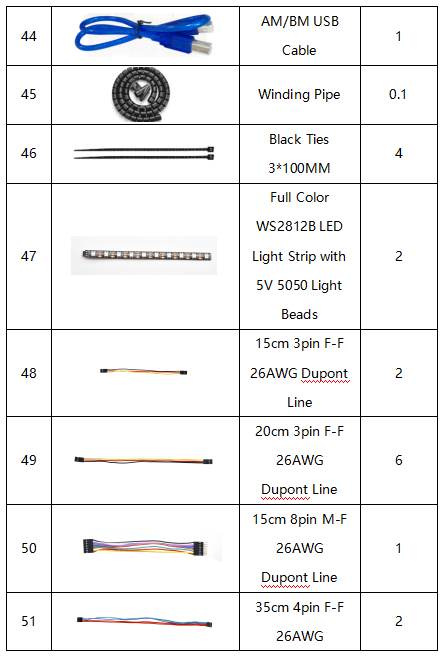
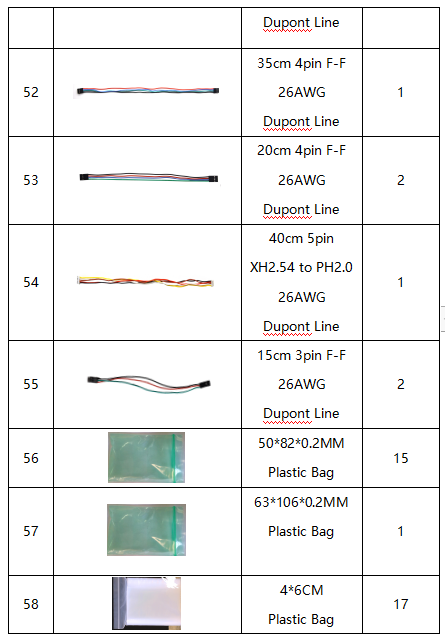
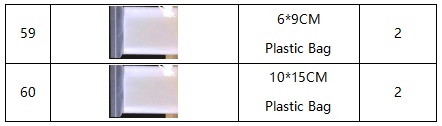
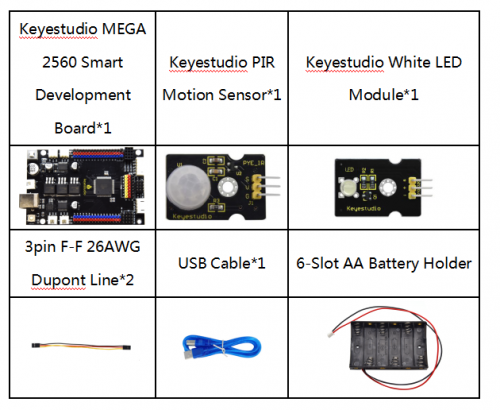
Remember to check if the components received are in line with the following product list when you getting this kit.
Getting Started with Arduino
Installing Arduino IDE
When we get control board, we need to download Arduino IDE and driver firstly.
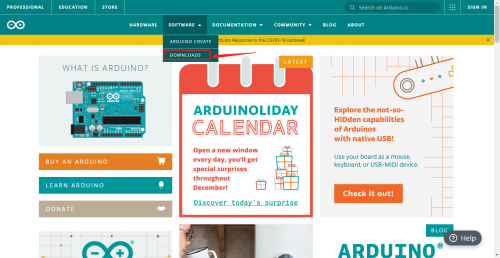
You could download Arduino IDE from the official website:
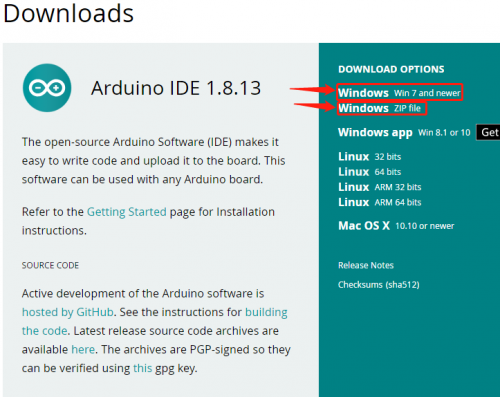
https://www.arduino.cc/, click the SOFTWARE on the browse bar, click“DOWNLOADS” to enter download page, as shown below:
You can download either Windows win7 and newer or Windows ZIP file.
The first one doesn’t require
There are two versions of IDE for WINDOWS system, you can choose from the Installer (.exe) and the Zip packages. We suggest you use the first one that installs directly everything you need to use the Arduino Software (IDE), including the drivers.
With the Zip package you need to install the drivers manually. The Zip file is also useful if you want to create a portable installation.
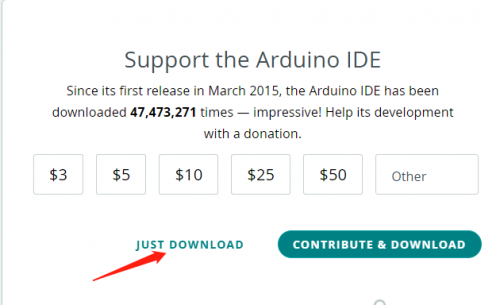
You just need to click JUST DOWNLOAD.
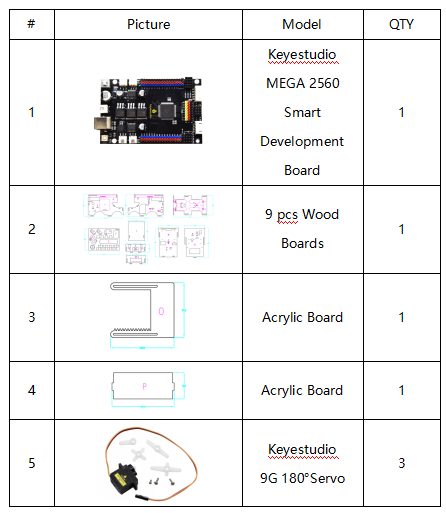
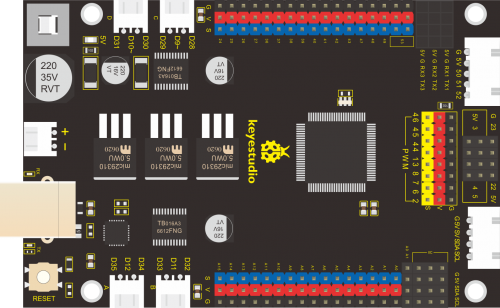
Keyestudio MEGA 2560 Smart Development Board
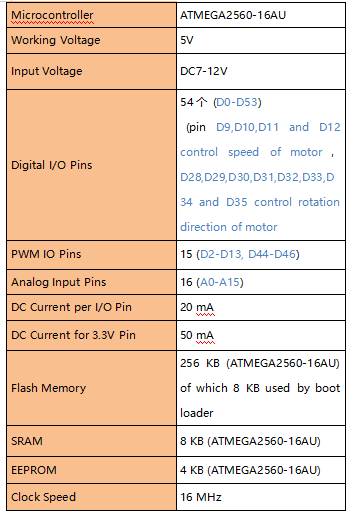
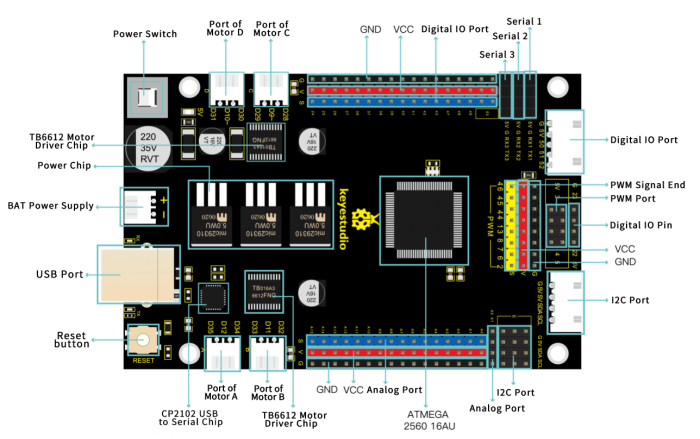
We need to know keyestudio MEGA 2560 development board, as a core of this smart car.
The processor core of MEGA 2560 board is ATMEGA2560-16AU, with the cp2102 chip.
It has 54 digital input/output pins (of which 15 can be used as PWM outputs), 16 analog inputs, 4 UARTs (hardware serial ports), a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, 1 ICSP header, and a reset button.
It can be interfaced computer with external power with a USB cable.
Install Driver on Windows System
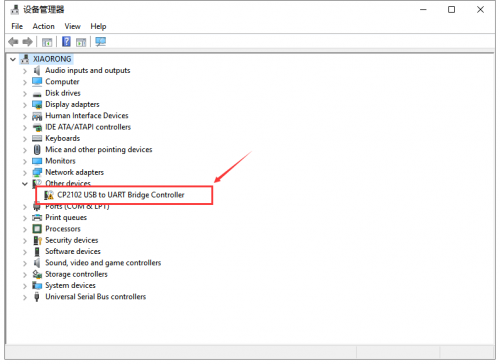
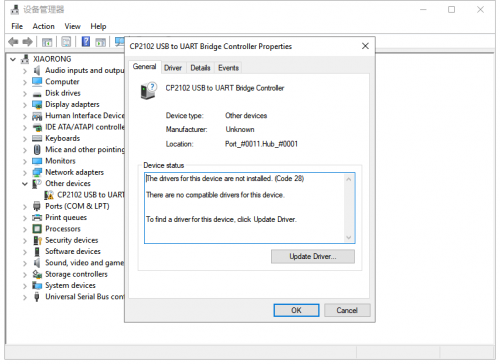
Let’s install the driver of keyestudio MEGA 2560 smart development board. The USB-TTL chip on this board adopts CP2102 serial chip. The driver program of this chip is included in Arduino 1.8 version and above, which is convenient. Plugged in USB port, the computer can recognize the hardware and automatically install the driver of CP2102.
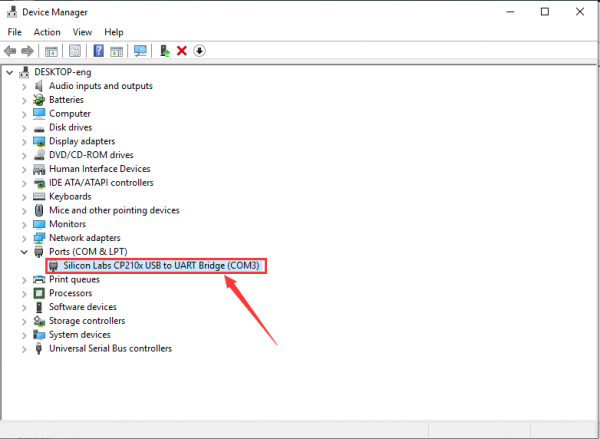
If install unsuccessfully, or you intend to install manually, open the device manager of computer. Right click Computer----- Properties----- Device Manager.
There is a yellow exclamation mark on the page, which implies installing unsuccessfully. Then we double click the hardware and update the driver.
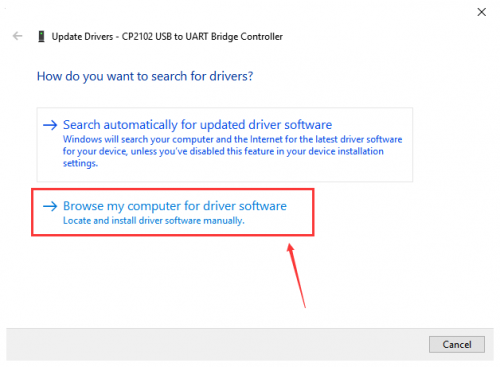
Click “OK” to enter the following page, click“browse my computer for updated driver software”, find out the installed or downloaded ARDUINO software. As shown below:
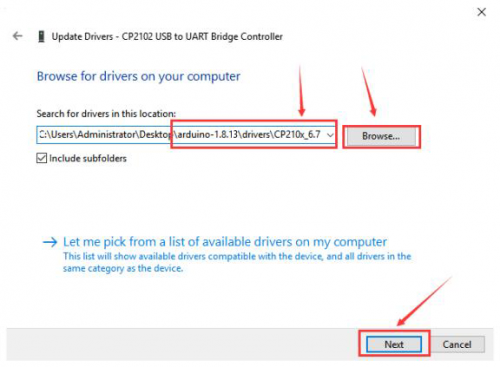
There is a DRIVERS folder in Arduino software installed package. Just open driver folder and you can see the driver of CP210X series chips.
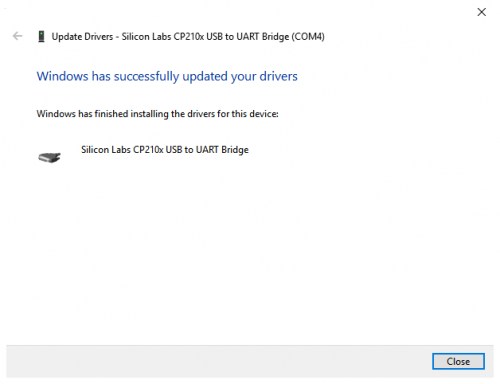
We click “Browse”, then find out the driver folder, or you could enter “driver” to search in rectangular box, then click“next”, the driver will be installed successfully. (I place Arduino software folder on the desktop, you can follow my way)
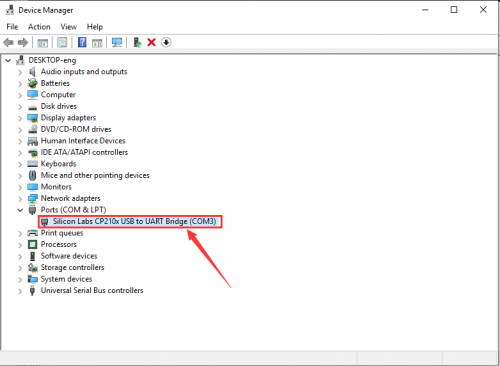
Open device manager, we will find the yellow exclamation mark disappear. The driver of CP2102 is installed successfully.
Install Driver on MAC System
The USB to serial chip of control board is CP2102. We install driver on MAC as follows: https://wiki.keyestudio.com/How_to_Install_the_Driver_of_CP2102_on_MAC_System
Arduino IDE Setting
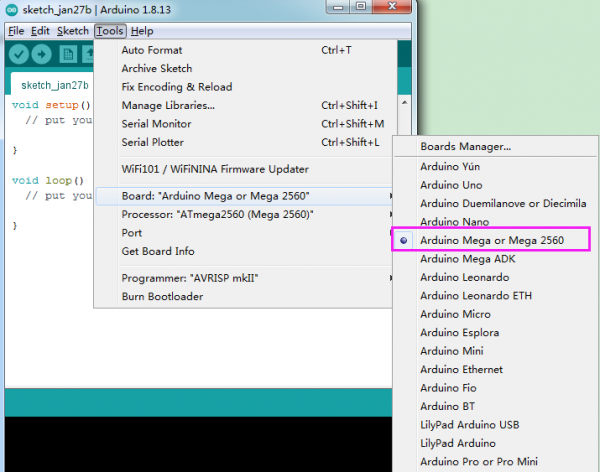
To avoid the errors when uploading the program to the board, you need to select the correct Arduino board that matches the board connected to your computer.
Then come back to the Arduino software, you should click Tools→Board, select the board. (as shown below)
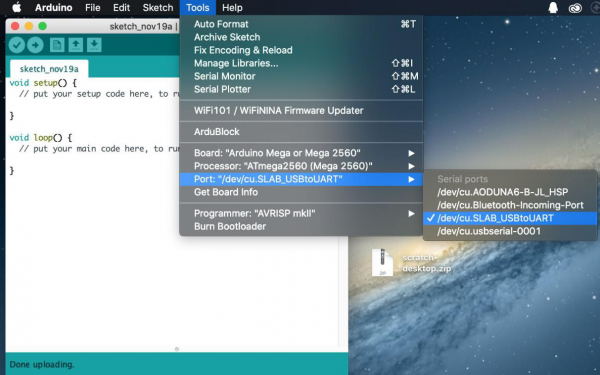
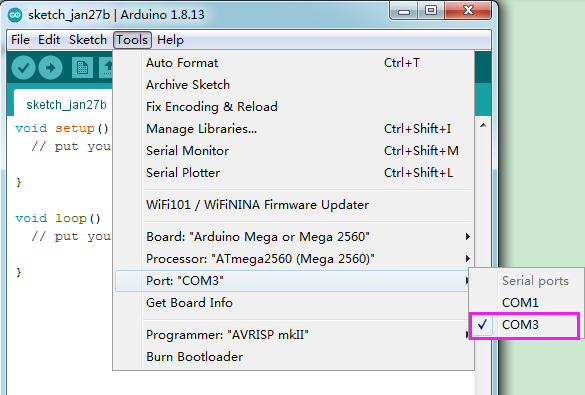
Then select the correct COM port (you can see the corresponding COM port after the driver is successfully installed)
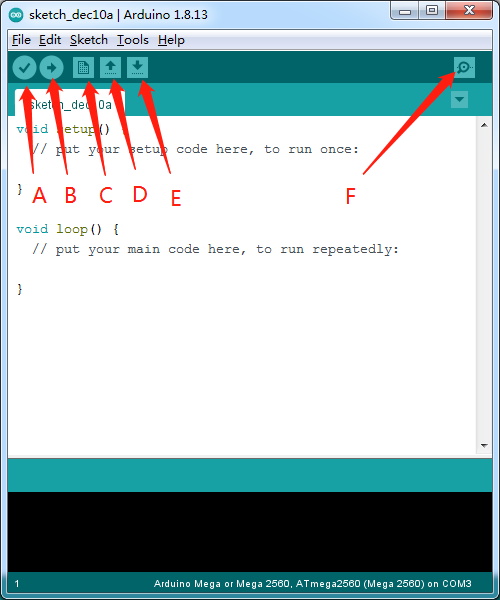
Before uploading the program to the board, let’s demonstrate the function of each symbol in the Arduino IDE toolbar.
- A- Used to verify whether there is any compiling mistakes or not.
- B- Used to upload the sketch to your Arduino board.
- C- Used to create shortcut window of a new sketch.
- D- Used to directly open an example sketch.
- E- Used to save the sketch.
- F- Used to send the serial data received from board to the serial monitor.
Note: the setting method on Mac system is same as on Windows system except different COM port, as shown below:
Start First Program
We’ve known how to download and install the driver of development board , next, we will burn a code to show“Hello World!”in the monitor.
Test Code
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// print out "Hello world!"
Serial.println("Hello world!");
delay(1000);// delay 1 second
}
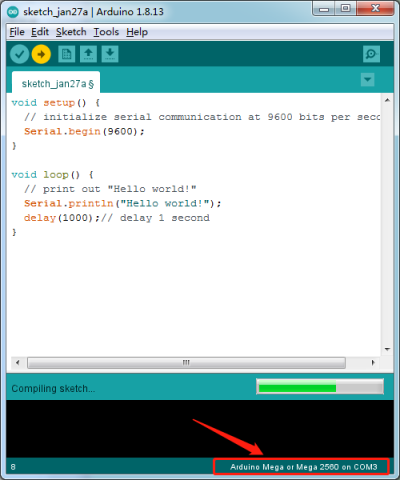
Open Arduino IDE, and set board as follows:
Set COM port, as shown below:
Click ![]() to start compiling the program, and check errors.
to start compiling the program, and check errors.
Click ![]() to upload the program, upload successfully.
to upload the program, upload successfully.
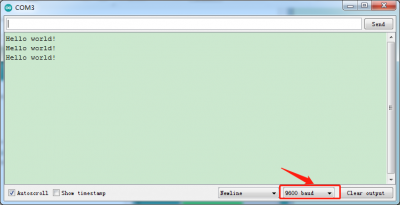
Upload the program successfully, open serial monitor and set baud rate to 9600. Monitor will print“Hello World!”each 1s.
Congratulation, you finish the first program.
Projects
For detailed projects, nevigated the website https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0507
The whole project begins with basic program. Starting from simple to complex, the lessons will guide you to assemble smart RV and absorb the knowledge of electronic and machinery step by step. I reckon that you might hardly sit still and itch to have a go, let’s get started.
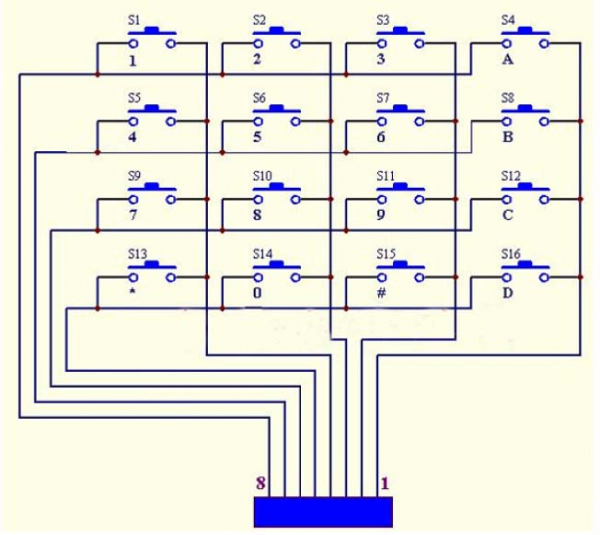
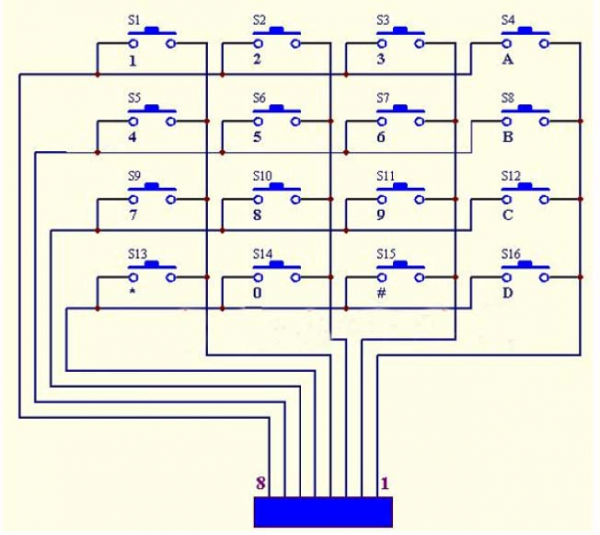
Note: (G), marked on each sensor and module, is negative pole and connected to“G”,“-”or“GND”on the sensor shield or control board ; (V) is positive pole and interfaced with“V”,“VCC”,“+”or“5V”on the sensor shield or control board.
Project 1: LED Blink
(1)Description:
For the starter and enthusiast, this is a fundamental program---LED Blink.
LED, the abbreviation of light emitting diodes, consist of Ga, As, P, N chemical compound and so on. It is often applied to numbers and text display as an indicator in the circuit.
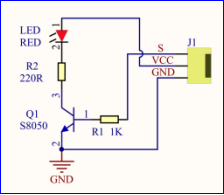
The LED can flash diverse color by altering the delay time in the test code. When in control, power on GND and VCC, the LED will be on if S end is high level; nevertheless, it will go off.
(2) Parameter:
- Control interface: digital port
- Working voltage: DC 3.3-5V
- Pin spacing: 2.54mm
- LED display color: red
(3) Component:
(4)Connection Diagram:
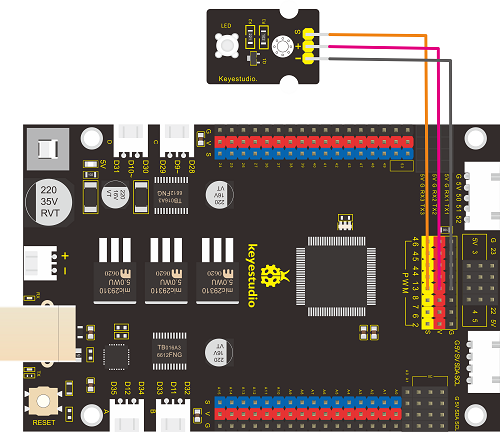
From the above diagram, pin -, + and S of LED module are respectively connected to pin G, 5V and D13 of expansion board. Then we compile the code as follows:
(5)Test Code:
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 1.1
Blink
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
#define LED 13 //define the pin of LED as D13
void setup()
{
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);// initialize digital pin LED as an output.
}
void loop() // the loop function runs over and over again forever
{
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
//*******************************************************************
(6)Test Result:
Upload the program, LED blinks with the interval of 1s.
(7)Code Explanation:
pinMode(LED,OUTPUT) - This function can denote that the pin is INPUT or OUTPUT.
digitalWrite(LED,HIGH) - When pin is OUTPUT, we can set it to HIGH(output 5V) or LOW(output 0V).
(8)Extension Practice:
The LED flashes for 1s through the test result, therefore, pins and delay time affect flash frequency.
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 1.2
Blink
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
#define LED 13 //Define the pin of LED as D13
void setup()
{
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);// initialize digital pin LED as an output.
}
void loop() // the loop function runs over and over again forever
{
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); // turn LED on (HIGH is the voltage level
delay(100); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED, LOW); // turn LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(100); // wait for a second
}
//****************************************************************
The LED flashes faster through the lesson 1.2 test.
Project 2: Adjust LED Brightness
(1)Description:
In previous lesson, we control LED on and off and make it blink.
In this project, we will control LED brightness through PWM to simulate breathing effect. Similarly, you can change the step length and delay time in the code so as to demonstrate different breathing effect.
PWM is a means of controlling the analog output via digital means. Digital control is used to generate square waves with different duty cycles (a signal that constantly switches between high and low levels) to control the analog output.In general, the input voltage of port are 0V and 5V. What if the 3V is required? Or what if switch among 1V, 3V and 3.5V? We can’t change resistor constantly. For this situation, we need to control by PWM.
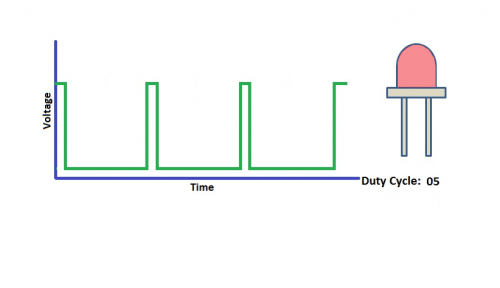
For the Arduino digital port voltage output, there are only LOW and HIGH, which correspond to the voltage output of 0V and 5V. You can define LOW as 0 and HIGH as 1, and let the Arduino output five hundred 0 or 1 signals within 1 second.
If output five hundred 1, that is 5V; if all of which is 1, that is 0V. If output 010101010101 in this way then the output port is 2.5V, which is like showing movie. The movie we watch are not completely continuous. It actually outputs 25 pictures per second. In this case, the human can’t tell it, neither does PWM. If want different voltage, need to control the ratio of 0 and 1. The more 0,1 signals output per unit time, the more accurately control.
(2)Component:
(3)Connection Diagram:
We keep connection diagram unchanged.
(4)Test Code:
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 2.1
PWM
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
#define LED 13 //Define the pin of LED as D13
int value;
void setup()
{
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);// initialize digital pin LED as an output.
}
void loop () {
for (value = 0; value < 255; value = value + 1) {
analogWrite (LED, value); // LED lights gradually light up
delay (5); // delay 5MS
}
for (value = 255; value > 0; value = value - 1) {
analogWrite (LED, value); // LED gradually goes out
delay (5); // delay 5MS
}
}
(5) Test Result:
Upload test code successfully, LED gradually becomes brighter then darker, like human breath.
(6) Code Explanation
When we need to repeat some statements, we could use FOR statement.
FOR statement format is shown below:

FOR cyclic sequence:
Round 1:1 → 2 → 3 → 4
Round 2:2 → 3 → 4
…
Until number 2 is not established, “for”loop is over,
After knowing this order, go back to code:
for (int value = 0; value < 255; value=value+1){
...}
for (int value = 255; value >0; value=value-1){
...}
The two“for”statements make value increase from 0 to 255, then reduce from 255 to 0, then increase to 255,....infinitely loop
There is a new function in the following ----- analogWrite()
We know that digital port only has two state of 0 and 1. So how to send an analog value to a digital value? Here,this function is needed. Let’s observe the Arduino board and find 6 pins marked“~”which can output PWM signals.
Function format as follows:
analogWrite(pin,value)
analogWrite() is used to write an analog value from 0~255 for PWM port, so the value is in the range of 0~255. Attention that you only write the digital pins with PWM function, such as pin 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11.
PWM is a technology to obtain analog quantity through digital method. Digital control forms a square wave, and the square wave signal only has two states of turning on and off (that is, high or low levels). By controlling the ratio of the duration of turning on and off, a voltage varying from 0 to 5V can be simulated. The time turning on(academically referred to as high level) is called pulse width, so PWM is also called pulse width modulation.
Through the following five square waves, let’s acknowledge more about PWM.
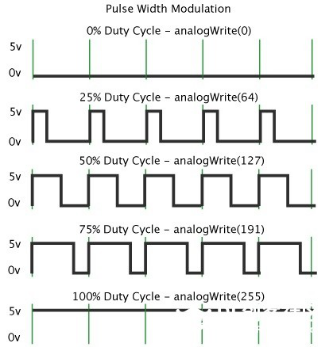
In the above figure, the green line represents a period, and value of analogWrite() corresponds to a percentage which is called Duty Cycle as well. Duty cycle implies that high-level duration is divided by low-level duration in a cycle. From top to bottom, the duty cycle of first square wave is 0% and its corresponding value is 0. The LED brightness is lowest, that is, turn off. The more time high level lasts, the brighter the LED. Therefore, the last duty cycle is 100%, which correspond to 255, LED is brightest. 25% means darker.
PWM mostly is used for adjusting the LED brightness or rotation speed of motor.
It plays vital role in controlling smart robot car. I believe that you can’t wait to enter next project.
(7) Extension Practice:
Let’s keep pins unchanged and change the delay value, then observe how LED changes.
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 2.2
PWM
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
#define LED 13 //Define the pin of LED as D13
int value;
void setup()
{
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);// initialize digital pin LED as an output.
}
void loop () {
for (value = 0; value < 255; value = value + 1) {
analogWrite (LED, value); // LED lights gradually light up
delay (20); // delay 30MS
}
for (value = 255; value > 0; value = value - 1) {
analogWrite (LED, value); // LED gradually goes out
delay (20); // delay 30MS
}
}
//**********************************************************
Upload code to development board, the LED’s blink frequency is slower, isn’t it?
Project 3: Button Module
(1)Description: In this project, we control LED brightness by button module. The low level(0) is output when the button is pressed; however, high level(1) is output when button is released.
(2)Specification:
- Operating Voltage: 3.3-5V (DC)
- Control Signal: Digital signal
- Detection Height: 0-3 cm
- Weight: 3.8g
- Dimension: 34*22*15mm
(3)Component:
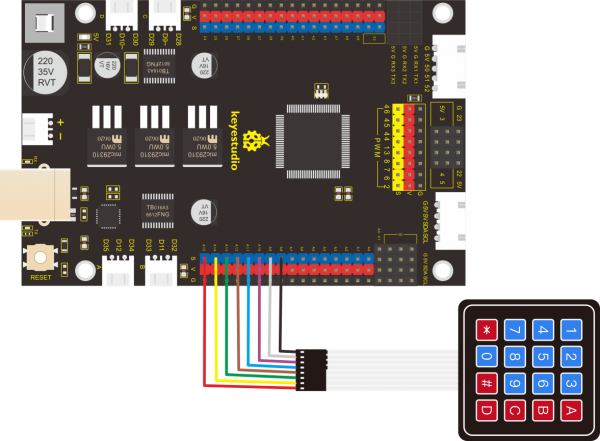
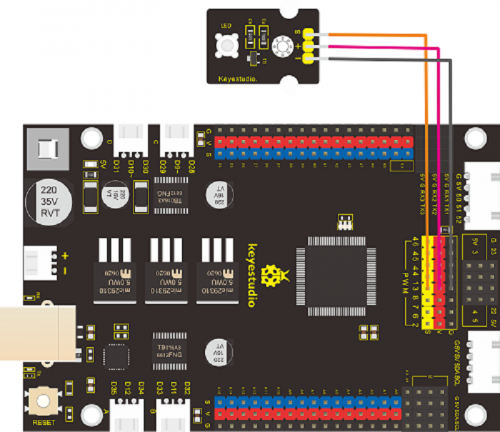
(4)Connection Diagram:
Note: the pin G, V and S of button sensor are interfaced with pin G, V and
D2 of expansion board, and connect pin G, V and S of LED module to G, V
and D13 of expansion board.
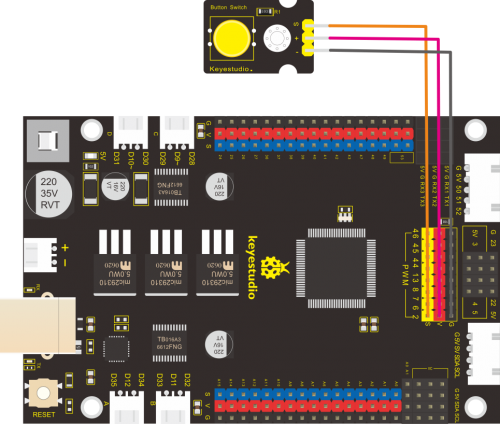
(5)Test Code:read the signal of button
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 3.1
button
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
#define button 2 //Define the pin of LED as D12
volatile int buttonState; //The output level state of button module
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);//set baud rate to 9600
pinMode(button, INPUT);// initialize digital pin button as an input.
}
void loop () {
buttonState = digitalRead(button);
Serial.println(buttonState); //auto wrap and output the digital signals from digital 2
delay(100);//delay in 100ms
}
(6)Test Result:
Upload code, open serial monitor to set baud rate to 9600. The number “1”shows up then“0”appears on the monitor.
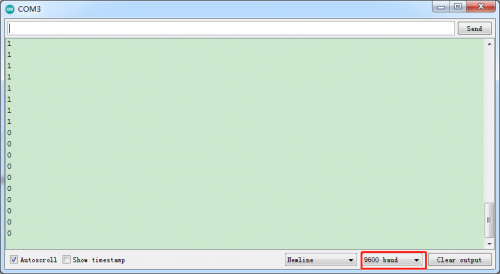
(7)Code Explanation:
Serial.begin(9600)- Initialize serial port, set baud rate to 9600
pinMode(pin, INPUT)-This function can denote that the pin is INPUT or OUTPUT
digitalRead(pin)-Read the state of pin, which are generally HIGH and LOW level. Function digitalRead() will come back to HIGH or LOW level if pins are not connected.
(8) Extension Practice:button-controlled LED
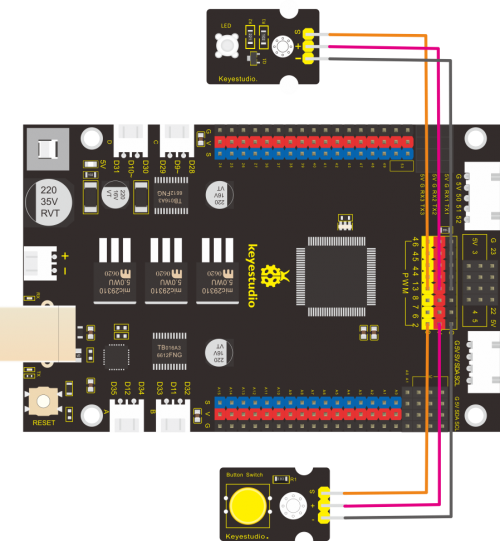
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 3.2
button
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
#define LED 13 //Define the pin of LED as D13
#define button 2 //Define the pin of button module as D2
volatile int buttonState; //the state of button
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //set baud rate to 9600
pinMode(button, INPUT); // initialize digital pin button as an input.
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); // initialize digital pin LED as an output.
}
void loop ()
{
buttonState = digitalRead(button); //read the status of button
if (buttonState == 0) //if the button is pressed
{
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); //Turn on LED
}
else
{
digitalWrite(LED, LOW); //turn off LED
}
delay(100); //dealy in 100ms
It turns out that LED is on when the button is pressed, and LED off when button is released.
Project 4: Line Tracking Sensor
(1)Description:

The tracking sensor is actually an infrared sensor. The component used here is the TCRT5000 infrared tube.
Its working principle is to use the different reflectivity of infrared light to the color, then convert the strength of the reflected signal into a current signal.
During the process of detection, black is active at HIGH level, but white is active at LOW level. The detection height is 0-3 cm.
Keyestudio 3-channel line tracking module has integrated 3 sets of TCRT5000 infrared tube on a single board, which is more convenient for wiring and control.
By rotating the adjustable potentiometer on the sensor, it can adjust the detection sensitivity of the sensor.The tracking sensor is actually an infrared sensor.
(2) Specification:
- Operating Voltage: 3.3-5V (DC)
- Interface: 5PIN
- Output Signal: Digital signal
- Detection Height: 0-3 cm
Note: Adjust the sensitivity by rotating the potentiometer before the test. The sensitivity is best when LED is at on and off state.
(3) Component:
thumb
(4)Connection Diagram:
(5)Test Code:
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 4.1
Line Track sensor
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
//Line Tracking Sensor
#define L_pin 50
#define M_pin 51
#define R_pin 52
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Set baud rate to 9600
pinMode(L_pin, INPUT); //set pins of line tracking sensor to INPUT
pinMode(M_pin, INPUT);
pinMode(R_pin, INPUT);
}
void loop ()
{
int L_val = digitalRead(L_pin); //read the value of left sensor
int M_val = digitalRead(M_pin); //read the value of middle sensor
int R_val = digitalRead(R_pin); //read the value of right sensor
Serial.print(L_val);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(M_val);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(R_val);
Serial.println(" ");
delay(100); //delay in 100ms
}//****************************************************************************
(6)Test Result:
Upload code to development board, open serial monitor to check the state of three line tracking sensors. When no signals are received, they are in high level state and“1”shows up ; however, 1 changes into 0 when covering sensor with white paper.
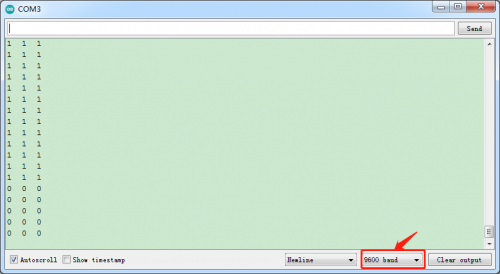
(7) Code Explanation:
Serial.begin(9600)-initialize the serial port, set serial baud rate to 9600
pinMode- define the PIN state(input and output) of MCU
digitalRead- read the level status of pin(HIGH, LOW)
(8)Extension Practice:
We’ve known how line tracking sensor works, next, we connect an LED at pin 13. We will control LED on and off by line tracking sensor, as shown below
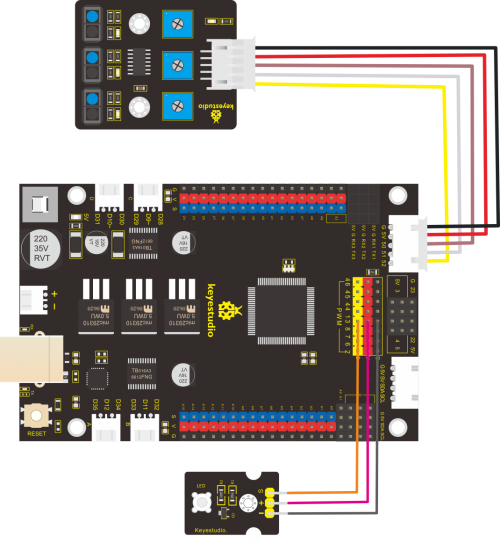
Test Code
/*
keyestudio smart RV
lesson 4.2
Line Track sensor
http://www.keyestudio.com
*/
//LED pin
#define LED 13
//Line Tracking Sensor
#define L_pin 50
#define M_pin 51
#define R_pin 52
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //set baud rate to 9600
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); //set LED to OUTPUT
pinMode(L_pin, INPUT); //set the pin of line tracking sensor to INPUT
pinMode(M_pin, INPUT);
pinMode(R_pin, INPUT);
}
void loop ()
{
int L_val = digitalRead(L_pin); //read the value of left sensor
int M_val = digitalRead(M_pin); //read the value of middle sensor
int R_val = digitalRead(R_pin); //read the value of right sensor
Serial.print(L_val);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(M_val);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(R_val);
Serial.println(" ");
delay(100); //delay in 100ms
if (L_val == 0 || M_val == 0 || R_val == 0) {
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
}
}
//****************************************************************************