Ks0001 keyestudio UNO R3 BOARD: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
<br>'''<br>''' | <br>'''<br>''' | ||
Revision as of 11:36, 25 July 2018
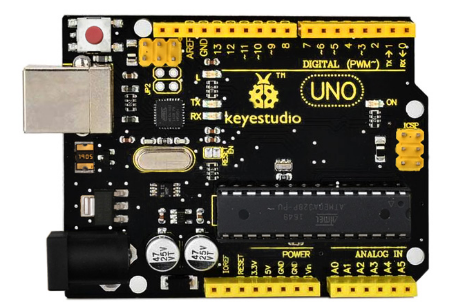
keyestudio UNO R3
Introduction
keyestudio Uno R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (datasheet), fully compatible with ARDUINO UNO REV3.
It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, 2 ICSP headers and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
Note that the two ICSP headers separately used to program the firmware to ATMEGA16U2-MU and ATMEGA328P-PU, but we have programmed the two chips, so generally no need to use them.
The Uno R3 differs from all preceding boards in that it does not use the FTDI USB-to-serial driver chip. Instead, it features the Atmega16U2 programmed as a USB-to-serial converter.
The UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can start playing with.
TECH SPECS
| Microcontroller | ATmega328P-PU |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 (of which 6 provide PWM output) |
| PWM Digital I/O Pins | 6 (D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, D11) |
| Analog Input Pins | 6 (A0-A5) |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 20 mA |
| DC Current for 3.3V Pin | 50 mA |
| Flash Memory | 32 KB (ATmega328) of which 0.5 KB used by bootloader |
| SRAM | 2 KB (ATmega328P-PU) |
| EEPROM | 1 KB (ATmega328P-PU) |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| LED_BUILTIN | D13 |
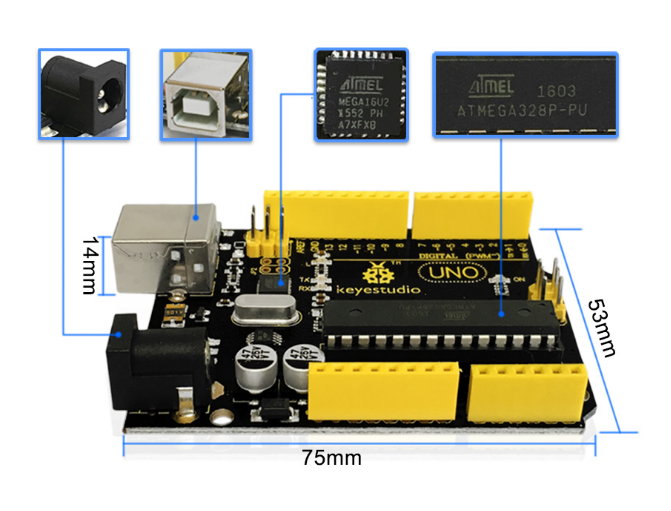
Dimensions
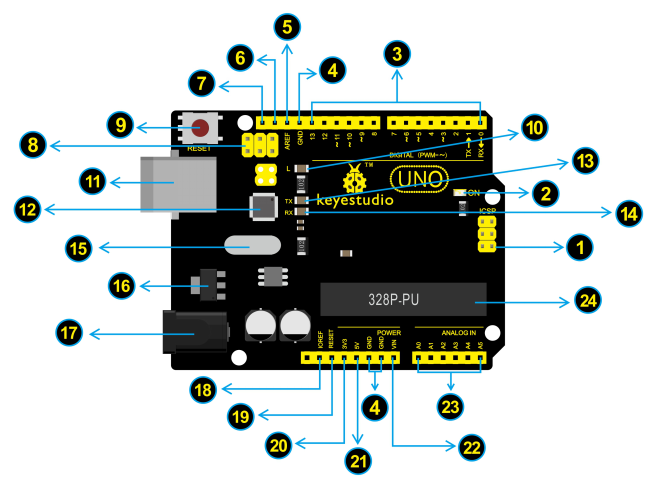
Element and Interfaces
Here is an explanation chart of what every element and interface of the board does:
Features
- 1.0 pinout: added SDA and SCL pins that are near to the AREF pin and two other new pins placed near to the RESET pin, the IOREF that allow the shields to adapt to the voltage provided from the board. In future, shields will be compatible with both the board that uses the AVR, which operates with 5V and with the Arduino Due that operates with 3.3V.
- The second one is a not connected pin, that is reserved for future purposes.
- Stronger RESET circuit.
- Atmega 16U2 replace the 8U2.
Pin definition and Rating
Usage
Download the Arduino environment
Get the latest version from the download page.
When the download finishes, unzip the downloaded file. Make sure to preserve the folder structure. Double-click the folder to open it. There should be a few files and sub-folders inside.
Connect the board
The Arduino Uno, Mega, Duemilanove and Arduino Nano automatically draw power from either the USB connection to the computer or an external power supply. If you're using an Arduino Diecimila, you'll need to make sure that the board is configured to draw power from the USB connection. The power source is selected with a jumper, a small piece of plastic that fits onto two of the three pins between the USB and power jacks. Check that it's on the two pins closest to the USB port.
Connect the Arduino board to your computer using the USB cable. The green power LED (labelled PWR) should go on.
Install the drivers
Installing drivers for the Arduino Uno or Arduino Mega 2560 with Windows 7, Vista, or XP:
Plug in your board and wait for Windows to begin it's driver installation process. After a few moments, the process will fail, despite its best efforts
Click on the Start Menu, and open up the Control Panel.
While in the Control Panel, navigate to System and Security. Next, click on System. Once the System window is up, open the Device Manager.
Look under Ports (COM & LPT). You should see an open port named "Arduino UNO (COMxx)". If there is no COM & LPT section, look under "Other Devices" for "Unknown Device".
Right click on the "Arduino UNO (COmxx)" port and choose the "Update Driver Software" option.
Next, choose the "Browse my computer for Driver software" option.
Finally, navigate to and select the driver file named "arduino.inf", located in the "Drivers" folder of the Arduino Software download (not the "FTDI USB Drivers" sub-directory). If you are using an old version of the IDE (1.0.3 or older), choose the Uno driver file named "Arduino UNO.inf"
Windows will finish up the driver installation from there.
See also: step-by-step screenshots for installing the Uno under Windows XP.
Installing drivers for the Arduino Duemilanove, Nano, or Diecimila with Windows7, Vista, or XP:
When you connect the board, Windows should initiate the driver installation process (if you haven't used the computer with an Arduino board before).
On Windows Vista, the driver should be automatically downloaded and installed. (Really, it works!)
On Windows XP, the Add New Hardware wizard will open:
When asked Can Windows connect to Windows Update to search for software? select No, not this time. Click next.
Select Install from a list or specified location (Advanced) and click next.
Make sure that Search for the best driver in these locations is checked; uncheck Search removable media; check Include this location in the search and browse to the drivers/FTDI USB Drivers directory of the Arduino distribution. (The latest version of the drivers can be found on the FTDI website.) Click next.
The wizard will search for the driver and then tell you that a "USB Serial Converter" was found. Click finish.
The new hardware wizard will appear again. Go through the same steps and select the same options and location to search. This time, a "USB Serial Port" will be found.
You can check that the drivers have been installed by opening the Windows Device Mananger (in the Hardware tab of System control panel). Look for a "USB Serial Port" in the Ports section; that's the Arduino board.
Launch the Arduino application
Double-click the Arduino application. (Note: if the Arduino software loads in the wrong language, you can change it in the preferences dialog. See the environment page for details.)
Open the blink example
Open the LED blink example sketch: File > Examples > 1.Basics > Blink.
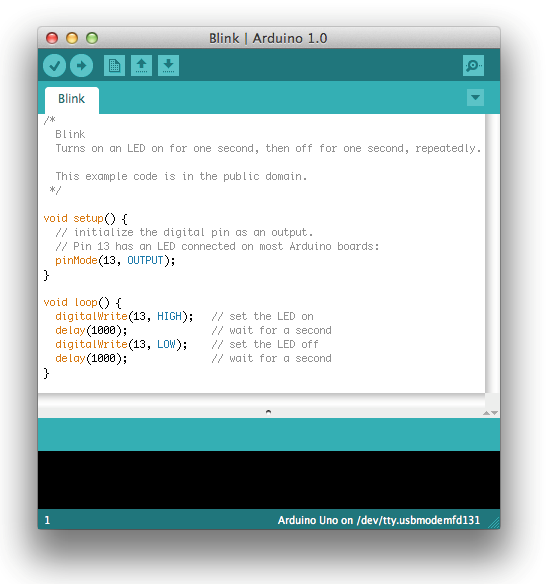
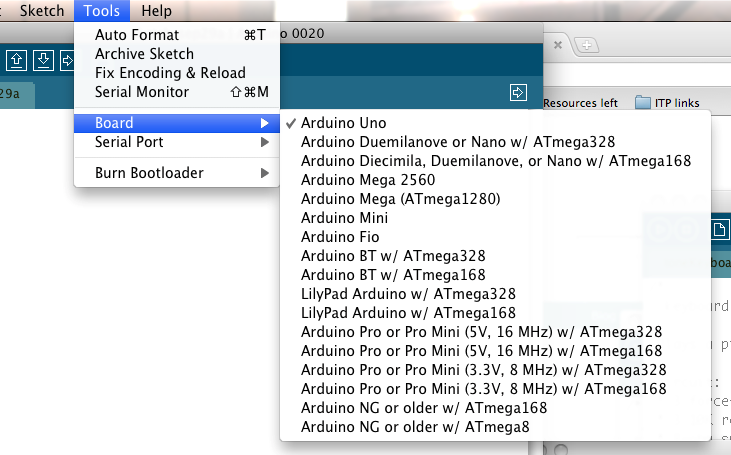
Select your board
You'll need to select the entry in the Tools > Board menu that corresponds to your Arduino.
Selecting an Arduino
For Duemilanove Arduino boards with an ATmega328 (check the text on the chip on the board), select Arduino Duemilanove or Nano w/ ATmega328. Previously, Arduino boards came with an ATmega168; for those, select Arduino Diecimila, Duemilanove, or Nano w/ ATmega168. (Details of the board menu entries are available on the environment page.)
===Select your serial port===
Select the serial device of the Arduino board from the Tools | Serial Port menu. This is likely to be COM3 or higher (COM1and COM2 are usually reserved for hardware serial ports). To find out, you can disconnect your Arduino board and re-open the menu; the entry that disappears should be the Arduino board. Reconnect the board and select that serial port.
Upload the program
Now, simply click the "Upload" button in the environment. Wait a few seconds - you should see the RX and TX leds on the board flashing. If the upload is successful, the message "Done uploading." will appear in the status bar. (Note: If you have an Arduino Mini, NG, or other board, you'll need to physically present the reset button on the board immediately before pressing the upload button.)
![]()
A few seconds after the upload finishes, you should see the pin 13 (L) LED on the board start to blink (in orange). If it does, congratulations! You've gotten Arduino up-and-running.
If you have problems, please see the troubleshooting suggestions.
You might also want to look at:
the examples for using various sensors and actuators
the reference for the Arduino language
The text of the Arduino getting started guide is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Code samples in the guide are released into the public domain.
Resources
Video:
http://www.keyestudio.com/wp/ks0001/
Datasheet:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1y8RXlk26EeU0FfdZ825LTaBoqxtsez-i
Get One Now
Official Website
http://www.keyestudio.com/ks0001.html
Get on Amazon
https://www.amazon.ca/keyestudio-ATmega328P-Development-Compatible-Arduino/dp/B0168B39N4/
From Ebay: [1]