KS0216 keyestudio RPI GPS Shield: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
==Usage== | ==Usage== | ||
''' | '''A.''' We use raspberry pi official system (2017-01-11-raspbian-jessie-lite), using SSH to log in, and you need to place a ssh file in the root directory.<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-3.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-3.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
''' | '''B.''' Bluetooth and Debug share the same serial port together and, but you can just use BT or Debug on one time. <br> | ||
For the Raspberry Pi 3 you need to explicitly enable the serial port on the GPIO pins. The reason for this is a change with the Pi 3 to use the hardware serial port for Bluetooth and instead of a slightly different software's serial port for the GPIO pins. <br> | For the Raspberry Pi 3 you need to explicitly enable the serial port on the GPIO pins. The reason for this is a change with the Pi 3 to use the hardware serial port for Bluetooth and instead of a slightly different software's serial port for the GPIO pins. <br> | ||
A side effect of this change is that the serial port will actually change speed as the Pi CPU clock throttles up and down--this will unfortunately cause problems for most serial devices like GPS receivers! <br> | A side effect of this change is that the serial port will actually change speed as the Pi CPU clock throttles up and down--this will unfortunately cause problems for most serial devices like GPS receivers! <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Step by step as shown below:<br> | '''Step by step as shown below:'''<br> | ||
1 | |||
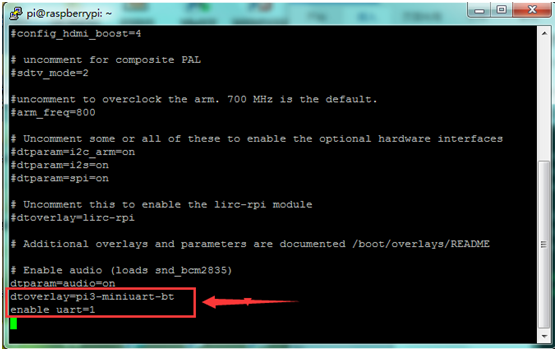
1) There is now a device tree file called pi3-miniuart-bt which makes the Raspberry Pi 3 disable the Bluetooth and map pl011 UART on pins 14 and 15 as before.<br> | |||
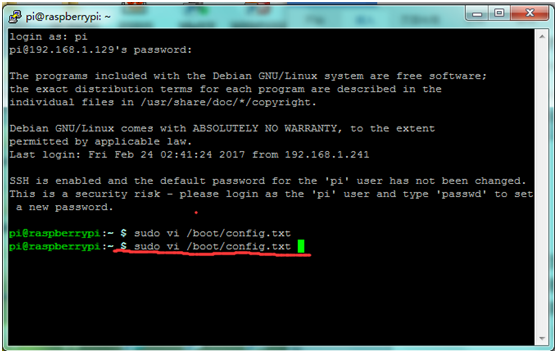
Add device tree to /boot/config.txt to disable the Raspberry Pi 3 bluetooth:<br> | Add device tree to /boot/config.txt to disable the Raspberry Pi 3 bluetooth:<br> | ||
* | * '''sudo vi /boot/config.txt''' <br> | ||
Add at the end of the file: <br> | Add at the end of the file: <br> | ||
* dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt <br> | * dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt <br> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
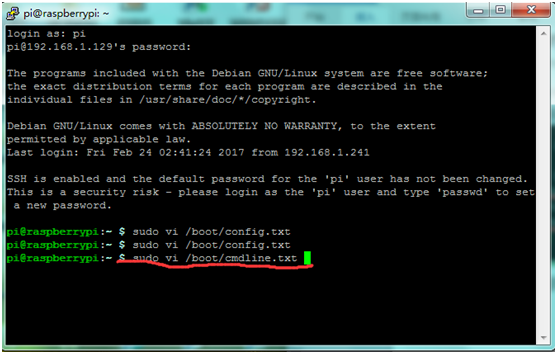
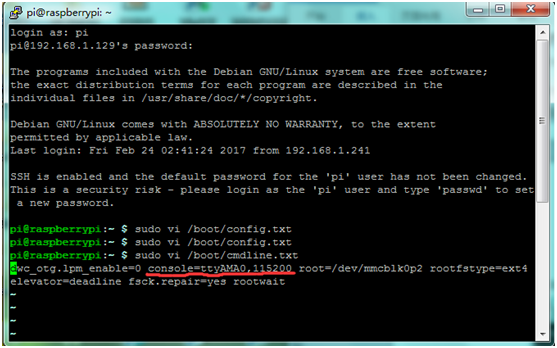
2 | 2) To enable the serial console, you need to edit the '''/boot/cmdline.txt''' file: <br> | ||
Change the file to the following: <br> | Change the file to the following: <br> | ||
* '''console=ttyAMA0,115200''' <br> | * '''console=ttyAMA0,115200''' <br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-6.png| | <br>[[File:ks0216-6.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-7.png| | <br>[[File:ks0216-7.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
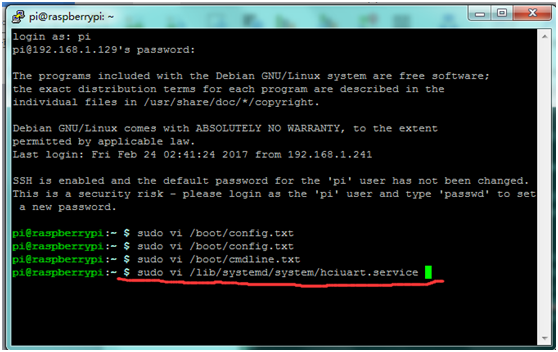
3 | 3) Edit '''/lib/systemd/system/hciuart.server''' <br> | ||
Change the file to the following: <br> | |||
ExecStart=/usr/bin/hciattach /dev/ttyAMA0 bcm43xx 115200 noflow -<br> | '''ExecStart=/usr/bin/hciattach /dev/ttyAMA0 bcm43xx 115200 noflow -''' <br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-8.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-8.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-9.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-9.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
4 | 4) Reboot the RPi <br> | ||
* '''sudo reboot''' <br> | * '''sudo reboot''' <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
''' | '''C.''' Write '''sudo raspi-config''' in the terminal,select '''Advanced Options ---> Serial ---> disable''' to close serial port debugging.<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-10.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-10.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-11.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-11.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 67: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
''' | '''D.''' Reboot the Pi <br> | ||
* '''sudo reboot''' <br> | * '''sudo reboot''' <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
''' | '''E.''' A great way to test out the serial port is to use the minicom program. When installing it, you may sometimes can’t find download path of source code. So you can write '''cd /etc/apt''' in the terminal, and then edit '''sudo vi sources.list''' to modify address. <br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-15.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-15.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 80: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Save your change and exit. Write sudo apt-get update in the terminal to update.<br> | Save your change and exit. Write sudo apt-get update in the terminal to update.<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-18.png| | <br>[[File:ks0216-18.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-19.png| | <br>[[File:ks0216-19.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
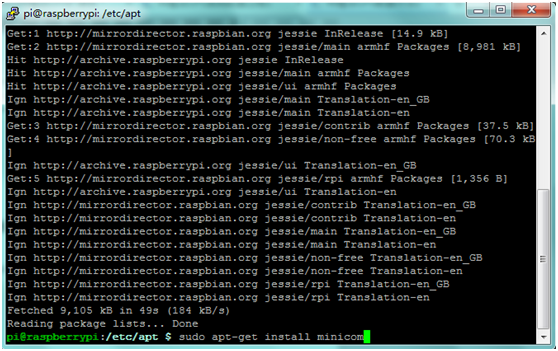
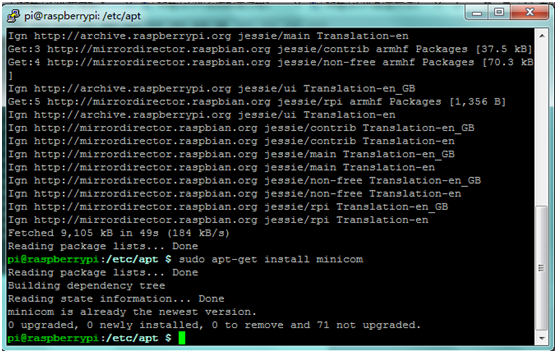
''' | '''F.''' You can install Minicom using the following command: <br> | ||
* '''sudo apt-get install minicom''' <br> | * '''sudo apt-get install minicom''' <br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-20.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-20.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 90: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
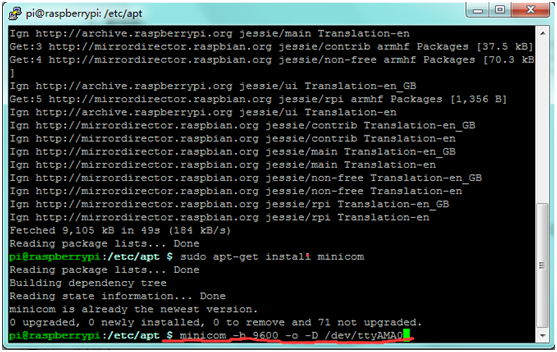
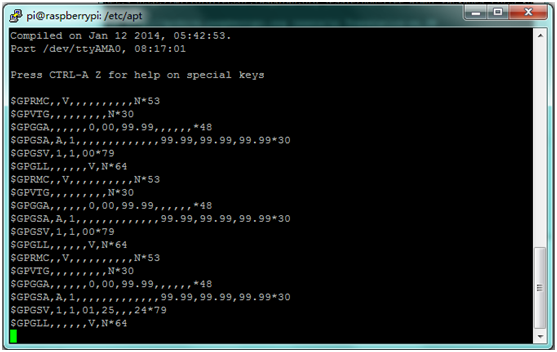
''' | '''G.''' You can then use Minicom to send and receive data over the serial port:<br> | ||
*'''minicom -b 9600 -o -D /dev/ttyAMA0''' <br> | *'''minicom -b 9600 -o -D /dev/ttyAMA0''' <br> | ||
'''-b''' to set baud rate, the same as that of module; <br> | '''-b''' to set baud rate, the same as that of module; <br> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 99: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
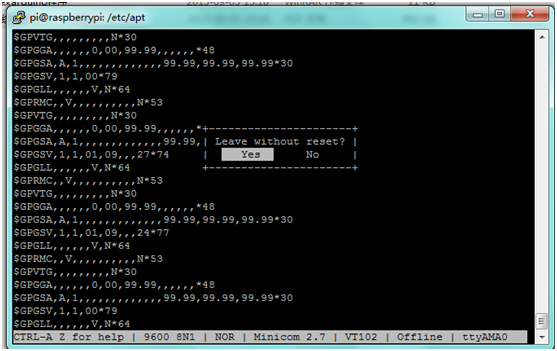
''' | '''H.''' '''Ctrl+A''' , press '''Q''' to exit.<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-24.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-24.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br>[[File:ks0216-25.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | <br>[[File:ks0216-25.png|700px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 105: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Get One Now == | == Get One Now == | ||
*[https://www.keyestudio.com/keyestudio-neo-6m-gps-shield-expansion-board-with-antenna-for-raspberry-pi-3-ce-certification-p0054-p0054.html '''Official website''' ] | *[https://www.keyestudio.com/keyestudio-neo-6m-gps-shield-expansion-board-with-antenna-for-raspberry-pi-3-ce-certification-p0054-p0054.html '''Official website''' ] | ||
*[https://www.aliexpress.com/store/product/2017-NEW-Keyestudio-RPI-GPS-Shield-for-Raspberry-Pi/1452162_32782759458.html?spm=2114.12010612.8148356.25.6e9660ffsewRl7 '''Shop on aliexpress''' ] | *[https://www.aliexpress.com/store/product/2017-NEW-Keyestudio-RPI-GPS-Shield-for-Raspberry-Pi/1452162_32782759458.html?spm=2114.12010612.8148356.25.6e9660ffsewRl7 '''Shop on aliexpress''' ] | ||
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0216 | |||
[[category:Raspberry Pi]] | [[category:Raspberry Pi]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 27 April 2021
Introduction
It is based on NEO-6 u blox 6 GPS module, compatible with Raspberry Pi 3. Plug it into Raspberry Pi 3. Upload correct codes to Raspberry Pi 3, and you can find your exact location within a few meters.
It also provides you with a very accurate time! It can be used in car navigation, personal positioning, fleet management, navigation and so on.
Features
- Using active GPS antenna
- With 40 pins, convenient to connect external devices.
- Comes with screws, nuts, copper pillars, easy to fix on Raspberry Pi.
Connection Method
To get started, hook the GPS module up to your Pi as follows, cross-connecting the TX and RX pins (TX on one device goes to RX on the other and vice versa), and supply 5V from the Pi to the VIN pin on the GPS module.

Usage
A. We use raspberry pi official system (2017-01-11-raspbian-jessie-lite), using SSH to log in, and you need to place a ssh file in the root directory.
![]()
B. Bluetooth and Debug share the same serial port together and, but you can just use BT or Debug on one time.
For the Raspberry Pi 3 you need to explicitly enable the serial port on the GPIO pins. The reason for this is a change with the Pi 3 to use the hardware serial port for Bluetooth and instead of a slightly different software's serial port for the GPIO pins.
A side effect of this change is that the serial port will actually change speed as the Pi CPU clock throttles up and down--this will unfortunately cause problems for most serial devices like GPS receivers!
Step by step as shown below:
1) There is now a device tree file called pi3-miniuart-bt which makes the Raspberry Pi 3 disable the Bluetooth and map pl011 UART on pins 14 and 15 as before.
Add device tree to /boot/config.txt to disable the Raspberry Pi 3 bluetooth:
- sudo vi /boot/config.txt
Add at the end of the file:
- dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt
- enable_uart=1
2) To enable the serial console, you need to edit the /boot/cmdline.txt file:
Change the file to the following:
- console=ttyAMA0,115200
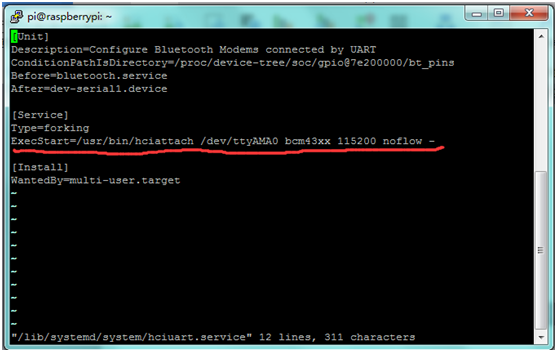
3) Edit /lib/systemd/system/hciuart.server
Change the file to the following:
ExecStart=/usr/bin/hciattach /dev/ttyAMA0 bcm43xx 115200 noflow -
4) Reboot the RPi
- sudo reboot
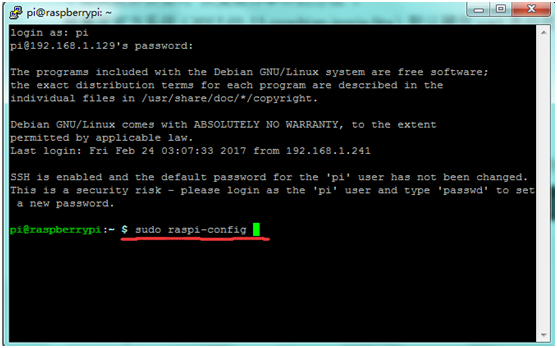
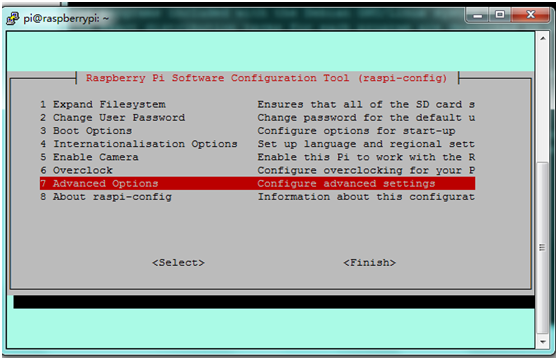
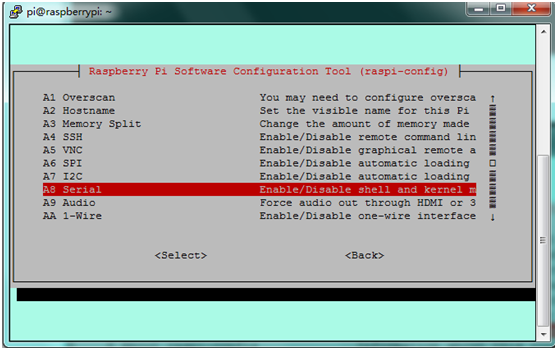
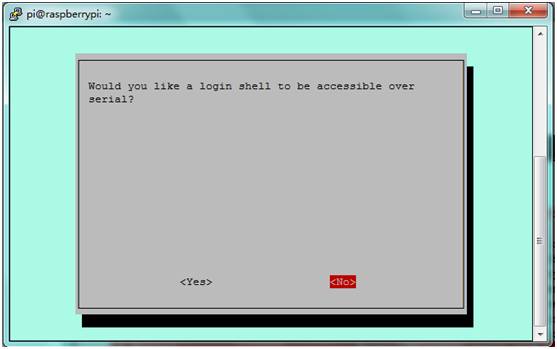
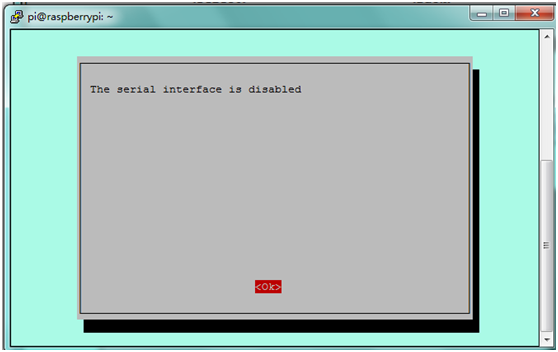
C. Write sudo raspi-config in the terminal,select Advanced Options ---> Serial ---> disable to close serial port debugging.
D. Reboot the Pi
- sudo reboot
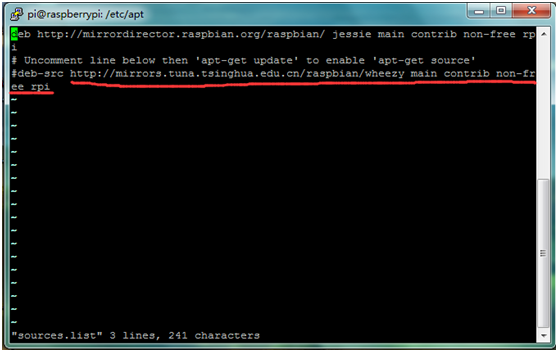
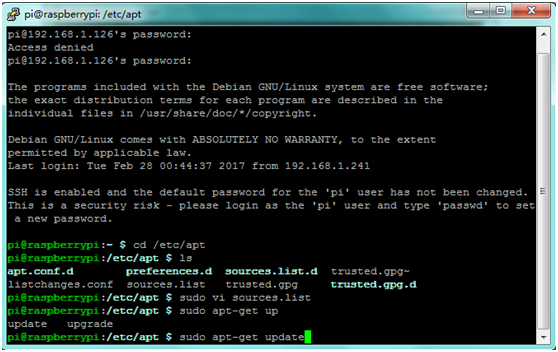
E. A great way to test out the serial port is to use the minicom program. When installing it, you may sometimes can’t find download path of source code. So you can write cd /etc/apt in the terminal, and then edit sudo vi sources.list to modify address.
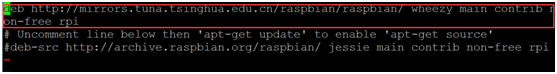
Change the path shown in the red box into:
- deb http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/raspbian/raspbian/ wheezy main contrib non-free rpi
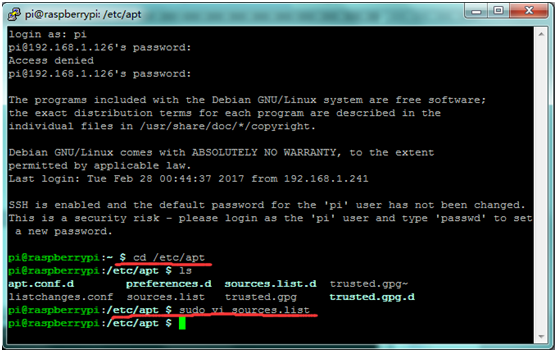
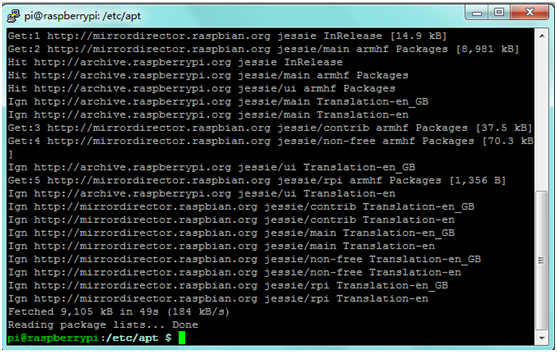
Save your change and exit. Write sudo apt-get update in the terminal to update.
F. You can install Minicom using the following command:
- sudo apt-get install minicom
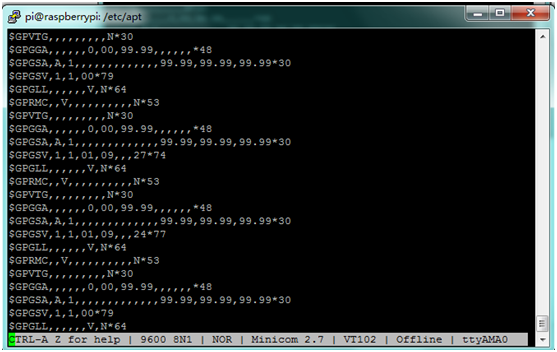
G. You can then use Minicom to send and receive data over the serial port:
- minicom -b 9600 -o -D /dev/ttyAMA0
-b to set baud rate, the same as that of module;
-o dis-initialized Mode and an unlock file;
-D define interface.