Ks0266 keyestudio Eight-channel Solid State Relay Module: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
==Connection Diagram == | ==Connection Diagram == | ||
<br>[[File:KS0266(3).png| | <br>[[File:KS0266(3).png|800px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
==Sample Code== | ==Sample Code== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Revision as of 17:11, 18 April 2019
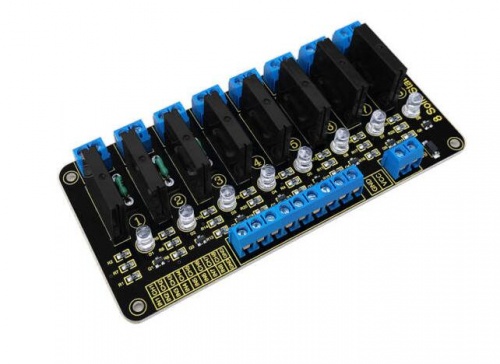
Keyestudio Eight-channel Solid State Relay Module
Introduction
Keyestudio eight-channel solid state relay is a high level effective solid state relay, that is to say, the input control signals is the high level (3.3-5 V), the relay is on; while the input control signal is high level (0-2.5 V), the relay is off.
Solid State Relay is a new kind of contactless switching device which is composed of all solid state electronic components. Compared with the electromagnetic relay, its reliability is more higher, with the features of non-contact, long service life, fast and less outside interference.
The output control terminal of the keyestudio solid-state relay must be connected to the circuit, and its working current needs to be bigger than 50mA, so that the solid state relay can be disconnected normally.
Performance Parameters
- Electrical parameters:
| Voltage | Static Current | Working Current | Trigger Voltage | Trigger Current | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel 1 | DC 5V | 0mA | 13.8mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 2 | DC 5V | 0mA | 26.8mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 3 | DC 5V | 0mA | 37mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 4 | DC 5V | 0mA | 48mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 5 | DC 5V | 0mA | 59mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 6 | DC 5V | 0mA | 70mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 7 | DC 5V | 0mA | 81mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
| Channel 8 | DC 5V | 0mA | 90mA | 3.3-5V | 2mA |
- Output port: AC240V/2A
Connection Diagram
Sample Code
int BASE = 3 ; //The first relay I/O port
int NUM = 8 ; //Total number of relay
void setup()
{
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
pinMode(i, OUTPUT); //Set the digital I/O port to output
}
}
void loop()
{
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
digitalWrite(i, HIGH); //Set the digital I/O port outputs to "HIGH", that is, gradually open relay
delay(200); //delay
}
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
digitalWrite(i, LOW); //Set the digital I/O port outputs to "LOW", that is, gradually close relay
delay(200); //delay
}
}
Result
Wiring as the above image, after powered-on, eight-channel solid state relays are first connected and then broken successively,repeating alternately.
Resource
- PDF:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1bVGkOans_UoWegSrJs8Ft3D4GEKakp-1

