Ks0198 keyestudio 4DOF Robot Mechanical Arm Kit for Arduino DIY: Difference between revisions
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Keyestudio (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* Three controlling methods: Wired JoyStick Control; Phone Bluetooth Control; Wireless PS2 JoyStick Control. | * Three controlling methods: Wired JoyStick Control; Phone Bluetooth Control; Wireless PS2 JoyStick Control. | ||
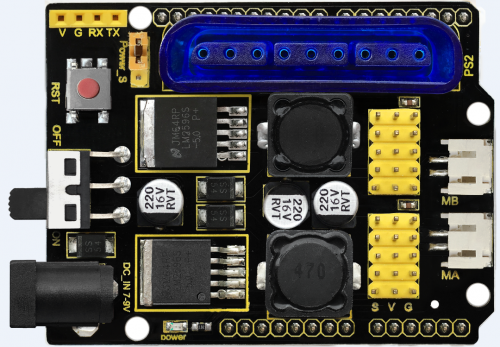
===The parameters of keyestudio TB6612FNG motor/servo drive expansion board are as follows:=== | |||
* VIN voltage: VIN = DC 7-15V | * VIN voltage: VIN = DC 7-15V | ||
* VIN current: 5A | * VIN current: 5A | ||
| Line 26: | Line 25: | ||
* PS2 interface: compatible with Sony PS2 receiver, can be plugged directly into the expansion board. | * PS2 interface: compatible with Sony PS2 receiver, can be plugged directly into the expansion board. | ||
* Dimensions: 73*53.34mm | * Dimensions: 73*53.34mm | ||
<br>[[File:TB6612.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
| align="center" | keyestudio TB6612FNG motor/servo drive shield | | align="center" | keyestudio TB6612FNG motor/servo drive shield | ||
| align="center" |1 | | align="center" |1 | ||
| align="center" | <br>[[File: | | align="center" | <br>[[File:TB6612.png|200px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 273: | Line 272: | ||
* M3 Hex Nut *8 | * M3 Hex Nut *8 | ||
* Black Acrylic plate *1 | * Black Acrylic plate *1 | ||
[[File:Spep1 1-1.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Then, screw the copper pillars with M3 hex nuts on the black Acrylic baseplate. | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 1-2.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
(2) Then install the control board, and prepare the components as follows: | |||
* M3*6MM round-head screw *3 | |||
* Keyestudio UNO R3 board *1 | |||
* keyestudio TB6612FNG motor shield *1 | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 2-1.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Firstly, screw the UNO R3 board on the pillar using three M3*6MM round-head screws. | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 2-2.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Then stack the motor drive shield onto the UNO R3 board. | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 2-3.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
(3) Completed the above assembly, let's mount the Pivot Servo Plate onto the base. | |||
* M3*12MM round-head screw *2 | |||
* M3 hex lock Nut *2 | |||
* Black 180° servo *1 | |||
* Acrylic plate * 4 | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 3-1.jpg|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
<span style="color: red">'''Note: ''' before install the servo, should set the servo angle to 80 degrees. </span> | |||
To set the servo angle, first connect the servo to A0 of motor shield, upload the code below to UNO R3 board, powered on, press the reset button, servo will rotate to 80°. | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 3-2.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
'''Code for 80° Servo:''' | |||
<pre> | |||
int servopin=A0;//Define digital interface A0 to connect servo steering gear signal line | |||
int myangle; //Define angle variables | |||
int pulsewidth; //Define pulse width variables | |||
void setup() | |||
{ | |||
pinMode(servopin,OUTPUT); //Set steering gear interface as Output | |||
} | |||
void servopulse(int servopin,int myangle) //Define Function | |||
{ | |||
pulsewidth=(myangle*11)+500; //Converts the Angle to a pulse width value of 500 - 2480 | |||
digitalWrite(servopin,HIGH); //The steering gear interface level is high | |||
delayMicroseconds(pulsewidth); //The microsecond number of the delay pulse width value | |||
digitalWrite(servopin,LOW); //Turn the steering gear interface level to low | |||
delay(20-pulsewidth/1000); | |||
} | |||
void loop() | |||
{ | |||
servopulse(servopin,80); //Set steering gear Angle | |||
} | |||
//0 Degree Code: | |||
// servopulse(servopin,0); | |||
//80 Degree Code: | |||
// servopulse(servopin,80); | |||
//180 Degree Code: | |||
// servopulse(servopin,180); | |||
</pre> | |||
<span style="color: red">'''Note: '''<br> | |||
Set well the servo angle and complete the below servo base plate assembly, power off the servo to avoid the angle error and make sure the servo can rotate freely. Don’t over-tighen the screws. </span> | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 3-3.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Adjusted well the servo motor, start to install the '''Servo Base Plate'''. Follow the marks. | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 3-4.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Firstly mount the acrylic plate② to the servo motor. | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 3-5.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
<br>[[File:Spep1 2-2.png|500px|frameless|thumb]]<br> | |||
Then mount the two acrylic plates ④ to the servo using two M3*12MM round-head screws. | |||
Revision as of 11:42, 30 November 2018
Kit Overview
How to DIY a robotic arm to complete multiple movements? Cool.With this keyestudio robotic arm kit, you are able to DIY your own controllable mechanical arm using ARDUINO microcontroller. It uses UNO R3 and 2 JoyStick modules to control the angle degree of 4 servos. When DIY this 4DOF robot arm kit, you could get everything needed for arm installation and debugging. There are 3 controlling methods are as follows: 1) Controlling through Wired JoyStick (included in the kit); 2) Phone Bluetooth Controlling (note: HC-06 Bluetooth module Not Included, only provide the test code for Bluetooth and APP for Android phone); 3) Wireless PS2 JoyStick Control (PS2 JoyStick module Not Included, we only provide the test code.) You are able to get all related information in the Arm kit. Take your brain on an inspiring journey through the world of programming. Get started now!
Kit Features
You can check out these features:
- Detailed installation instructions
- Detailed debugging methods, starting Arduino from entry.
- Three controlling methods: Wired JoyStick Control; Phone Bluetooth Control; Wireless PS2 JoyStick Control.
The parameters of keyestudio TB6612FNG motor/servo drive expansion board are as follows:
- VIN voltage: VIN = DC 7-15V
- VIN current: 5A
- Two-way 5V output: 5V/3A
- TB6612FNG: VIN input DC 7-15V; average drive current 1.2A; peak current 3.2A
- PS2 interface: compatible with Sony PS2 receiver, can be plugged directly into the expansion board.
- Dimensions: 73*53.34mm
Part List
You can see a pretty beautiful packaging box for the arm kit, and inside the packaging you will find all the parts and screws listed below.
Assembly Guide
Follow the assembly steps below to build your own robot arm, believe you will be full of delight to experience the robot arm DIY. If still confused, you can refer to the assembly video.
Step1: Begin with the Baseplate Assembly
(1) Firstly, you should prepare the components as follows:
- M3*30+5MM single-pass copper pillar *4
- M3*6mm+6mm single-pass copper pillar *4
- M3 Hex Nut *8
- Black Acrylic plate *1
Then, screw the copper pillars with M3 hex nuts on the black Acrylic baseplate.
thumb
(2) Then install the control board, and prepare the components as follows:
- M3*6MM round-head screw *3
- Keyestudio UNO R3 board *1
- keyestudio TB6612FNG motor shield *1
Firstly, screw the UNO R3 board on the pillar using three M3*6MM round-head screws.
thumb
Then stack the motor drive shield onto the UNO R3 board.
thumb
(3) Completed the above assembly, let's mount the Pivot Servo Plate onto the base.
- M3*12MM round-head screw *2
- M3 hex lock Nut *2
- Black 180° servo *1
- Acrylic plate * 4
Note: before install the servo, should set the servo angle to 80 degrees.
To set the servo angle, first connect the servo to A0 of motor shield, upload the code below to UNO R3 board, powered on, press the reset button, servo will rotate to 80°.
thumb
Code for 80° Servo:
int servopin=A0;//Define digital interface A0 to connect servo steering gear signal line
int myangle; //Define angle variables
int pulsewidth; //Define pulse width variables
void setup()
{
pinMode(servopin,OUTPUT); //Set steering gear interface as Output
}
void servopulse(int servopin,int myangle) //Define Function
{
pulsewidth=(myangle*11)+500; //Converts the Angle to a pulse width value of 500 - 2480
digitalWrite(servopin,HIGH); //The steering gear interface level is high
delayMicroseconds(pulsewidth); //The microsecond number of the delay pulse width value
digitalWrite(servopin,LOW); //Turn the steering gear interface level to low
delay(20-pulsewidth/1000);
}
void loop()
{
servopulse(servopin,80); //Set steering gear Angle
}
//0 Degree Code:
// servopulse(servopin,0);
//80 Degree Code:
// servopulse(servopin,80);
//180 Degree Code:
// servopulse(servopin,180);
Note:
Set well the servo angle and complete the below servo base plate assembly, power off the servo to avoid the angle error and make sure the servo can rotate freely. Don’t over-tighen the screws.
thumb
Adjusted well the servo motor, start to install the Servo Base Plate. Follow the marks.
thumb
Firstly mount the acrylic plate② to the servo motor.
thumb
thumb
Then mount the two acrylic plates ④ to the servo using two M3*12MM round-head screws.