Ks0157 keyestudio EASY plug learning kit for Arduino super makers
EASY plug learning kit for Arduino starters
EASY plug starter kit for Arduino
Based on open-source hardware
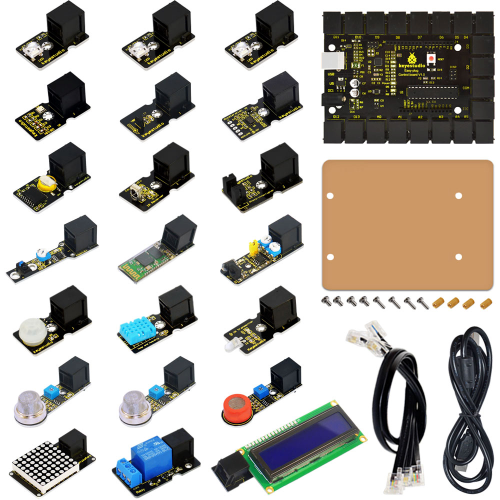
19 various sensors in one box
For you to make interesting projects
Summary
What about you and your kids being makers? What about getting creative and making your ideas come true? Well, let's get started right away!
EASY plug learning kit is developed not only for professional electronic enthusiasts, but also for friends in other lines of work. Even if you have no electronics related knowledge, you can use it to realize your ideas as long as you want to.
The tutorial of this kit has fully considered the learning interest of beginners. Starting from the basics to more complex lessons, well-arranged content and a connection diagram for every lesson help you get started easily and quickly in learning Arduino.
Its unique EASY plug interface makes the wire connection easier than ever! You never have to worry about wrong connection or complicated soldering, avoiding component damage due to wrong wiring or wrong soldering. It's both safe and environmental-friendly.
Kit List
Lesson List
1.Who's blinking
2.Flowing light
3.My LCD display
4.Running light
5.Control electricity
6.Black or white
7.Is there something upfront
8.Is the light blocked
9.It’s moving
10.Make a clock
11.What’s the air pressure
12.Bluetooth so easy
13.I receive a signal
14.Transmit a signal
15.How’s the air quality
16.Is there a gas leakage
17.Did he drink
18.Somebody is in this area
19.What’s the temperature
20.How humid & hot is the air
Lesson Details
Lesson 1: Who's blinking
Introduction As the first lesson of this kit, we will begin with something simple. In this lesson, all you need to do is to connect an LED to one of the digital pins of main board. With the program we provided here, you can easily control the blinking of an LED.
Hardware required
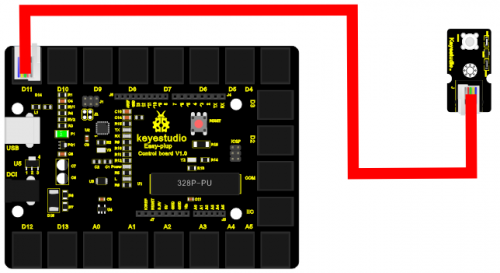
EASY plug controller Board *1
EASY plug cable *1
USB cable *1
EASY plug Piranha LED Module *1
First, let’s take a look at this Piranha LED Module.

This is a special LED module. When you connect it to ARDUINO, after program, it can emit beautiful light. Of course, you can also control it using PWM. It will be like fireflies at night. Isn’t it cool? We can also combine it with other sensors to do various interesting interactive experiments. Below are its specifications:
Module type: digital
Working voltage: 5V
Distance between pins: 2.54mm
Size: 33.7*20mm
Weight: 3g
Connection Diagram
Now, let’s connect this module to the D11 port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable, just as simple as that!
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
int ledPin = 11; // define digital pin 11
void setup()
{
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);// define LED pin as output
}
void loop()
{
analogWrite(ledPin,255); //set the LED on, regulate light brightness, ranging from 0-255, 255 is the brightest
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // set the LED off
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
Result
The LED will be on for one second, and then off for one second with an interval of one second, just like a shining eye blinking.
Lesson 2: Flowing light
Introduction LED can do many things. I believe you have seen billboards with lights changing to form various patterns. Now, you can make one! This lesson is called Flowing light. We will need 2 more EASY plug cables and 2 more LEDs than the previous lesson.
Hardware required
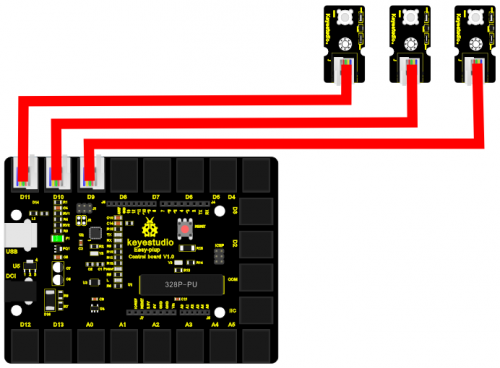
EASY plug controller Board *1
EASY plug cable *3
USB cable *1
EASY plug Piranha LED Module *3
Connection Diagram Now, connect the LED modules one by one to D9, D10 and D11 ports of the controller board using the EASY plug cables.
Sample Code
Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
int BASE = 9 ; // the I/O pin for the first LED
int NUM = 3; // number of LEDs
void setup()
{
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
pinMode(i, OUTPUT); // set I/O pins as output
}
}
void loop()
{
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
digitalWrite(i, HIGH); //set I/O pins as “high”, turn on LEDs one by one
delay(200); // wait 0.2S
}
for (int i = BASE; i < BASE + NUM; i ++)
{
digitalWrite(i, HIGH); // set I/O pins as “low”, turn off LEDs one by one
delay(200); // wait 0.2S
}
}
Result
3 LEDs turn on one by one, and then turn off one by one, just like flowing light.
Lesson 3: My LCD display
Introduction LCDs are very common and useful in our life. It’s widely applied on phone screens and TV screens. In this lesson, we will introduce you a 1602 LCD module to help you understand how it works.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x1
EASY plug 1602 I2C Module x1
First, let’s take a look at this 1602 I2C Module.
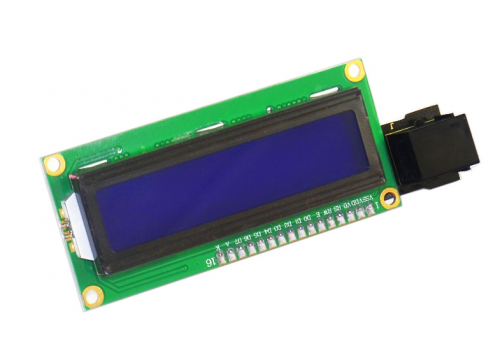
EASY plug 1602 I2C module is a 16 character by 2 line LCD display with blue background and white backlight. This LCD is ready-to-use because it is compatible with the Arduino Liquid Crystal Library. The original 1602 LCD needs 7 IO ports to be up and running, this easy plug design makes the wire connection easier than ever. Below are its specifications:
I2C Address: 0x27
Back lit (Blue with white char color)
Supply voltage: 5V
Adjustable contrast
Size: 98*36mm
Weight: 4g
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the LCD module to the IIC port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable.
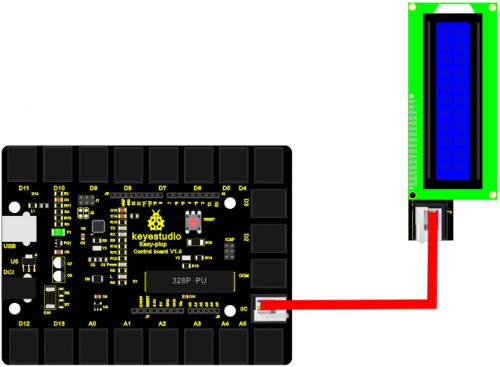
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
//YWROBOT
//Compatible with the Arduino IDE 1.0
//Library version:1.1
#include <Wire.h> // Place file “Wire.h” under the directory “library” of Arduino
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // Place file “LiquidCrystal_I2C.h” under the directory “library” of Arduino
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27,16,2); // set the LCD address to 0x27 for a 16 chars and 2 line display
void setup()
{
lcd.init(); // initialize the lcd
lcd.init();
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(2,0);
lcd.print("Hello, world!");
lcd.setCursor(2,1);
lcd.print("Hello, keyes!");
}
void loop()
{
}
Result
After power is on, the first line of LCD will display “Hello, world!”, and the second line will display “Hello, keyes!”.

Lesson 4: Running light
Introduction Walking down a business street a night, you must be amazed by all the beautiful lights around you. In this lesson, we will make one of our own and learn how those beautiful lights are achieved.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x1
EASY plug I2C 8x8 LED Matrix x1
Let’s first meet this EASY plug I2C 8x8 LED Matrix.
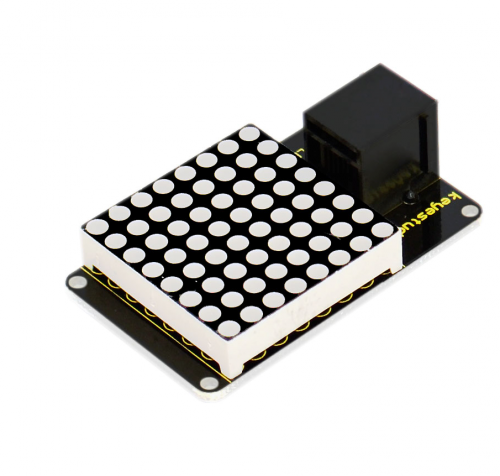

What's better than a single LED? Lots of LEDs! A fun way to make a small display is to use an 8x8 matrix. This matrix uses a driver chip that does all the heavy lifting for you: They have a built in clock so they multiplex the display. They use constant-current drivers for ultra-bright, consistent color, 1/16 step display dimming, all via a simple I2C interface. Below are its specifications:
Supply voltage: 4.5V-5.5V
Maximum display: 16*8
Size: 53*32mm
Weight: 4g
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the module to the IIC port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable.
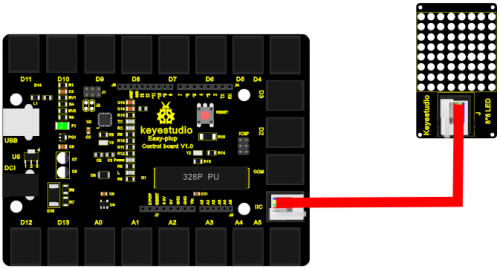
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
#include <Wire.h> // Place file “Wire.h” under the directory “library” of Arduino
#include "Adafruit_LEDBackpack.h" // Place file “Adafruit_LEDBackpack.h” under the directory “library” of Arduino
#include "Adafruit_GFX.h" // Place file “Adafruit_GFX.h” under the directory “library” of Arduino
#define _BV(bit) (1<<(bit))
#endif
Adafruit_LEDBackpack matrix = Adafruit_LEDBackpack();
uint8_t counter = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("HT16K33 test");
matrix.begin(0x70); // pass in the address
}
void loop() {
// paint one LED per row. The HT16K33 internal memory looks like
// a 8x16 bit matrix (8 rows, 16 columns)
for (uint8_t i=0; i<8; i++) {
// draw a diagonal row of pixels
matrix.displaybuffer[i] = _BV((counter+i) % 16) | _BV((counter+i+8) % 16) ;
}
// write the changes we just made to the display
matrix.writeDisplay();
delay(100);
counter++;
if (counter >= 16) counter = 0;
}
Result
After all the above are done (circuit connection, program uploading), press the “reset” button on the main board. The LED matrix begins to display a beautiful light pattern, as pictures show below.
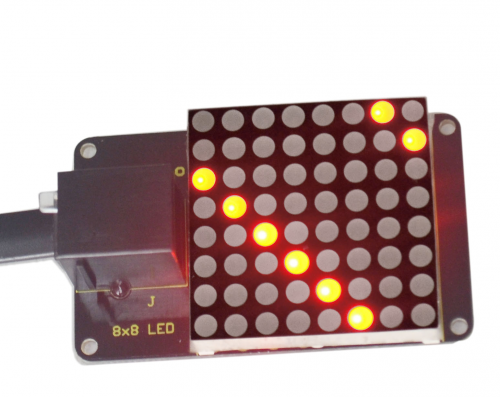
Lesson 5: Control electricity
Introduction In this lesson, we will learn to use a very important element in the switch family. It’s called relay. Relay is specially used in controlling a high-power circuit by a low-power signal. Here, we will only do a simple module test due to limited resources while you can expend the circuit and the program to have more fun with it.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x1
EASY plug Single Relay Module x1
Next is a brief introduction of this relay module.
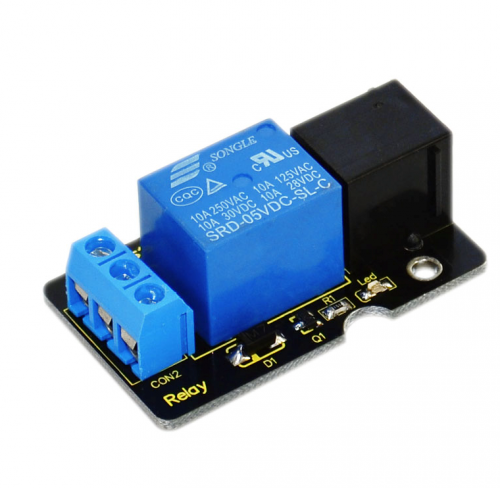

Relay is an automatic switch element with isolation function. It's widely used in remote control, remote sensing, communication, automatic control, mechatronics and electronic devices. It is one of the most important control elements. Besides, it’s easy to control and use just by inputting different level signals to corresponding ports of the relay. The single relay we introduced here has a status indicator light, convenient for you to observe the on and off status of the relay. Below are its specifications:
Type: Digital
Rated current: 10A (NO) 5A (NC)
Maximum switching voltage: 150VAC 24VDC
Digital interface
Control signal: TTL level
Rated load: 8A 150VAC (NO) 10A 24VDC (NO), 5A 250VAC (NO/NC) 5A 24VDC (NO/NC)
Maximum switching power: AC1200VA DC240W (NO) AC625VA DC120W (NC)
Contact action time: 10ms
Size: 46.5*28mm
Weight: 15g
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the module to the IIC port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable.Now, let’s connect this module to the D8 port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable.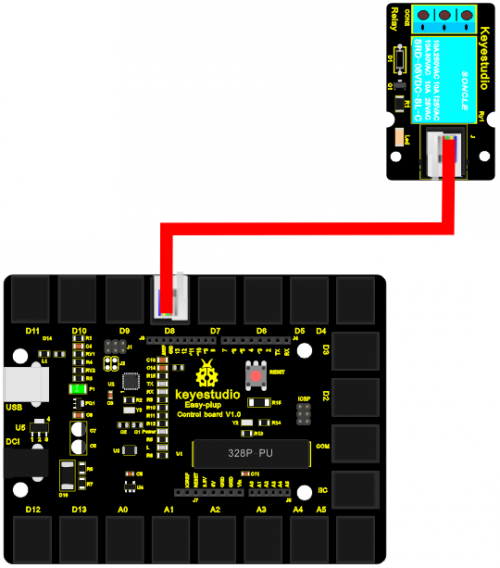
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
int Relay = 8;
void setup()
{
pinMode(Relay, OUTPUT); //Set Pin3 as output
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(Relay, HIGH); //Turn on relay
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(Relay, LOW); //Turn on relay
delay(1000);
}
Result After all the above are done, you can hear the relay module is ticking, and the LED on the module is being on for 1S (“ON” contacts are connected), and off for 1S (“ON” contacts are connected).
Lesson 6: Black or white
Introduction Have you seen a line tracking smart car? That is a car going along a line with specific color. In this lesson, we will learn how to achieve such result. Here, we will use a Line Tracking Sensor and a Piranha LED Module to help you better understand how it works.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x2
EASY plug Piranha LED Module x1
EASY plug Line Tracking Sensor x1
First, we will learn something about this Line Tracking Sensor.
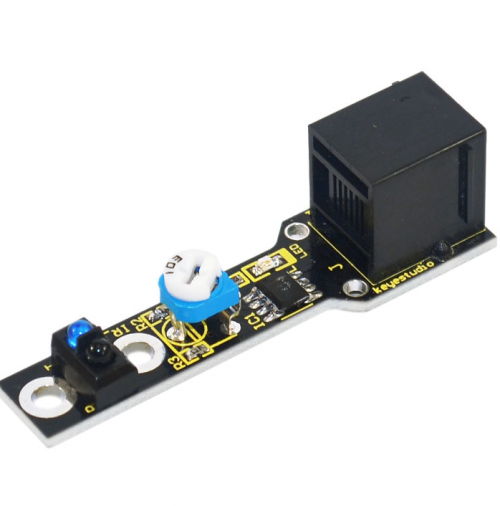

This Line Tracking Sensor can detect white line in black and black line in white. The single line-tracking signal provides a stable output signal TTL for a more accurate and more stable line. Multi-channel option can be easily achieved by installing required number of line-tracking sensors.
The working principle is simple, using infrared light's different reflectivity of different color, and converting the strength of the reflected signal into current signal.
Below are its specifications:
Power supply: +5V
Operating current: <10mA
Operating temperature range: 0°C ~ + 50°C
Output interface: 3-wire interface (1 - signal, 2 - power, 3 - power supply negative)
Output Level: TTL level
Size: 56.8*16mm
Weight: 3g
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the LED module to the D10 port of the controller board, and line tracking sensor module to D3 port using the EASY plug cables.
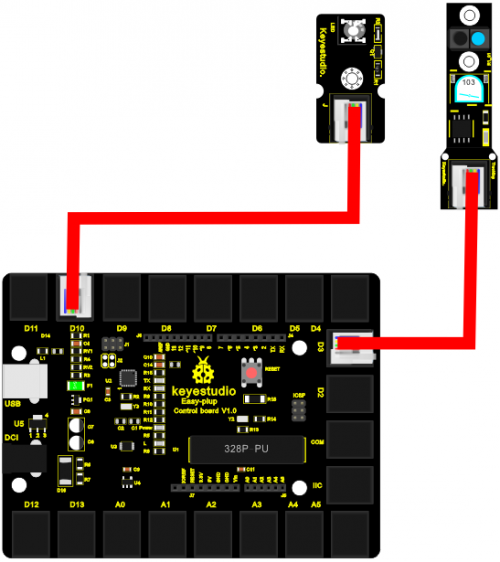
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
#define Sensor 3
#define ledpin 10
void setup()
{
pinMode(Sensor,INPUT);
pinMode(ledpin,OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
int val =digitalRead(Sensor);
digitalWrite(ledpin,val);
Serial.println(val); // print the data from the sensor
delay(200);
}
Result After power is on, open serial monitor, you can see the current value is 1, the LED on the module remains off and the Piranha LED is on. When you place a white card in front of the sensor, you can see the LED on the module turns on, the value changes to 0 and the Piranha LED turns off. Now, place a black card in front of the sensor, you can see the result is the same with when there is nothing in front of the sensor. This principle is applied to line tracking smart car by programming the result.
Lesson 7: Is there something upfront
Introduction If you are interested in smart cars, you might be intrigued in how they avoid obstacles. It’s not like the smart cars have eyes, right? In this lesson, we will learn how to use a infrared obstacle avoidance sensor. This sensor is widely applied in obstacle avoidance, fall prevention of smart cars, product counting etc. After this lesson, you will know how obstacle avoidance function of smart cars can be achieved.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x2
EASY plug Piranha LED Module x1
EASY plug Infrared obstacle avoidance sensor x1
Below is a brief introduction of this infrared obstacle avoidance sensor.
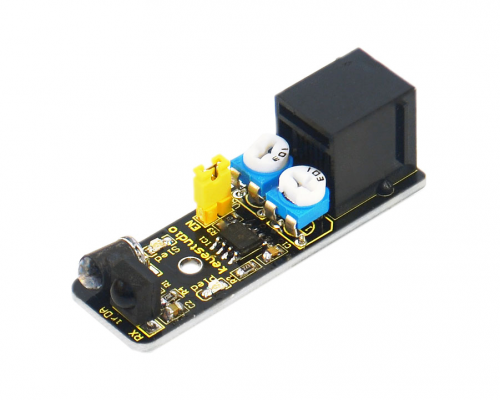

Infrared obstacle avoidance sensor is equipped with distance adjustment function and is especially designed for wheeled robots. This sensor has strong adaptability to ambient light and is of high precision. It has a pair of infrared transmitting and receiving tube. When infrared ray launched by the transmitting tube encounters an obstacle (its reflector), the infrared ray is reflected to the receiving tube, and the indicator will light up. A robot mounted with the sensor can sense changes in the environment. Below are its specifications:
Working voltage: DC 3.3V-5V
Working current: ≥20mA
Working temperature: -10℃—+50℃
Detection distance: 2-1000px
IO Interface: 4 wire interface (-/+/S/EN)
Output signal: TTL voltage
Accommodation mode: Multi-circle resistance regulation
Effective Angle: 35°
Size: 51*16.5mm
Weight: 5g
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the LED module to the D10 port of the controller board and obstacle avoidance sensor to D3 port using the EASY plug cables.
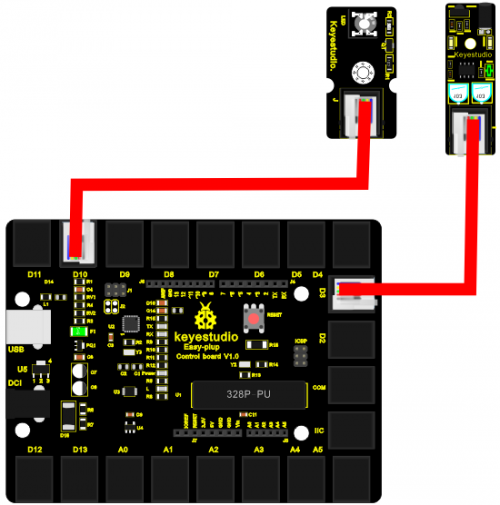
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
const int sensorPin = 3; // the number of the sensor pin
const int ledPin = 10; // the number of the LED pin
int sensorState = 0; // variable for reading the sensor status
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT); }
void loop(){
// read the state of the sensor value:
sensorState = digitalRead(sensorPin);
// if it is, the sensorState is HIGH:
if (sensorState == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}}
Result When power is on, use a screw driver to adjust the two knobs on the module. P LED is always on and S LED is out. At this time, the piranha LED is on. Now, put your hand in front of the sensor, you can see the S LED front of the sensor turns on and the piranha LED is out. If you open the serial monitor, you can see when it detects an object, the output is “0”; no object, output is “1”. These different outputs can be used as a switch signal to control smart car actions and that’s how smart cars realize obstacle avoidance function.
Lesson 8: Is the light blocked
Introduction If you have seen a production line, you must be wondering how the machines do the workpiece counting. Well, in this lesson, we will show you how this technology is achieved.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x2
EASY plug Piranha LED Module x1
EASY plug Photo Interrupter Module x1
In realizing the counting process, below is a critical part called Photo Interrupter Module.
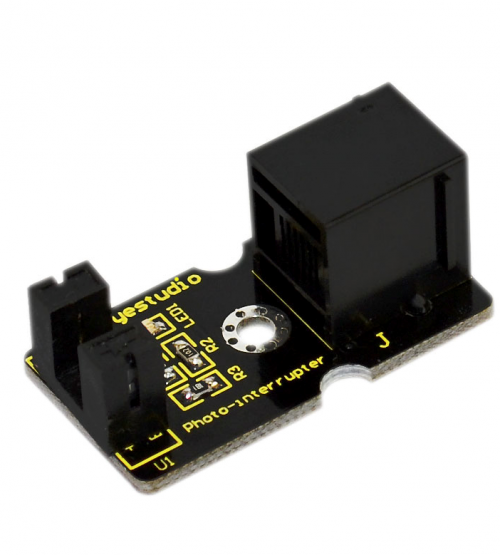

Upright part of this sensor is an infrared emitter and on the other side, it’s a shielded infrared detector. By emitting a beam of infrared light from one end to another end, the sensor can detect an object when it passes through the beam. It is used for many applications including optical limit switches, pellet dispensing, general object detection, etc. Below are its specifications:
Supply Voltage: 3.3V to 5V
Interface: Digital
Size: 38x20mm
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the LED module to the D10 port of the controller board and Photo Interrupter Module to D3 port using the EASY plug cables.
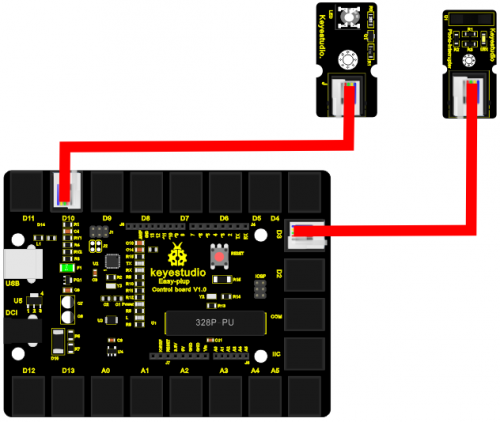
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
// photo interrupter module
int Led = 10 ;// define LED Interface
int buttonpin = 3; // define the photo interrupter sensor interface
int val ;// define numeric variables val
void setup ()
{
pinMode (Led, OUTPUT) ;// define LED as output interface
pinMode (buttonpin, INPUT) ;// define the photo interrupter sensor output interface
}
void loop ()
{
val = digitalRead (buttonpin) ;// digital interface will be assigned a value of 3 to read val
if (val == HIGH) // When the light sensor detects a signal is interrupted, LED flashes
{
digitalWrite (Led, HIGH);
}
else
{
digitalWrite (Led, LOW);
}
}
Result After the above are done, the LED on the module will be on and the piranha LED will be off; place a paper card between the two ends of the module, you can see the LED on the module is off, and the piranha will be on. Now, you have a clear idea of how piece counting is done.
Lesson 9: It’s moving
Introduction In this lesson, we will learn how to measure the static acceleration of an object in its X, Y and Z direction using an ADXL345 three axis acceleration module. This module is also suitable for measuring dynamic acceleration.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x1
EASY plug ADXL345 Three Axis Acceleration Module x1
Below is a brief introduction of this module.

The ADXL345 module is a 3-axis MEMS accelerometer with low power consumption and compact design. It’s of high resolution of 13-bit, measurement up to ±16g(gravitational force). Digital output data is formatted as 16-bit twos complement and is accessible through either a SPI (3- or 4-wire) or I2C digital interface. Below are its specifications:
2.0-3.6VDC Supply Voltage
Ultra Low Power: 40uA in measurement mode, 0.1uA in standby@ 2.5V
Tap/Double Tap Detection
Free-Fall Detection
SPI and I2C interfaces
Size: 40*20mm
Weight: 3g
Connection Diagram
Now, let’s connect this module to the IIC port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable.
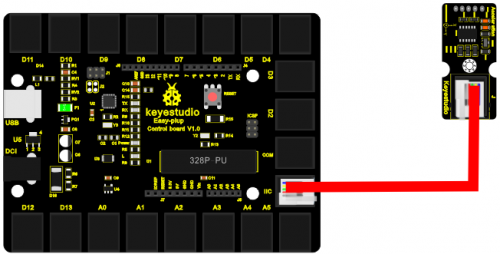
Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
#include <Wire.h> // place file “Wire.h” under the directory “libraries” of Arduino
// Registers for ADXL345
#define ADXL345_ADDRESS (0xA6 >> 1) // address for device is 8 bit but shift to the
// right by 1 bit to make it 7 bit because the
// wire library only takes in 7 bit addresses
#define ADXL345_REGISTER_XLSB (0x32)
int accelerometer_data[3];
// void because this only tells the cip to send data to its output register
// writes data to the slave's buffer
void i2c_write(int address, byte reg, byte data) {
// Send output register address
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
// Connect to device
Wire.write(reg);
// Send data
Wire.write(data); //low byte
Wire.endTransmission();
}
// void because using pointers
// microcontroller reads data from the sensor's input register
void i2c_read(int address, byte reg, int count, byte* data) {
// Used to read the number of data received
int i = 0;
// Send input register address
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
// Connect to device
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Connect to device
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
// Request data from slave
// Count stands for number of bytes to request
Wire.requestFrom(address, count);
while(Wire.available()) // slave may send less than requested
{
char c = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
data[i] = c;
i++;
}
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void init_adxl345() {
byte data = 0;
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x31, 0x0B); // 13-bit mode +_ 16g
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x2D, 0x08); // Power register
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x1E, 0x00); // x
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x1F, 0x00); // Y
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x20, 0x05); // Z
// Check to see if it worked!
i2c_read(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0X00, 1, &data);
if(data==0xE5)
Serial.println("it work Success");
else
Serial.println("it work Fail");
}
void read_adxl345() {
byte bytes[6];
memset(bytes,0,6);
// Read 6 bytes from the ADXL345
i2c_read(ADXL345_ADDRESS, ADXL345_REGISTER_XLSB, 6, bytes);
// Unpack data
for (int i=0;i<3;++i) {
accelerometer_data[i] = (int)bytes[2*i] + (((int)bytes[2*i + 1]) << 8);
}
}
// initialise and start everything
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i) {
accelerometer_data[i] = 0;
}
init_adxl345();
}
void loop() {
read_adxl345();
Serial.print("ACCEL: ");
Serial.print(float(accelerometer_data[0])*3.9/1000);//3.9mg/LSB scale factor in 13-bit mode
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(float(accelerometer_data[1])*3.9/1000);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(float(accelerometer_data[2])*3.9/1000);
Serial.print("\n");
delay(100);
}
Result
Now, open serial monitor, you can see it displays data as pic 1; when you move the module towards different direction, you can see the data changes as pic 2.
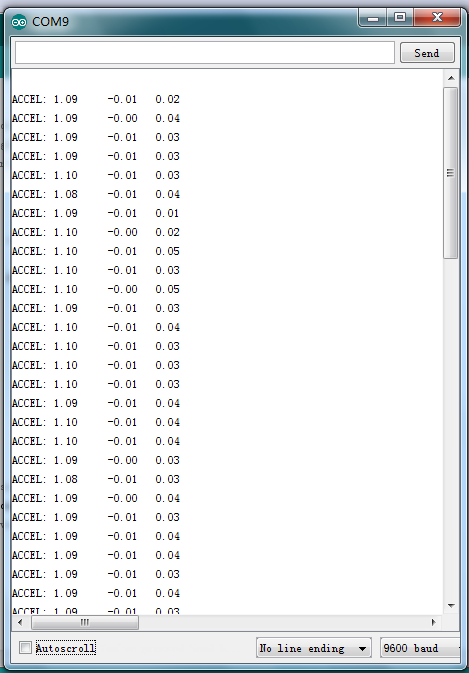
Pic 1
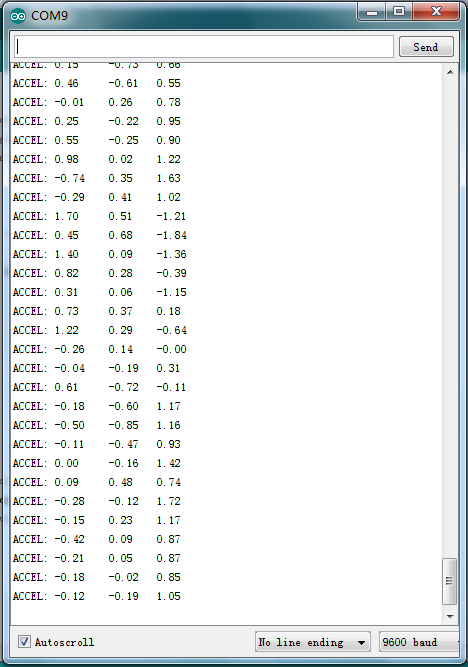
pic 2
Lesson 10: Make a clock
Introduction Time is of essence in our life. We have all sort of stuff that tells time. In this lesson, we will make a device of our own using the DS3231 clock module. Combine with a buzzer, you can make an alarm or just a time telling device when combined with an LCD.
Hardware required
EASY plug controller Board x1
USB cable x1
EASY plug cable x1
EASY plug DS3231 Clock Module x1
Below is a brief introduction of this module.

The DS3231 is a low-cost, extremely accurate I2C real-time clock (RTC) with an integrated temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO) and crystal. The device incorporates a battery input, and maintains accurate timekeeping when main power to the device is interrupted. The integration of the crystal resonator enhances the long-term accuracy of the device as well as reduces the piece-part count in a manufacturing line. The DS3231 is available in commercial and industrial temperature ranges, and is offered in a 16-pin, 300-mil SO package. Below are its specifications:
Temperature range: -40 to +85; Timing accuracy : ± 5ppm (±0.432 seconds / day)
Device package and function compatible with DS3231
Two calendar clock
Output: 1Hz and 32.768kHz
Reset output and Input Debounce of Pushbutton
High speed (400kHz), I2C serial bus
Supply voltage: +3.3V to +5.5V
Digital temperature sensor with a precision of±3℃
Working temperature: -40 ~ ℃ to +85 ~ ℃
16 pins Small Outline Package (300mil)
Certified by American Association of Underwriters Laboratories (UL)
Size: 38*20mm
Weight: 4g
Connection Diagram
Now, connect the DS3231 module to the IIC port of the controller board using the EASY plug cable.

Sample Code Connect the board to your PC using the USB cable; copy below code into Arduino IDE, and click upload to upload it to your board.
#include <Wire.h> // place file “Wire.h” under the directory “libraries” of Arduino
#include "DS3231.h" // place file “DS3231.h” under the directory “libraries” of Arduino
DS3231 RTC; //Create the DS3231 object
char weekDay[][4] = {"Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat" };
//year, month, date, hour, min, sec and week-day(starts from 0 and goes to 6)
//writing any non-existent time-data may interfere with normal operation of the RTC.
//Take care of week-day also.
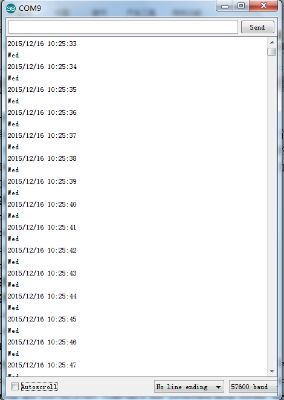
DateTime dt(2015, 12, 16, 10,25, 33, 3);//open the series port and you can check time here or make a change to the time as needed.
void setup ()
{ Serial.begin(57600);//set baud rate to 57600
Wire.begin();
RTC.begin();
RTC.adjust(dt); //Adjust date-time as defined 'dt' above
}
void loop ()
{ DateTime now = RTC.now(); //get the current date-time
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.date(), DEC);
Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.second(), DEC);
Serial.println();
Serial.print(weekDay[now.dayOfWeek()]);
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
Result
Now, open serial monitor, set baud rate to 57600, it will display the date we set in the program. You can change the code for it to display different dates; the module will then begin time counting, as below picture shows.