Getting Started with Arduino: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Double-click the icon of Arduino to enter the desired development environment, you should see as below. | Double-click the icon of Arduino to enter the desired development environment, you should see as below. | ||
<br>[[Image:717.png| | <br>[[Image:717.png|500px|frameless]]<br> | ||
<br> | |||
The functions of each button on the Toolbar are listed below: | The functions of each button on the Toolbar are listed below: | ||
<br>[[Image:IDE.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | <br>[[Image:IDE.png|600px|frameless]]<br> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | '''Verify/Compile''' | ! align="center" scope="col" | <br>[[Image:IDE 1.png|600px|frameless]]<br> '''Verify/Compile''' | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | Check the code for errors | ! align="center" scope="col" | Check the code for errors | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | '''Upload''' | ! align="center" scope="col" | <br>[[Image:IDE 2.png|600px|frameless]]<br> '''Upload''' | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | Upload the current Sketch to the Arduino | ! align="center" scope="col" | Upload the current Sketch to the Arduino | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | '''New''' | ! align="center" scope="col" | <br>[[Image:IDE 3.png|600px|frameless]]<br> '''New''' | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | Creat a new blank Sketch | ! align="center" scope="col" | Creat a new blank Sketch | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | '''Open''' | ! align="center" scope="col" | <br>[[Image:IDE 4.png|600px|frameless]]<br> '''Open''' | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | Show a list of Sketches | ! align="center" scope="col" | Show a list of Sketches | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | '''Save''' | ! align="center" scope="col" | <br>[[Image:IDE 5.png|600px|frameless]]<br> '''Save''' | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | Save the current Sketch | ! align="center" scope="col" | Save the current Sketch | ||
|- | |- | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | '''Serial Monitor''' | ! align="center" scope="col" | <br>[[Image:IDE 6.png|600px|frameless]]<br> '''Serial Monitor''' | ||
! align="center" scope="col" | Display the serial data being sent from the Arduino | ! align="center" scope="col" | Display the serial data being sent from the Arduino | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 16:17, 23 July 2018
What is Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. Arduino boards are able to read inputs - light on a sensor, a finger on a button, or a Twitter message - and turn it into an output - activating a motor, turning on an LED, publishing something online. You can tell your board what to do by sending a set of instructions to the microcontroller on the board. To do so you use the Arduino programming language (based on Wiring), and the Arduino Software (IDE) , based on Processing.
Click the link below to get more info.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/Introduction
Getting Started with Arduino and Genuino products
The Arduino Platform
Arduino is composed of two major parts:
The Arduino board , which is the piece of hardware you work on when you build your objects. Arduino senses the environment by receiving inputs from many sensors, and affects its surroundings by controlling lights, motors, and other actuators.
The Arduino IDE , the piece of software you run on your computer. You use the IDE to create a sketch (a little computer program) that you upload to the Arduino board. The sketch tells the board what to do.
You can tell your Arduino what to do by writing code in the Arduino programming language and using the Arduino development environment .
Not too long ago, working on hardware meant building circuits from scratch, using hundreds of different components with strange names like resistor, capacitor,LED, transistor, and so on. Every circuit was "wired" to do one specific application, and making changes required you to cut wires, solder connections, and more.
With the appearance of digital technologies and microprocessors, these functions, which were once implemented with wires, were replaced by software
programs.
Software is easier to modify than hardware. With a few keypresses, you can radically change the logic of a device and try two or three versions in the same amount of time that it would take you to solder a couple of resistors.
Click here to get the Arduino Language Reference
The Arduino software icon is showed below.

Double-click the icon of Arduino to enter the desired development environment, you should see as below.
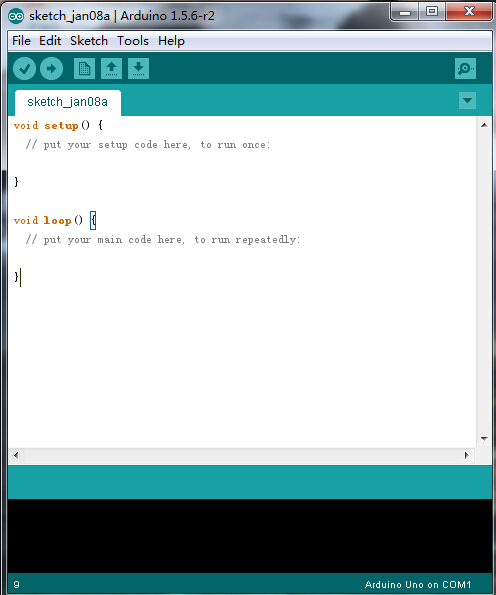
The functions of each button on the Toolbar are listed below:
![]()
The Arduino Hardware
The Arduino board is a small microcontroller board,which is a small circuit (the board) that contains a whole computer on a small chip (the microcontroller). It is a lot cheaper and very useful to build interesting devices.
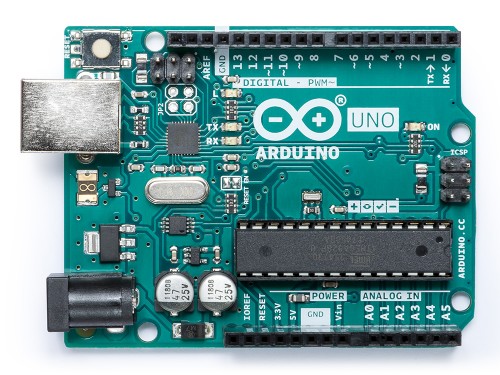
The UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can start playing with. The UNO is the most used and documented board of the whole Arduino family.
Look at the Arduino UNO REV3 Board:
At first,all those connectors might be a little confusing. Here is an explanation of what every element of the board does: https://store.arduino.cc/arduino-uno-rev3
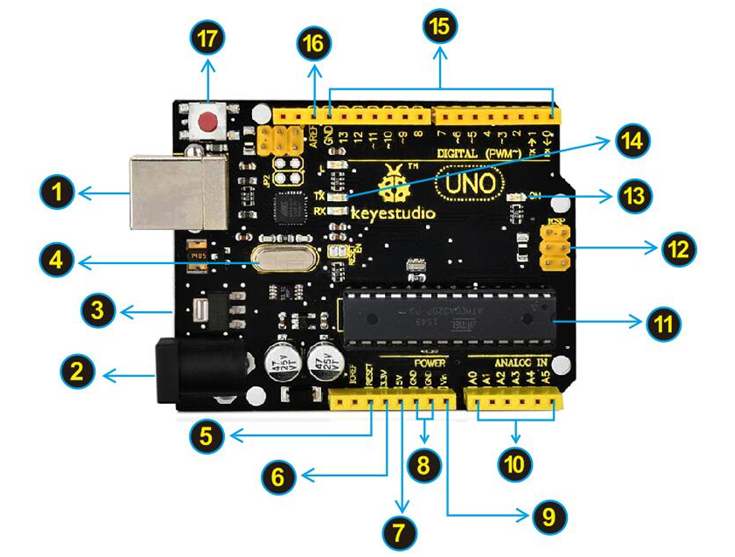
keyestudio UNO Development Board
Let's take a look at the details of this development board with the following chart: