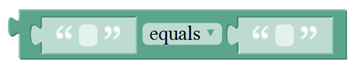Getting Started with Mixly: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 226: | Line 226: | ||
| align="center" | 2 | | align="center" | 2 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-2.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Click to select the Arithmetic Operators: | | align="center" | Click to select the Arithmetic Operators: | ||
[https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/arithmetic-operators/subtraction/ '''+(addition); -(subtraction)''']; | [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/arithmetic-operators/subtraction/ '''+(addition); -(subtraction)''']; | ||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
| align="center" | 3 | | align="center" | 3 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-3.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Click to select the [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitwiseand/ '''& (bitwise end)''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitwiseor/ '''l (bitwise or)''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitshiftleft/ '''<< (bitshift left)''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitshiftright/ '''>> (bitshift right)'''] | | align="center" | Click to select the [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitwiseand/ '''& (bitwise end)''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitwiseor/ '''l (bitwise or)''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitshiftleft/ '''<< (bitshift left)''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/bitwise-operators/bitshiftright/ '''>> (bitshift right)'''] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 4 | | align="center" | 4 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-4.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Click to select the [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/functions/trigonometry/sin/ '''sin''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/functions/trigonometry/cos/ '''cos''']; '''tan; asin; acos; atan; ln; log10; e^; 10^;''' [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/compound-operators/increment/ '''++ (increment)'''] ; | | align="center" | Click to select the [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/functions/trigonometry/sin/ '''sin''']; [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/functions/trigonometry/cos/ '''cos''']; '''tan; asin; acos; atan; ln; log10; e^; 10^;''' [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/compound-operators/increment/ '''++ (increment)'''] ; | ||
[https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/compound-operators/decrement/ '''-- (decrement)'''] | [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/structure/compound-operators/decrement/ '''-- (decrement)'''] | ||
| Line 245: | Line 245: | ||
| align="center" | 5 | | align="center" | 5 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-5.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Click to select the '''Round; Ceil; Floor; abs; sq; sqrt''' | | align="center" | Click to select the '''Round; Ceil; Floor; abs; sq; sqrt''' | ||
'''Round:''' Returns the integer part a number using around. | '''Round:''' Returns the integer part a number using around. | ||
| Line 256: | Line 256: | ||
| align="center" | 6 | | align="center" | 6 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-6.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | If select the '''max''', returns the larger number; | | align="center" | If select the '''max''', returns the larger number; | ||
if select the '''min''', returns the smaller number. | if select the '''min''', returns the smaller number. | ||
| Line 263: | Line 263: | ||
| align="center" | 7 | | align="center" | 7 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-7.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Initialize the random seed | | align="center" | Initialize the random seed | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 8 | | align="center" | 8 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-8.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Return a random integer between the two specified limits, inclusive. | | align="center" | Return a random integer between the two specified limits, inclusive. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 9 | | align="center" | 9 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-9.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Constrain a number to be between the specified limits (inclusive). | | align="center" | Constrain a number to be between the specified limits (inclusive). | ||
(generally used to constrain an analog value read from sensor) | (generally used to constrain an analog value read from sensor) | ||
| Line 279: | Line 279: | ||
| align="center" | 10 | | align="center" | 10 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.4-10png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | Map a number from the first interval to the second interval. | | align="center" | Map a number from the first interval to the second interval. | ||
(For instance, potentiometer-controlled servo, map the range of potentiometer (0, 1023) to the angle of servo (0, 180)). | (For instance, potentiometer-controlled servo, map the range of potentiometer (0, 1023) to the angle of servo (0, 180)). | ||
| Line 297: | Line 297: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 1 | | align="center" | 1 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-1.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | character string: a letter, word, or line of text. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 2 | | align="center" | 2 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-2.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | A character | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 3 | | align="center" | 3 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-3.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
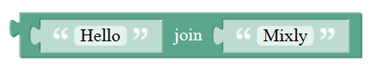
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Creates a piece of text by joining together two piece of text. | ||
( Here Hello join Mixly equals HelloMixly) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 4 | | align="center" | 4 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-4.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Converts a string into an integer or an float. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 5 | | align="center" | 5 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-5.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Returns the char corresponding to an ASCII code | ||
(Decimal number 97 corresponding to a) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 6 | | align="center" | 6 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-6.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Returns the ASCII code corresponding to a char. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 7 | | align="center" | 7 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-7.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Converts a number into a string. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 8 | | align="center" | 8 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-8.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Calculates the length of a string | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 9 | | align="center" | 9 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3. | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-9.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" | Output the char of a string (the char at 0 of hello is h) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | 10 | | align="center" | 10 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.3- | | align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-10.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| align="center" | | | align="center" |The first string equals or startsWith or endsWith the second string, returns 1, otherwise returns 0. | ||
( | (if equals, both strings are abc, returns 1.) | ||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 11 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-11.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" |Returns a decimal value of the first string subtracts the second string. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
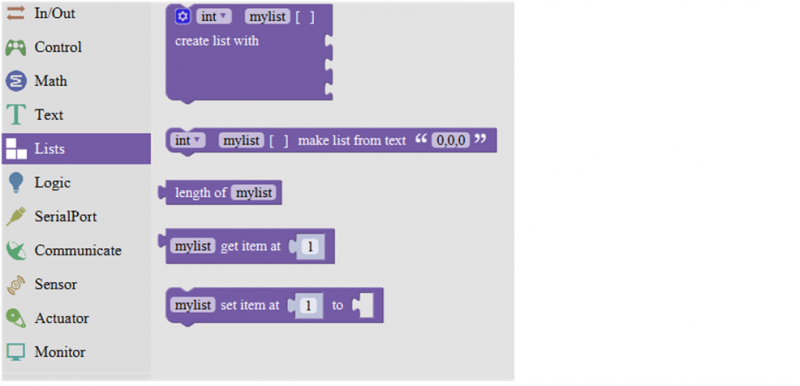
===List Block=== | |||
<br>[[Image:3.6.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
{| width="80%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | No. | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | BLOCK ICON | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | DEFINITION | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 1 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.6-1.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Create a list with any number of items | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 2 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.6-2.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Creats a list from a text. (int mylist [ ]={0,0,0};) | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 3 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.6-3.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Creats a list from a text. (int mylist [ ]={0,0,0};) | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 4 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.6-4.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Returns the value of at the specified position in a list. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 5 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.6-5.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Sets the value of at the specified position in a list. | |||
Set the first item in mylist to another item. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
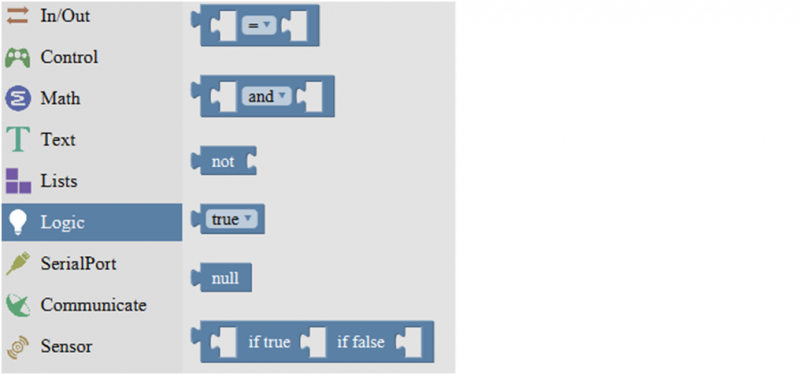
===Logic Block=== | |||
<br>[[Image:3.7.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
{| width="80%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | No. | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | BLOCK ICON | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | DEFINITION | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 1 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-1.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | '''logic comparision''' | |||
'''=:''' Return true if both inputs equal each other. | |||
'''≠:''' Return true if both inputs are not equal to each other. | |||
'''<:''' Return true if the first input is smaller than the second input. | |||
'''≤ :''' Return true if the first input is smaller than or equal to the second input. | |||
'''>:''' Return true if the first input is greater than the second input. | |||
'''≥ :''' Return true if the first input is greater than or equal to the second input. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 2 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.7-2.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | '''and:'''Return true if both inputs are true; | |||
'''or:''' Return true if at least one of the inputs is true | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 3 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.7-3.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Returns true if the input is false. Returns false if the input is true. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 4 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.7-4.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Returns either true or false. | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 5 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.7-5.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Returns null | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 6 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.7-6.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | If the first number is true, the second number is returned, otherwise the third number. | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
<br>[[Image:3.7.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
{| width="80%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | No. | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | BLOCK ICON | |||
! align="center" scope="col" | DEFINITION | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 1 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.5-1.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Declare and initialize a variable. | |||
Click to select [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/int/ '''int'''], [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/long/ '''long'''],[https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/float/ '''float'''], [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/boolean/ '''boolean'''], '''[https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/byte/ byte'''],[https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/char/ '''char'''], [https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/variables/data-types/string/ '''string'''] | |||
|- | |||
| align="center" | 2 | |||
| align="center" | <br>[[Image:3.7-2.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
| align="center" | Define the data types | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''For example: LED breath''' | |||
You need an Arduino Uno and one LED module. Connect the control pin of LED module to Pin 3 of Uno board (or other pins with “~”,that is, those pins can output PWM signal). LED will gradually light then gradually dim, repeatedly. | |||
<br>[[Image:3.8 LED breath.png|800px|frameless]]<br> | |||
Revision as of 10:25, 23 August 2018
Introduction for Mixly
Mixly is a free open-source graphical Arduino programming software, based on Google’s Blockly graphical programming framework, and developed by Mixly Team@ BNU.
It is a free open-source graphical programming tool for creative electronic development; a complete support ecosystem for creative e-education; a stage for maker educators to realize their dreams.
Although there is an Ardublock graphical programming software launched by Arduino official, Ardublock is not perfect enough, and many common functions cannot be realized.
The figure below shows the functional comparison between Ardublock and Mixly.
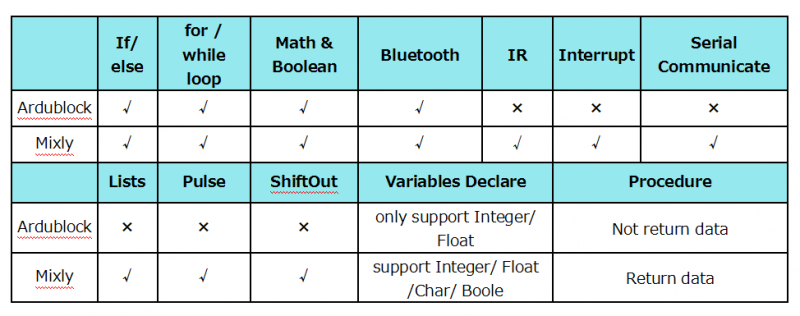
It can be said that Mixly is the most versatile and smoothest Arduino graphical programming software, which can replace the Arduino programming tool IDE.
Design Concept and User Groups
Design Concept
(1) Usability
Mixly is designed to be completely green. Currently Mixly supports win, ubuntu, mac. Windows users can download the Mixly package directly from the Internet, and unzip it to run on Windows XP and above (download link is attached below).
(2) Simplicity
Mixly uses the Blockly graphical programming engine to replace complex text manipulation with graphical building blocks, providing a good foundation for beginners to get started quickly.
① Use the different color icons to represent different types of functional blocks, very convenient for users to classify.
② Provide default options in the composite function block to effectively reduce the number of user drags.
③ Integrate all the features of the software in the same interface.
④ Provide the reference tutorial and code examples.
(3) Functionality
It has versatile functions. Mixly can almost implement all the functions that Arduino IDE has. Support all official development boards of arduino.
(4) Continuity
The goal of the graphical programming system is definitely not to replace the original text programming method, but to better understand the programming principles and program thinking through graphical programming, and lay the foundation for future text programming.
It is also the design philosophy for Mixly. More continuous content has been added to the design of the software to protect the user's learning outcomes. To be specific, it includes the introduction of variable types, the consistency of text programming as much as possible in the design of the module, and the support of both graphical and text programming.
(5) Ecological
The most important design concept of Mixly is its ecological feature, which can distinguish it from other Arduino graphical programming.
In order to achieve sustainable development, Mixly is designed to allow manufacturers to develop their own unique modules (currently supports DfRobot, StartLab, MakeBlock, Sense, Seeed, Lubot. But users require JavaScript programming foundation to make this part of the module).
It also allows users directly use Mixly's graphical programming function to generate common modules (such as LED digital display, buzzer broadcast, etc. Users are able to make this part of the module only using Mixly).
Both of the two kinds of modules mentioned above can be imported into the Mixly system through the "Import" function, thereby realizing the user's own value in the popularity of Mixly software.
User Groups
From the above design concept, it can be seen that Mixly is suitable for primary and secondary school students to cultivate programming thinking. It is also available for quick programming when creating a work. Of course, it is good for those lovely friends who don't want to learn text programming, but want to do some small works with intelligent control.
Interface Functions of Mixly
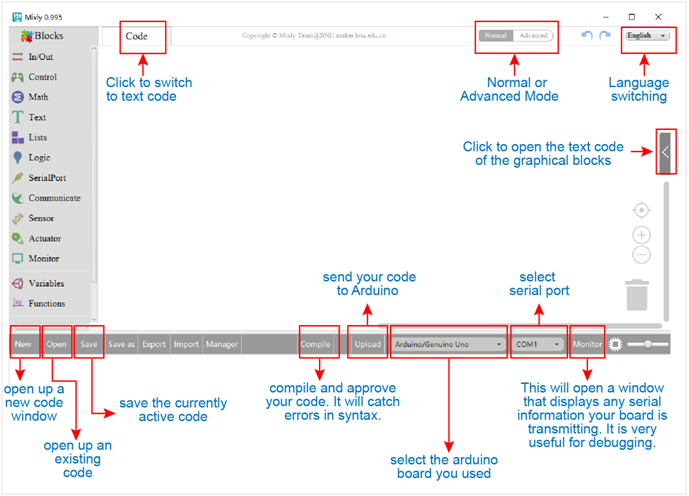
System Functions
Look at the main interface of Mixly, it includes five parts, that is, Blocks selection, code edit, text code (hidden), system function and message prompt area. Shown below.
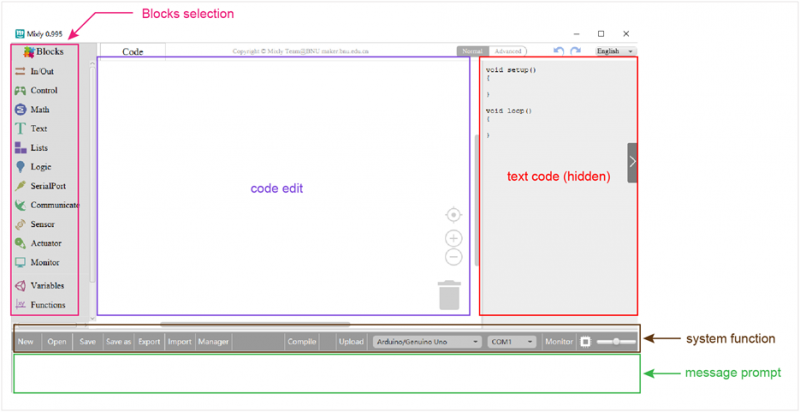
Some common functions:
Through this interface, you can complete the code compile、upload、save and manage. It support four remove methods: drag it left out code window, or drag to Recycle Bin, delete key, or right-click to delete block. It supports four languages: English、Español (Spanish)、中文简体(Chinese Simplified)、中文繁体(Chinese Traditional).
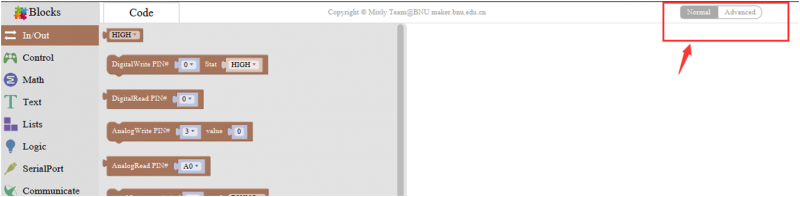
In/Out Block
For example
Connect your Arduino Uno board, then follow the steps below to light the Pin13 led on Arduino UNO.
File:3.2 led D13.png
Control Block
| No. | BLOCK ICON | DEFINITION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Initialization (run only once) |
| 2 |  |
End the program, means the program will stop running when use this block. |
| 3 |  |
Delay function, click to select ms or us
(pause the program for the amount of time (in milliseconds) specified as parameter. There are 1000 milliseconds in a second.) |
| 4 |  |
if_do function (first evaluate a value be true or false, if a value is true, then do some statement.
You can click the blue gear icon to select the else if block or else block.) |
| 5 |  |
switch function. You can click the blue gear icon to select the case block or default block. (used to evaluate several programs then execute the corresponding function matched with program.) |
| 6 |  |
Equal to for statement. |
| 7 |  |
A while loop statement. |
| 8 |  |
break function, used to exit from the containing loop. |
| 9 |  |
millis() function, returns the system running time since the program started.
(The unit can be ms (milliseconds) or μs(microsecond)). |
| 10 | File:3.3-10png |
Timer interrupt function, that is, set a trigger interrupt for the amount of time (in milliseconds) specified as parameter. |
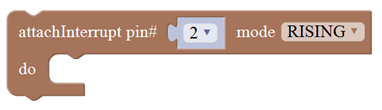
| 11 |  |
Timer interrupt start block |
| 12 |  |
Timer interrupt stop block |
For example
Compile and upload the program below to your Arduino board, you should see Pin13 LED on Arduino UNO continue to flash.(with an interval of 1s, equal to 1000ms)
File:3.3 flash.png
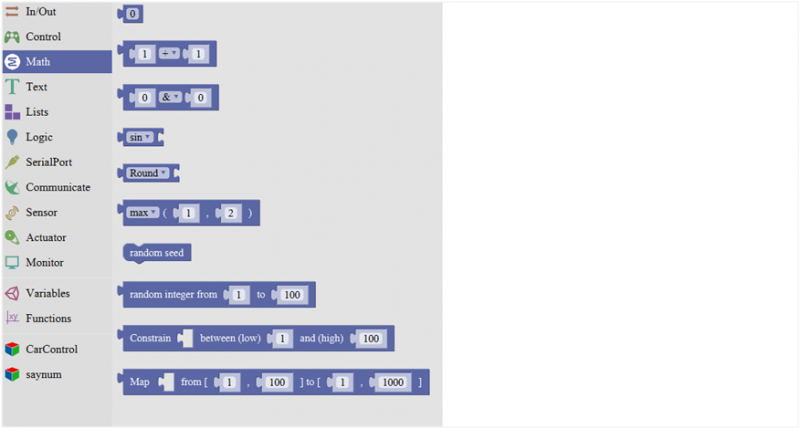
Math Block
| No. | BLOCK ICON | DEFINITION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
A number |
| 2 |  |
Click to select the Arithmetic Operators:
+(addition); -(subtraction); x (Multiplication); ÷ (division); % (remainder); ^ (bitwise xor) |
| 3 |  |
Click to select the & (bitwise end); l (bitwise or); << (bitshift left); >> (bitshift right) |
| 4 |  |
Click to select the sin; cos; tan; asin; acos; atan; ln; log10; e^; 10^; ++ (increment) ; |
| 5 |  |
Click to select the Round; Ceil; Floor; abs; sq; sqrt
Round: Returns the integer part a number using around. Ceil: Returns the integer part a number using ceil. Floor: Returns the integer part a number using floor. abs: Return the absolute value of a number. sq: Return the square of a number. sqrt: Return the square root of a number. |
| 6 |  |
If select the max, returns the larger number;
if select the min, returns the smaller number. |
| 7 |  |
Initialize the random seed |
| 8 |  |
Return a random integer between the two specified limits, inclusive. |
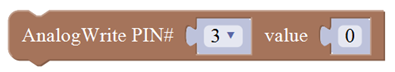
| 9 | Constrain a number to be between the specified limits (inclusive).
(generally used to constrain an analog value read from sensor) | |
| 10 | File:3.4-10png |
Map a number from the first interval to the second interval.
(For instance, potentiometer-controlled servo, map the range of potentiometer (0, 1023) to the angle of servo (0, 180)). |
Text Block
List Block
Logic Block
| No. | BLOCK ICON | DEFINITION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Declare and initialize a variable. |
| 2 | 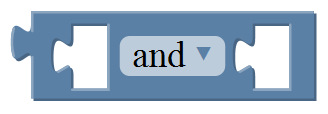 |
Define the data types |
For example: LED breath
You need an Arduino Uno and one LED module. Connect the control pin of LED module to Pin 3 of Uno board (or other pins with “~”,that is, those pins can output PWM signal). LED will gradually light then gradually dim, repeatedly.
File:3.8 LED breath.png