Ks0288 keyestudio CNC GRBL V0.9
Keyestudio CNC GRBL V0.9
Introduction
Keyestudio CNC GRBL V0.9 is a motherboard developed for various robots such as laser engraving, CNC, writing robot and so on. It has complete interfaces with cheap price, and can connect external drive, very suitable for DIY or factory use.
Specification
- Microprocessor:MEGA328p
- Input voltage: DC 12V
- File supporting format:Gcode
- Supporting machine structure:CNC,laser engraving,writing robot.
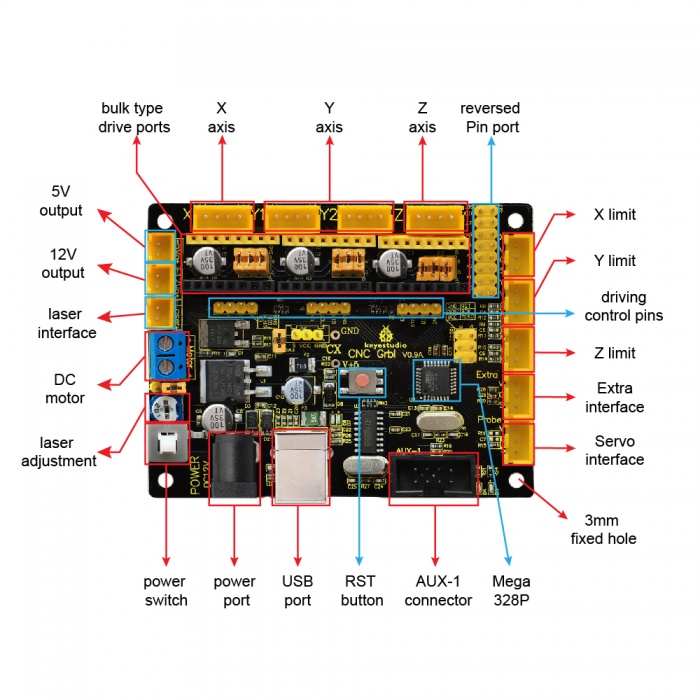
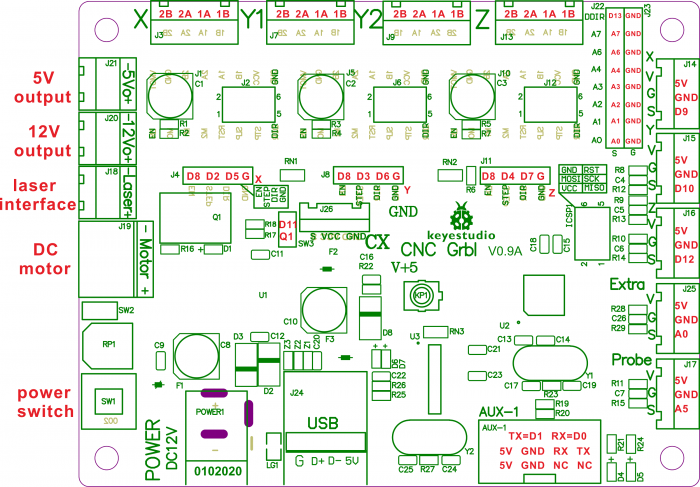
Pin Explanation
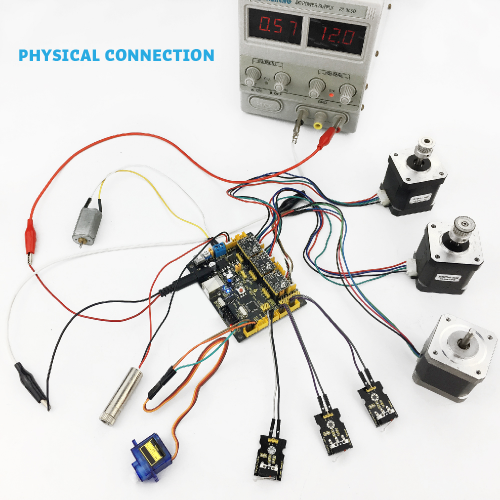
Wiring Diagram
Install Driver and Development Environment Software IDE
(1)Install Driver Software
For different operating system, there may be slight difference in installation method. Below is an example in WIN 7.
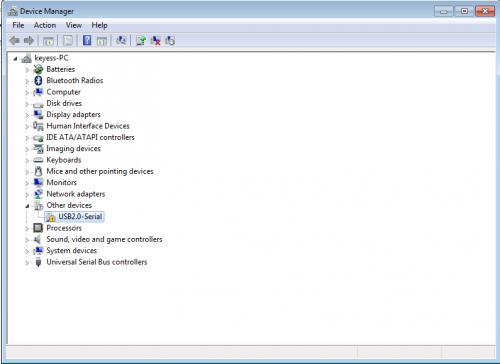
a.When you connect Keyestudio CNC GRBL V0.9 to your computer at the first time, right click “Computer” —>“Properties”—> “Device manager”, you can see “USB2.0-Serial”. Shown below.
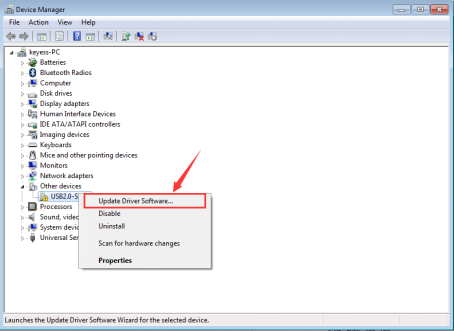
b.Click “USB2.0-Serial”, select “Update Driver software”.
c.Then, click “Browse my computer for driver software”.
d.Find the “usb_ch341_3.1.2009.06” file.
e.Click “Next”,Installation completed; click “Close”.
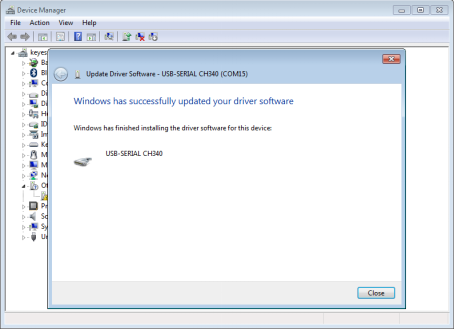
f.After driver is installed, go to “Device manager” again. right click “Computer” —> “Properties”—> “Device manager”, you can see the Board and Com port as below figure shown.
thumb
(2) Install Development Environment Software IDE
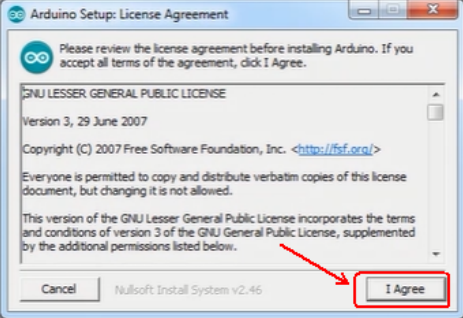
a.Double click arduino-1.5.6-r2-windows to start.
Select “I Agree”to accept license agreement.
b.Select components to install and click “Next”.
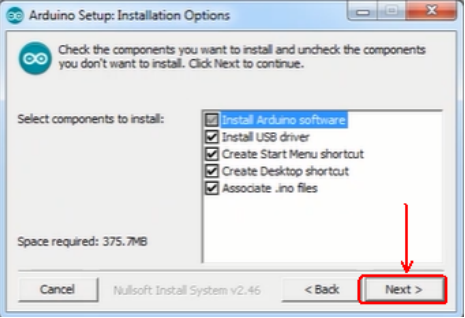
c.Click “Browse” and select another folder. Click “Install” to start the installation.
d.Finally, wait for a few minutes to finish.
Testing
Open Arduino IDE, compile and upload the below code to keyestudio CNC GRBL V0.9, then wire it up as above connection diagram, you can check every interface function.
Code:
#define Light1 13
#define Light2 A1
#define Light3 A2
#define Light4 A3
#define Light5 A4
#define Light6 A5
#define EN1 8
#define X_DIR 5 //X axis direction control of stepper motor
#define Y_DIR 6 //y axis direction control of stepper motor
#define Z_DIR 7 //z axis direction control of stepper motor
#define X_STP 2 //x axis stepper control
#define Y_STP 3 //y axis stepper control
#define Z_STP 4 //z axis stepper control
#define X_LIMIT 9 //X limit
#define Y_LIMIT 10 //Y limit
#define Laser 11 //motor or laser controlling pin
#define Z_LIMIT 12 //Z limit
#define E_LIMIT A0 //E limit
const int Button_A7 = A7;
const int Button_A6 = A6;
int Button_value_A7 = 0;
int Button_value_A6 = 0;
int Button_valueX = 0;
int Button_valueY = 0;
int Button_valueZ = 0;
int Button_valueE = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(Light1, OUTPUT); pinMode(Light2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Light3, OUTPUT); pinMode(Light4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Light5, OUTPUT); pinMode(Light6, OUTPUT);
pinMode(EN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(X_DIR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Y_DIR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Z_DIR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(X_STP, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Y_STP, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Z_STP, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Button_A7, INPUT);
pinMode(Button_A6, INPUT);
pinMode(E_LIMIT, INPUT);
pinMode(X_LIMIT, INPUT);
pinMode(Y_LIMIT, INPUT);
pinMode(Z_LIMIT, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void EN()
{
digitalWrite(EN1, LOW);
}
//stepper motor turns and reverse
void turn(boolean dir, int steps)
{
EN();
digitalWrite(X_DIR,dir);
digitalWrite(Y_DIR,dir);
digitalWrite(Z_DIR,dir);
delay(100);
for(int i=0;i<steps;i++)
{
digitalWrite(X_STP, HIGH);
digitalWrite(Y_STP, HIGH);
digitalWrite(Z_STP, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(100);
digitalWrite(X_STP, LOW);
digitalWrite(Y_STP, LOW);
digitalWrite(Z_STP, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(100);
}
}
//laser is on
void Laser_ON()
{
digitalWrite(Laser, HIGH);
delay(500);
//digitalWrite(Laser, LOW);
//delay(500);
}
//laser is off
void Laser_OFF()
{
digitalWrite(Laser, LOW);
delay(500);
//digitalWrite(Laser, LOW);
//delay(500);
}
void loop()
{
Button_valueX = digitalRead(X_LIMIT);
if(Button_valueX == LOW)
{
digitalWrite(Light3, HIGH);
turn(true, 4000);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(Light3, LOW);
}
Serial.print("Button_valueX = ");
Serial.println(Button_valueX);
Button_valueY = digitalRead(Y_LIMIT);
if(Button_valueY == LOW)
{
digitalWrite(Light4, HIGH);
turn(false, 4000);
}
else digitalWrite(Light4, LOW);
Serial.print("Button_valueY = ");
Serial.println(Button_valueY);
Button_valueZ = digitalRead(Z_LIMIT);
if(Button_valueZ == LOW) digitalWrite(Light5, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(Light5, LOW);
Serial.print("Button_valueZ = ");
Serial.println(Button_valueZ);
Button_value_A7 = analogRead(Button_A7);
if(Button_value_A7 == 0) digitalWrite(Light1, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(Light1, LOW);
Serial.print("Button_value_A7 = ");
Serial.println(Button_value_A7);
Button_value_A6 = analogRead(Button_A6);
if(Button_value_A6 == 0) digitalWrite(Light2, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(Light2, LOW);
Serial.print("Button_value_A6 = ");
Serial.println(Button_value_A6);
Button_valueE = analogRead(E_LIMIT);
if(Button_valueE == 0)
{
digitalWrite(Light6, HIGH);
Laser_ON();
}
else
{
digitalWrite(Light6, LOW);
Laser_OFF();
}
Serial.print("Button_valueE = ");
Serial.println(Button_valueE);
}
Install Firmware and Grbl Controller
a. Write test program to keyestudio UNO R3
copy the folder GRBL_ Arduino_Library_keyes in the data packet and paste it to the folder libraries in your Arduino IDE document installation.
Code:
#include <grblmain.h>
void setup(){
startGrbl();
}
void loop(){}
//Burn the code above to keyestudio UNO R3
b. Install GrblController361 Software
Grbl Controller is a piece of software which is used to send GCode to CNC Machines. Run Grbl Controller361 Setup in your installation packet, the interface below will come out:
Click Next to continue.
For a license agreement, please check I accept the agreement and click Next.
When you are ready to continue with Setup, click Next.
To continue, click Next. If you would like to select a different folder to install, click Browse.
To continue, click Next. If you would like to select a different folder to place program’s shortcuts, click Browse.
Select the additional tasks you would like Setup to perform while installing Grbl Controller, then click Next.
Click Install to continue with the installation.
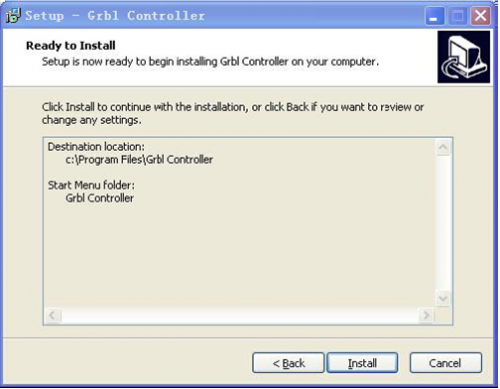
At last, click ”Finish” to finish the installation.
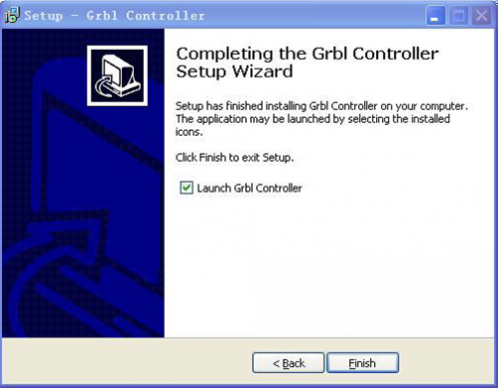
At last, click ”Finish” to finish the installation.
c. Test G-Code on Grbl Controller
Power the main board using a USB cable and connect correctly all your external devices, then run Grbl Controller.
Choose Port name the same as IDE COM port and click “Open” to open the series port, connecting CNC Machines with computer.
After opening the series port, the “Open” button change into “Close/Reset” and get red!
At this time you can click the X axis、Y axis、Z axis as shown in below diagram to adjust the motion direction of motors.
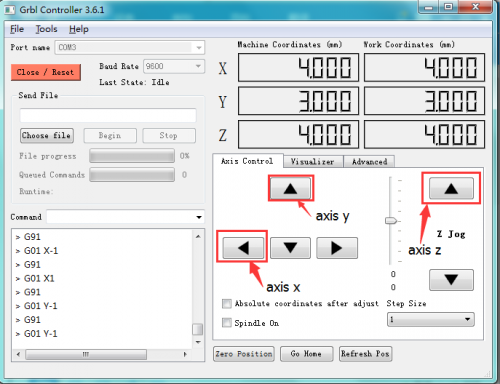
Note: after adjusting the axies, before beginning G-Code file, you must close and open again.
Now, it is time to have a try! Click ”Choose file” to choose one G-Code file named cn. to test in the data packet for a beginner, and the interface will come out:
GrblController
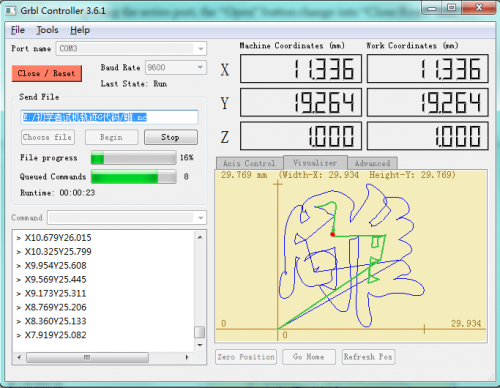
Click “Begin” , and you can see how the motors move on coordinates.
Documents
- All information download:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1UR3X9ZXmy_-bBTqhLOH1insBts5SyEsJ
- Arduino IDE Download:
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/OldSoftwareReleases#1.5.x
- GRBL_Arduino_Library_keyes (Firmware) Download:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1mmaspMTJAiPvFNpW5ihM-YqeTWKboTKt
- Driver Download:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1IwohNN5tsgm3LzU0kdrBcekGQm--PoPf
- G-Code for Testing Download:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1N5n5n5u4JIh2WLbFyW5VyBaabE2sZb84
- Grbl Controller361 Setup Download:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1Ds6qJSpFfatAwthNaO-6sfFm_xbwCUDS
- PDF
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1jlxNQYn2taZQnf1CBoVAsRhP9O0poDdw