KS0443 Keyestudio W5500 Network Shield
Description
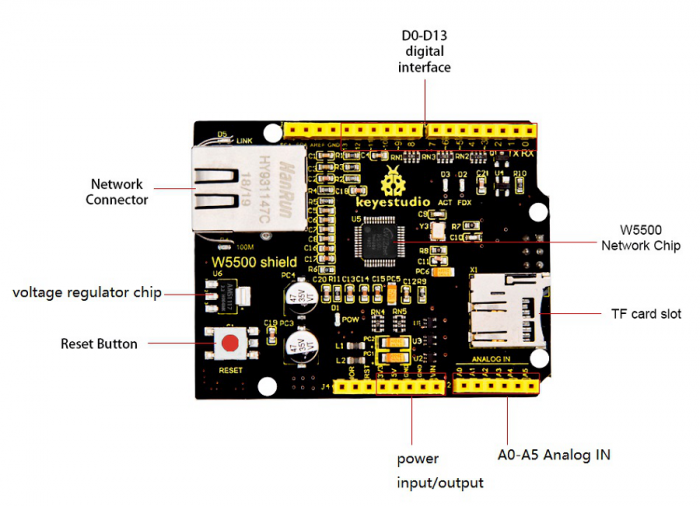
Keyestudio W5500 network shield comes with W5500 network module as core.
It can make as simple Web server, or write and read the High/Low level of digital pins, or analog value of analog pins via network control.
It is compatible with both keyestudio UNO R3 and Mega 2560 R3 development board.
When using, stack the W5500 shield onto UNO board, and upload the program to control board, which can make a simple Web server.
You can quickly make your controller access to internet to build your network application.
At the same time, it also supports mini SD card (TF card) read and write.
You can direct stack the W5500 Network shield onto control board, or stack other expansion boards on this Network shield.
The shield has four 3mm fixing holes, easy to mount on any other devices.
Technical Parameters
- Input voltage: DC 5V
- Working voltage: DC 3.3V
- Working current: about 380mA
- Maximum power: 3W
- Working temperature: -55℃ ~ +75℃
- Network transformer interface type: RJ-45
- Female header pitch: 2.54mm
- TF socket: self-popping
- Fixed hole diameter: 3mm
- Dimensions: 65mm*50mm*27mm
- Weight: 25g
W5500 full hardware TCP/IP protocol stack network chip
- Support high speed SPI bus (SPI mode 0, 3);
- Support hardware TCP/IP protocol: TCP, UDP, ICMP, IPv4ARP, IGMP, PPPoE;
- Embedded 10/100Mbps Ethernet physical layer;
- Support auto answer (full duplex / half duplex mode);
- Multiple indicator signal outputs (full/half duplex);
- Support 8 independent ports to connect at the same time;
- Internal 32K byte memory for TX/RX buffer;
- Support sleep mode and network wake-up;
- 3.3V working voltage, I/O port can withstand 5V voltage
- Ultra small 48P/N LQFP lead-free package
Test Code
Before upload the test code, don’t forget to place the necessary library into libraries folder of Adruino IDE.
Code A:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet55.h>
// set MAC address
#if defined(WIZ550io_WITH_MACADDRESS) // Use assigned MAC address of WIZ550io
;
#else
byte mac[] = {0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED};
#endif
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
if (Ethernet.begin(mac) == 0)
{
Serial.println("Failed to configure Ethernet using DHCP");
// connection fails, stop program run.
for(;;);
}
// print out your local IP address
Serial.print("My IP address: ");
for (byte thisByte = 0; thisByte < 4; thisByte++)
{
// print out four byte IP address
Serial.print(Ethernet.localIP()[thisByte], DEC);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println();
}
void loop()
{
}
Code B:
//in testing, check IP address of reticle through GET_IP routine
//for example, the tested IP address is 192.168.1.113
//namely intranet address allocated to testing reticle
#include <SdFat.h>
#include <SdFatUtil.h>
#include <Ethernet55.h>
#include <SPI.h>
/************ ETHERNET STUFF ************/
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED }; //MAC address
byte ip[] = { 192, 168, 1, 133 }; //IP address
EthernetServer server(80);
/************ SDCARD STUFF ************/
Sd2Card card;
SdVolume volume;
SdFile root;
SdFile file;
// store error strings in flash to save RAM
#define error(s) error_P(PSTR(s))
void error_P(const char* str) {
PgmPrint("error: ");
SerialPrintln_P(str);
if (card.errorCode()) {
PgmPrint("SD error: ");
Serial.print(card.errorCode(), HEX);
Serial.print(',');
Serial.println(card.errorData(), HEX);
}
while(1);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
PgmPrint("Free RAM: ");
Serial.println(FreeRam());
// initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with
// breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance.
pinMode(10, OUTPUT); // set the SS pin as an output (necessary!)
digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // but turn off the W5500 chip!
if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, 4)) error("card.init failed!");
// initialize a FAT volume
if (!volume.init(&card)) error("vol.init failed!");
PgmPrint("Volume is FAT");
Serial.println(volume.fatType(),DEC);
Serial.println();
if (!root.openRoot(&volume)) error("openRoot failed");
// list file in root with date and size
PgmPrintln("Files found in root:");
root.ls(LS_DATE | LS_SIZE);
Serial.println();
// Recursive list of all directories
PgmPrintln("Files found in all dirs:");
root.ls(LS_R);
Serial.println();
PgmPrintln("Done");
// Debugging complete, we start the server!
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
server.begin();
}
void ListFiles(EthernetClient client, uint8_t flags) {
// This code is just copied from SdFile.cpp in the SDFat library
// and tweaked to print to the client output in html!
dir_t p;
root.rewind();
client.println("<ul>");
while (root.readDir(&p) > 0) {
// done if past last used entry
if (p.name[0] == DIR_NAME_FREE) break;
// skip deleted entry and entries for . and ..
if (p.name[0] == DIR_NAME_DELETED || p.name[0] == '.') continue;
// only list subdirectories and files
if (!DIR_IS_FILE_OR_SUBDIR(&p)) continue;
// print any indent spaces
client.print("<li><a href=\"");
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
if (p.name[i] == ' ') continue;
if (i == 8) {
client.print('.');
}
client.print((char)p.name[i]);
}
client.print("\">");
// print file name with possible blank fill
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
if (p.name[i] == ' ') continue;
if (i == 8) {
client.print('.');
}
client.print((char)p.name[i]);
}
client.print("</a>");
if (DIR_IS_SUBDIR(&p)) {
client.print('/');
}
// print modify date/time if requested
if (flags & LS_DATE) {
root.printFatDate(p.lastWriteDate);
client.print(' ');
root.printFatTime(p.lastWriteTime);
}
// print size if requested
if (!DIR_IS_SUBDIR(&p) && (flags & LS_SIZE)) {
client.print(' ');
client.print(p.fileSize);
}
client.println("</li>");
}
client.println("</ul>");
}
// How big our line buffer should be. 100 is plenty!
#define BUFSIZ 100
void loop()
{
char clientline[BUFSIZ];
int index = 0;
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client) {
// an http request ends with a blank line
boolean current_line_is_blank = true;
// reset the input buffer
index = 0;
while (client.connected()) {
if (client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
// If it isn't a new line, add the character to the buffer
if (c != '\n' && c != '\r') {
clientline[index] = c;
index++;
// are we too big for the buffer? start tossing out data
if (index >= BUFSIZ)
index = BUFSIZ -1;
// continue to read more data!
continue;
}
// got a \n or \r new line, which means the string is done
clientline[index] = 0;
// Print it out for debugging
Serial.println(clientline);
// Look for substring such as a request to get the root file
if (strstr(clientline, "GET / ") != 0) {
// send a standard http response header
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println();
// print all the files, use a helper to keep it clean
client.println("<h2>Files:</h2>");
ListFiles(client, LS_SIZE);
} else if (strstr(clientline, "GET /") != 0) {
// this time no space after the /, so a sub-file!
char *filename;
filename = clientline + 5; // look after the "GET /" (5 chars)
// a little trick, look for the " HTTP/1.1" string and
// turn the first character of the substring into a 0 to clear it out.
(strstr(clientline, " HTTP"))[0] = 0;
// print the file we want
Serial.println(filename);
if (! file.open(&root, filename, O_READ)) {
client.println("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println();
client.println("<h2>File Not Found!</h2>");
break;
}
Serial.println("Opened!");
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/plain");
client.println();
int16_t c;
while ((c = file.read()) > 0) {
// uncomment the serial to debug (slow!)
//Serial.print((char)c);
client.print((char)c);
}
file.close();
} else {
// everything else is a 404
client.println("HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println();
client.println("<h2>File Not Found!</h2>");
}
break;
}
}
// give the web browser time to receive the data
delay(1);
client.stop();
}
}
Test Result
- 1)Before testing, don’t forget to place the necessary library into libraries folder of Adruino IDE.
- 2)During testing, connect the control board to computer’s USB port with a USB cable. Stack the W5500 shield onto control board; connect the network cable to the network transformer port on the W5500 shield; then insert the mini SD card (TF card) into TF card slot.
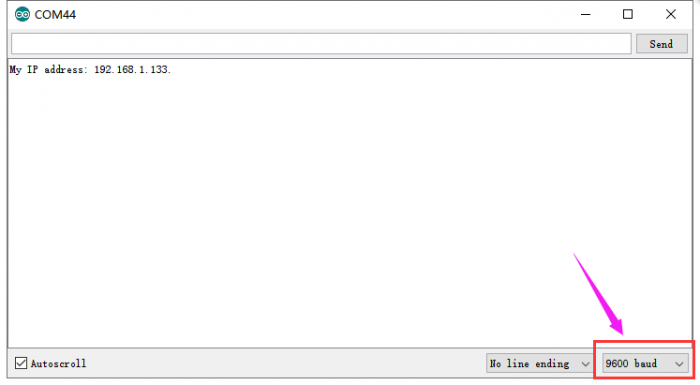
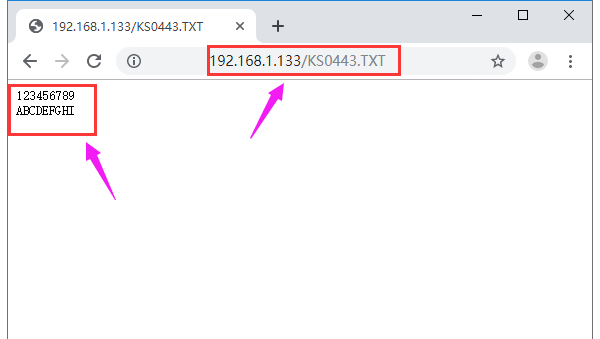
- 3)Upload the Code A to control board; if done uploading, open the serial monitor and set the baud rate to 9600. Press the reset button, you can see the corresponding network IP address 192.168.1.133 shown below.
- 4)Upload the Code B, the IP address in the code B should change as the same as the IP address obtained by Code A.
![]()
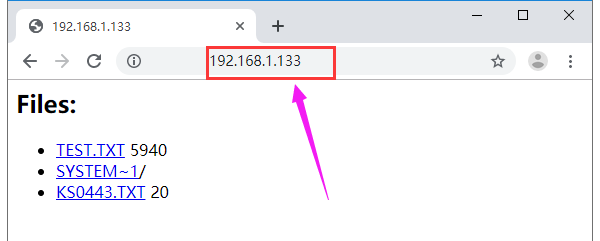
Done uploading the code, open the browser and enter the acquired IP address on the address bar. Later, the webpage will show the content of SD card.
If has TXT. file, able to click to check the file content. As shown below.
Resource
Get One Now
- [ Official website]
- [ Get one now on aliexpress store]