KS0478 Keyestudio Micro:bit Honeycomb Dot Matrix Module (Black and Eco-friendly)
Description
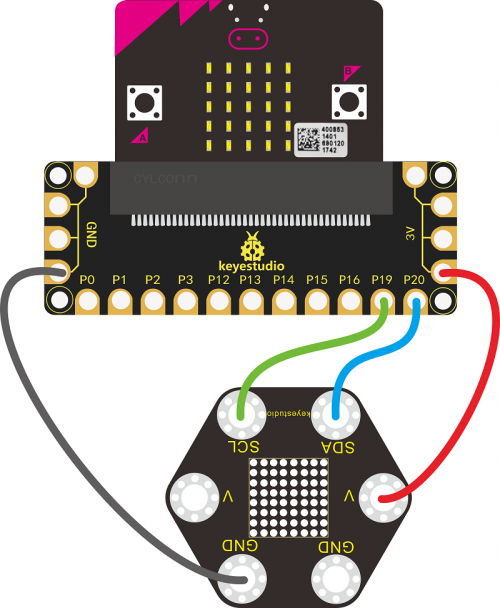
The keyestudio micro:bit honeycomb dot matrix module is a sensor that is fully compatible with the micro:bit control board. This module uses an HT16K33 chip to drive an 8 * 8 dot matrix and controls dot matrix via I2C communication port of the microcontroller, which greatly saves the microcontroller resources. In the experiment, we connect this module to the keyestudio micro:bit golden finger IO shield via a crocodile clip cable, then insert Micro:bit control board to shield. Therefore, we can control dot matrix to display different patterns by setting the corresponding code on the micro:bit control board.
Technical Parameters
- Working voltage: DC 3.0-3.3V
- Control port: I2C communication port
- Environmental attributes: ROHS
Connection Diagram
Test Code
Special attention: Setting is complicated because the chip drives the dot matrix, so the program is written in Python when setting the code. from microbit import *
class ht16k33:
ADDRESS = 0x70
BLINK_CMD = 0x80
CMD_BRIGHTNESS = 0xE0
def __init__(self):
self.buffer = bytearray([0]*16)
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, b'\x21')
# 0 to 3
self.blink_rate(0)
# 0 to 15
self.set_brightness(10)
# self.clear()
def set_brightness(self, b):
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, bytes([self.CMD_BRIGHTNESS | b]))
def blink_rate(self, b):
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, bytes([self.BLINK_CMD | 1 | (b << 1)]))
def Display(self, num):
if num == 0:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([126]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([195]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([195]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([126]) + bytearray([0]*4)
elif num == 1:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([1]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([255]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([65]) + \
bytearray([0]*6)
elif num == 2:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([121]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([201]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([201]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([79]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 3:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([127]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([201]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([201]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([73]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 4:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([24]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([255]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([24]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([248]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 5:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([79]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([201]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([201]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([121]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 6:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([79]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([201]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([201]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([127]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 7:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([127]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([192]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([192]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([64]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 8:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([127]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([201]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([201]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([127]) + bytearray([0]*5)
elif num == 9:
dat = bytearray([0]*5) + bytearray([127]) + bytearray([0]) + \
bytearray([201]) + bytearray([0]) + bytearray([201]) + \
bytearray([0]) + bytearray([121]) + bytearray([0]*5)
else:
return
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, dat)
def test(self):
data = bytearray([0]) + bytearray([255]*16)
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, data)
self.blink_rate(1)
sleep(3000)
data = bytearray([0]) + bytearray([0]*16)
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, data)
self.blink_rate(0)
def clear(self):
self.buffer = bytearray([0]*16)
i2c.write(self.ADDRESS, self.buffer)
# declare an instance
keyes = ht16k33()
keyes.test()
while True:
for a in range(0, 10):
keyes.Display(a)
sleep(1000)
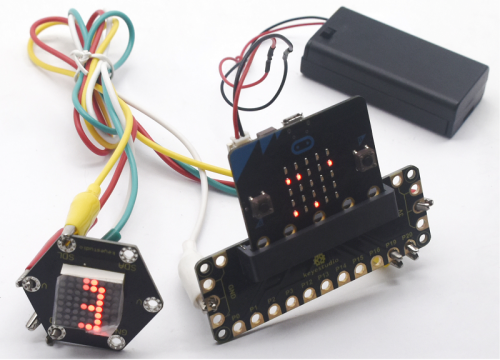
Test Result
Wire according to connection diagram, upload the test code successfully, and after power- on, the dot matrix on the keyestudio micro:bit honeycomb dot matrix module will display 0-9 10 digital patterns in a loop.
Resource
Test Code:
https://fs.keyestudio.com/KS0478
Buy from
- [ Official Website]
- [ Shop on Aliexpress ]