Ks0128 keyestudio EASY plug ADXL345 Three Axis Acceleration Module
Revision as of 10:46, 16 February 2017 by Keyestudio (talk | contribs)
EASY plug ADXL345 Three Axis Acceleration Module
Introduction
The ADXL345 module is a 3-axis MEMS accelerometer with low power consumption and compact design. It’s of high resolution of 13-bit, measurement up to ±16g(gravitational force). Digital output data is formatted as 16-bit twos complement and is accessible through either a SPI or I2C digital interface.
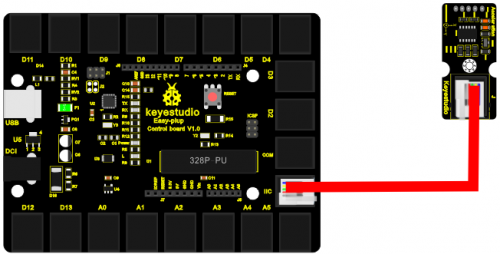
Note: this module needs to be used together with EASY plug control board.
Specification
- Interface: Easy plug
- 2.0-3.6VDC Supply Voltage
- Ultra Low Power: 40uA in measurement mode, 0.1uA in standby@ 2.5V
- Tap/Double Tap Detection
- Free-Fall Detection
- Size: 40*20mm
- Weight: 5g
Connection Diagram
Sample Code
#include <Wire.h> // place file “Wire.h” under the directory “libraries” of Arduino
// Registers for ADXL345
#define ADXL345_ADDRESS (0xA6 >> 1) // address for device is 8 bit but shift to the
// right by 1 bit to make it 7 bit because the
// wire library only takes in 7 bit addresses
#define ADXL345_REGISTER_XLSB (0x32)
int accelerometer_data[3];
// void because this only tells the cip to send data to its output register
// writes data to the slave's buffer
void i2c_write(int address, byte reg, byte data) {
// Send output register address
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
// Connect to device
Wire.write(reg);
// Send data
Wire.write(data); //low byte
Wire.endTransmission();
}
// void because using pointers
// microcontroller reads data from the sensor's input register
void i2c_read(int address, byte reg, int count, byte* data) {
// Used to read the number of data received
int i = 0;
// Send input register address
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
// Connect to device
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.endTransmission();
// Connect to device
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
// Request data from slave
// Count stands for number of bytes to request
Wire.requestFrom(address, count);
while(Wire.available()) // slave may send less than requested
{
char c = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
data[i] = c;
i++;
}
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void init_adxl345() {
byte data = 0;
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x31, 0x0B); // 13-bit mode +_ 16g
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x2D, 0x08); // Power register
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x1E, 0x00); // x
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x1F, 0x00); // Y
i2c_write(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0x20, 0x05); // Z
// Check to see if it worked!
i2c_read(ADXL345_ADDRESS, 0X00, 1, &data);
if(data==0xE5)
Serial.println("it work Success");
else
Serial.println("it work Fail");
}
void read_adxl345() {
byte bytes[6];
memset(bytes,0,6);
// Read 6 bytes from the ADXL345
i2c_read(ADXL345_ADDRESS, ADXL345_REGISTER_XLSB, 6, bytes);
// Unpack data
for (int i=0;i<3;++i) {
accelerometer_data[i] = (int)bytes[2*i] + (((int)bytes[2*i + 1]) << 8);
}
}
// initialise and start everything
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i) {
accelerometer_data[i] = 0;
}
init_adxl345();
}
void loop() {
read_adxl345();
Serial.print("ACCEL: ");
Serial.print(float(accelerometer_data[0])*3.9/1000);//3.9mg/LSB scale factor in 13-bit mode
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(float(accelerometer_data[1])*3.9/1000);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(float(accelerometer_data[2])*3.9/1000);
Serial.print("\n");
delay(100);
}
Resources
Datasheet
http://www.keyestudio.com/files/index/download/id/1464240188/